Abstract
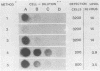
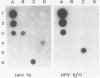
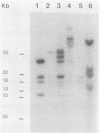
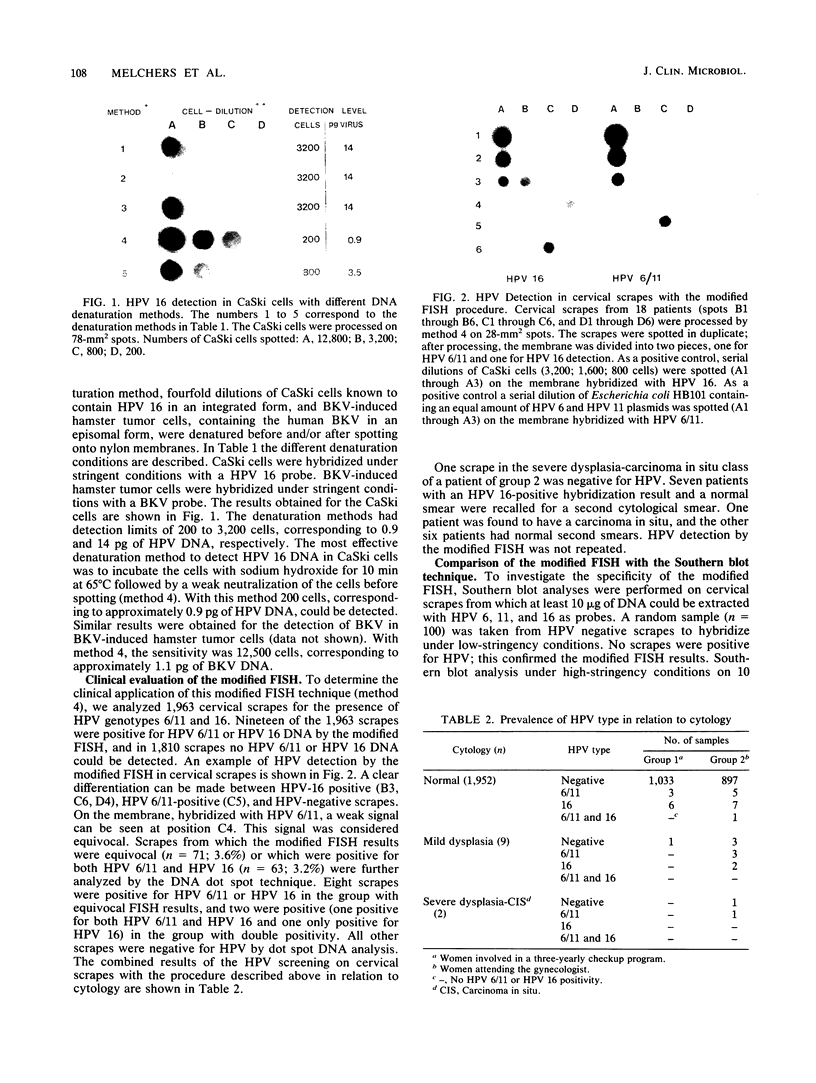
Optimal conditions for the screening of cervical scrapes for human papillomavirus (HPV) were investigated by using filter in situ hybridization. Since integrated and episomal HPV can be found, cell lines containing viral DNA in an integrated form (HPV in CaSki) or in an episomal state (BK virus-induced hamster tumor cells) were used for optimization experiments. An increase in sensitivity was achieved by alkaline denaturation and neutralization before the specimens were spotted onto the membrane. This increase was 5-fold for the episomal virus and 16-fold for the integrated virus in the model system, as compared with other methods. To evaluate this method on clinical material, 1,963 cervical scrapes were screened for the presence of HPV 6/11 and HPV 16. Nineteen scrapes were positive for HPV 6/11 or HPV 16; and in 1,810 scrapes, no HPV 6/11 or HPV 16 could be detected by the modified filter in situ hybridization technique. Scrapes from which the interpretation of the modified filter in situ hybridization results were equivocal (n = 71, 3.6%) or in which positivity was detected for both HPV 6/11 and HPV 16 (n = 63, 3.2%) were further analyzed by the DNA dot spot technique. Eight scrapes with an equivocal result and only one scrape showing a double positivity by the modified filter in situ hybridization technique could be confirmed in the dot spot assay. In the total group 12 scrapes were positive for HPV 6/11 DNA, 15 were positive for HPV 16 DNA, and 1 was positive for both HPV 6/11 and HPV 16 DNA. Southern blot analysis on modified filter in situ hybridization-positive and -negative scrapes revealed a 100% correlation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beaudenon S., Kremsdorf D., Croissant O., Jablonska S., Wain-Hobson S., Orth G. A novel type of human papillomavirus associated with genital neoplasias. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):246–249. doi: 10.1038/321246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Gissmann L., Ikenberg H., Kleinheinz A., Scheurlen W., zur Hausen H. A new type of papillomavirus DNA, its presence in genital cancer biopsies and in cell lines derived from cervical cancer. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1151–1157. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01944.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campion M. J., McCance D. J., Cuzick J., Singer A. Progressive potential of mild cervical atypia: prospective cytological, colposcopic, and virological study. Lancet. 1986 Aug 2;2(8501):237–240. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92067-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crum C. P., Mitao M., Levine R. U., Silverstein S. Cervical papillomaviruses segregate within morphologically distinct precancerous lesions. J Virol. 1985 Jun;54(3):675–681. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.3.675-681.