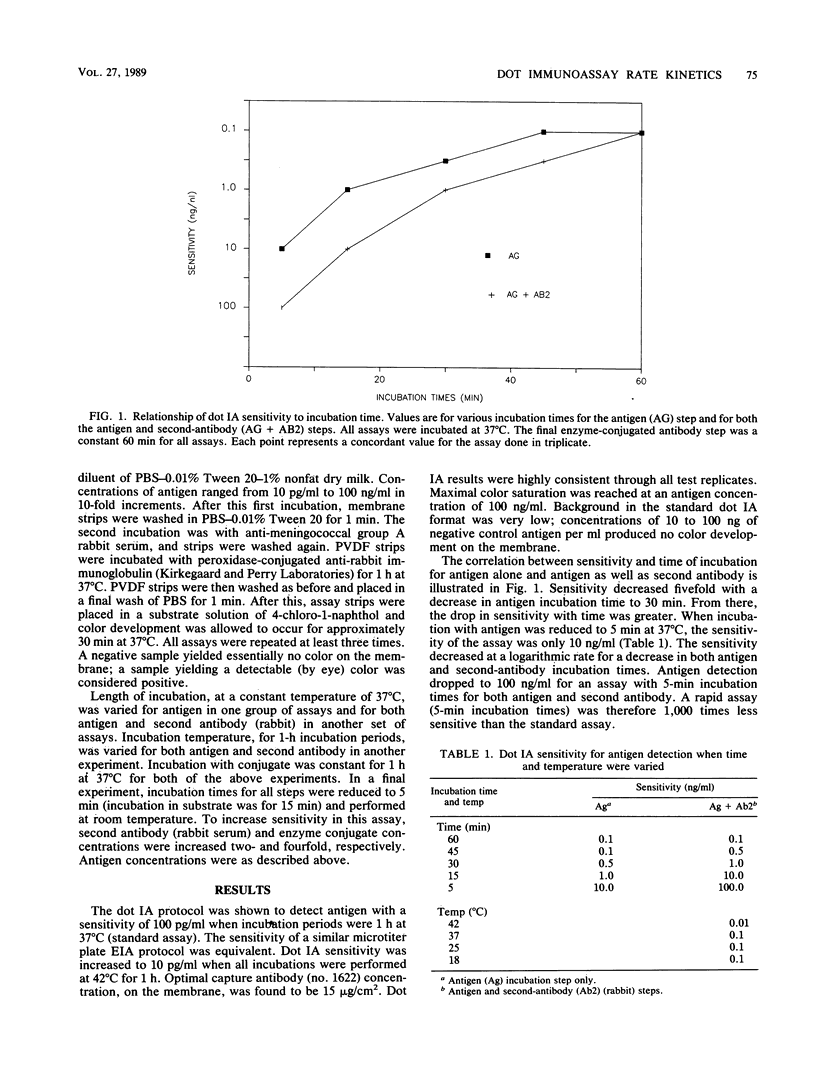
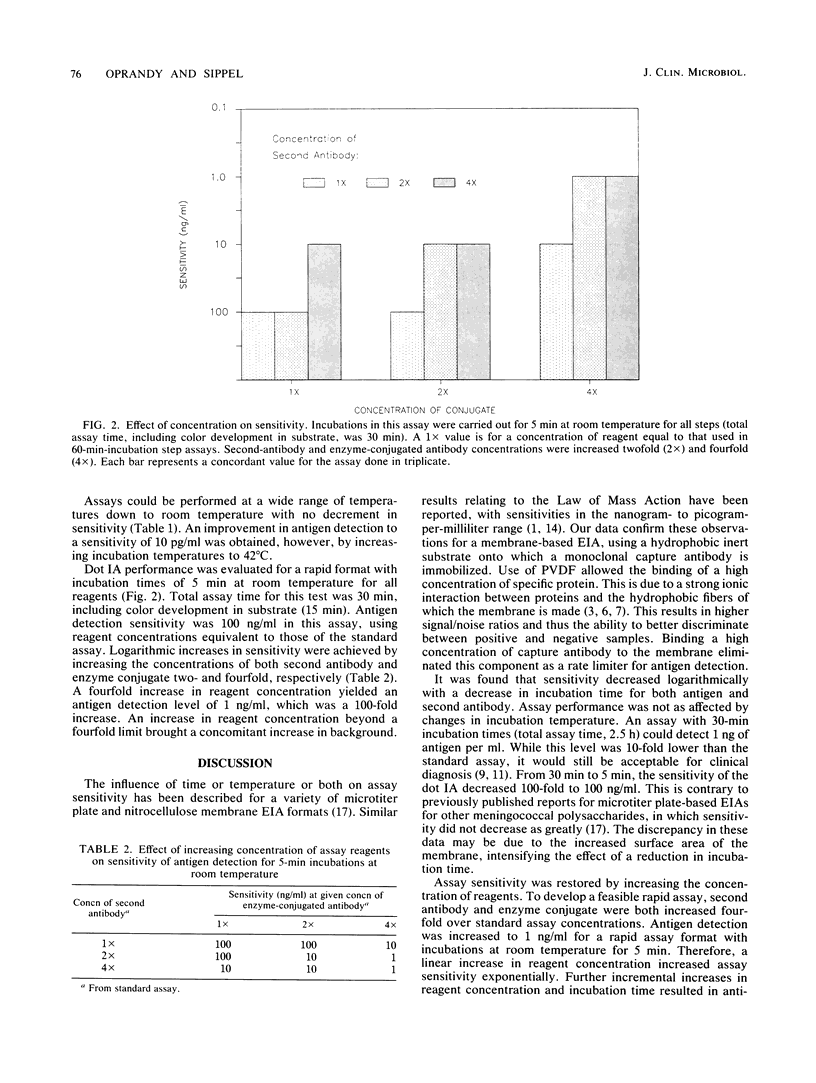
Abstract
Increasingly, membrane-based enzyme immunoassays are being developed as the preferred solid-phase enzyme immunoassay format. We describe the rate kinetics of a polyvinylidene difluoride membrane-based dot immunoassay for meningococcal group A polysaccharide. Antigen detection sensitivity decreased logarithmically with linear decreases in incubation time. The sensitivity of a 30-min assay (5-min incubation steps) was increased to nearly the level of the standard assay (1-h incubation steps) by increasing the concentration of assay reagents fourfold. These results support the idea that existing microtiter plate assays can be transferred to rapid dot immunoassay formats with little or no loss of sensitivity.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beutin L., Bode L., Richter T., Peltre G., Stephan R. Rapid visual detection of Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae Heat-labile enterotoxins by nitrocellulose enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Mar;19(3):371–375. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.3.371-375.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calisher C. H., Fremount H. N., Vesely W. L., el-Kafrawi A. O., Mahmud M. I. Relevance of detection of immunoglobulin M antibody response in birds used for arbovirus surveillance. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Nov;24(5):770–774. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.5.770-774.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrah S. R., Shah D. O., Ingram L. O. Effects of chaotropic and antichaotropic agents on elution of poliovirus adsorbed on membrane filters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1229–1232. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildreth S. W., Beaty B. J. Detection of eastern equine encephalomyelitis virus and Highlands J virus antigens within mosquito pools by enzyme immunoassay (EIA). I. A laboratory study. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1984 Sep;33(5):965–972. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1984.33.965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oprandy J. J., Olson J. G., Scott T. W. A rapid dot immunoassay for the detection of serum antibodies to eastern equine encephalomyelitis and St. Louis encephalitis viruses in sentinel chickens. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1988 Jan;38(1):181–186. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1988.38.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider Z. Aliphatic alcohols improve the adsorptive performance of cellulose nitrate membranes--application in chromatography and enzyme assays. Anal Biochem. 1980 Oct;108(1):96–103. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90697-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott T. W., Olson J. G. Detection of eastern equine encephalomyelitis viral antigen in avian blood by enzyme immunoassay: a laboratory study. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1986 May;35(3):611–618. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1986.35.611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sippel J. E., Prato C. M., Girgis N. I., Edwards E. A. Detection of Neisseria meningitidis group A, Haemophilus influenzae type b, and Streptococcus pneumoniae antigens in cerebrospinal fluid specimens by antigen capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Aug;20(2):259–265. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.2.259-265.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. B., Repetti C. F. Evaluation of a rapid screening immunoassay for antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Nov;25(11):2207–2208. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.11.2207-2208.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugasawara R. J., Prato C. M., Sippel J. E. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with a monoclonal antibody for detecting group A meningococcal antigens in cerebrospinal fluid. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):230–234. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.230-234.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Gordon J. Immunoblotting and dot immunobinding--current status and outlook. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Sep 4;72(2):313–340. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90001-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai T. F., Bolin R. A., Montoya M., Bailey R. E., Francy D. B., Jozan M., Roehrig J. T. Detection of St. Louis encephalitis virus antigen in mosquitoes by capture enzyme immunoassay. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Feb;25(2):370–376. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.2.370-376.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velick S. F., Parker C. W., Eisen H. N. EXCITATION ENERGY TRANSFER AND THE QUANTITATIVE STUDY OF THE ANTIBODY HAPTEN REACTION. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Nov;46(11):1470–1482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.11.1470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. C., Thomas L. A., Peacock M. G. Identification of phase-specific antigenic fractions of Coxiella burnetti by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Dec;24(6):929–934. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.6.929-934.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA): a practical tool for rapid diagnosis of viruses and other infectious agents. Yale J Biol Med. 1980 Jan-Feb;53(1):85–92. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Leister F. J. Investigation of enzyme immunoassay time courses: development of rapid assay systems. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Apr;13(4):738–741. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.4.738-741.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