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gissmann L., Wolnik L., Ikenberg H., Koldovsky U., Schnürch H. G., zur Hausen H. Human papillomavirus types 6 and 11 DNA sequences in genital and laryngeal papillomas and in some cervical cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):560–563. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson B. R., Thompson C. H., Rose B. R., Cossart Y. E., Morris B. J. Detection of specific types of human papillomavirus in cervical scrapes, anal scrapes, and anogenital biopsies by DNA hybridization. J Med Virol. 1987 Apr;21(4):381–393. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890210410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCance D. J., Campion M. J., Clarkson P. K., Chesters P. M., Jenkins D., Singer A. Prevalence of human papillomavirus type 16 DNA sequences in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and invasive carcinoma of the cervix. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1985 Nov;92(11):1101–1105. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1985.tb03019.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchers W. J., Herbrink P., Quint W. G., Walboomers J. M., Meijer C. J., Lindeman J. Prevalence of genital HPV infections in a regularly screened population in The Netherlands in relation to cervical cytology. J Med Virol. 1988 May;25(1):11–16. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890250103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. B. Evaluation of the impact of screening for cancer of the cervix. IARC Sci Publ. 1986;(76):149–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richart R. M., Barron B. A. Screening strategies for cervical cancer and cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. Cancer. 1981 Mar 1;47(5 Suppl):1176–1181. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19810301)47:5+<1176::aid-cncr2820471321>3.0.co;2-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syrjänen K., de Villiers E. M., Saarikoski S., Castren O., Väyrynen M., Mäntyjärvi R., Parkkinen S. Cervical papillomavirus infection progressing to invasive cancer in less than three years. Lancet. 1985 Mar 2;1(8427):510–511. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92102-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner D., Ikenberg H., Boehm N., Gissmann L. Identification of human papillomavirus in cervical swabs by deoxyribonucleic acid in situ hybridization. Obstet Gynecol. 1984 Dec;64(6):767–772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Villiers E. M., Wagner D., Schneider A., Wesch H., Miklaw H., Wahrendorf J., Papendick U., zur Hausen H. Human papillomavirus infections in women with and without abnormal cervical cytology. Lancet. 1987 Sep 26;2(8561):703–706. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ter Schegget J., Voves J., van Strien A., van der Noordaa J. Free viral DNA in BK virus-induced hamster tumor cells. J Virol. 1980 Aug;35(2):331–339. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.2.331-339.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]