Abstract
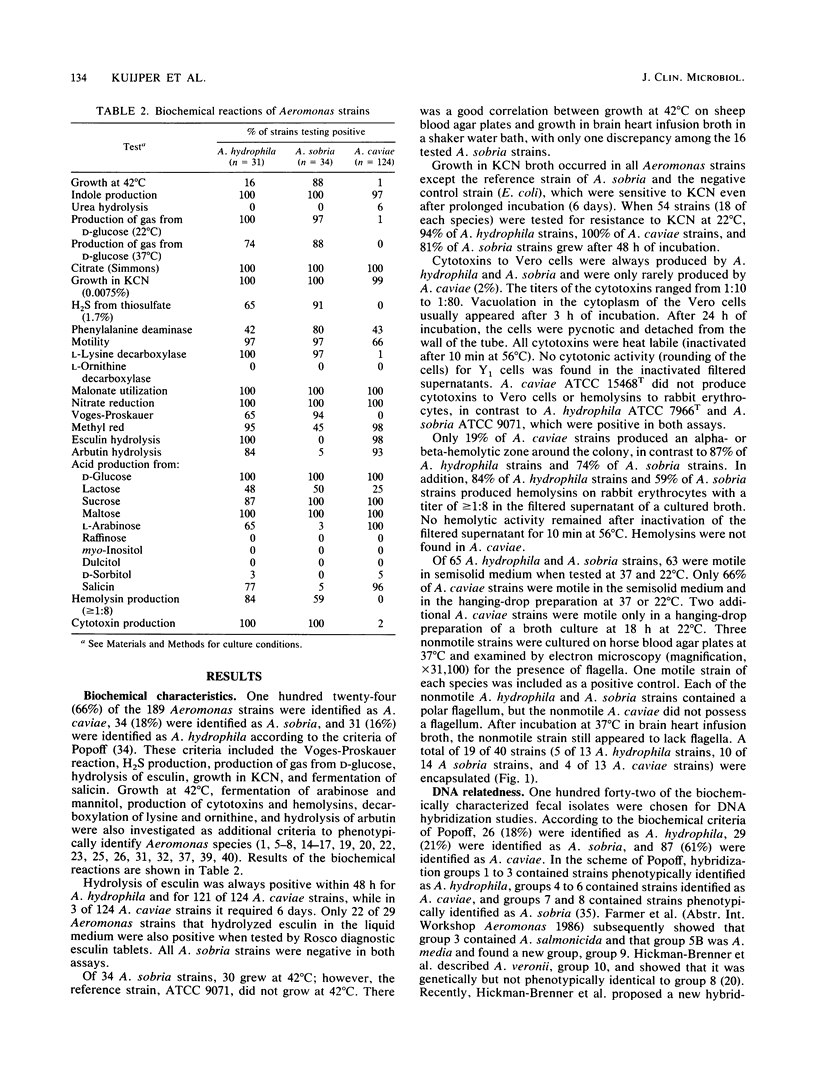
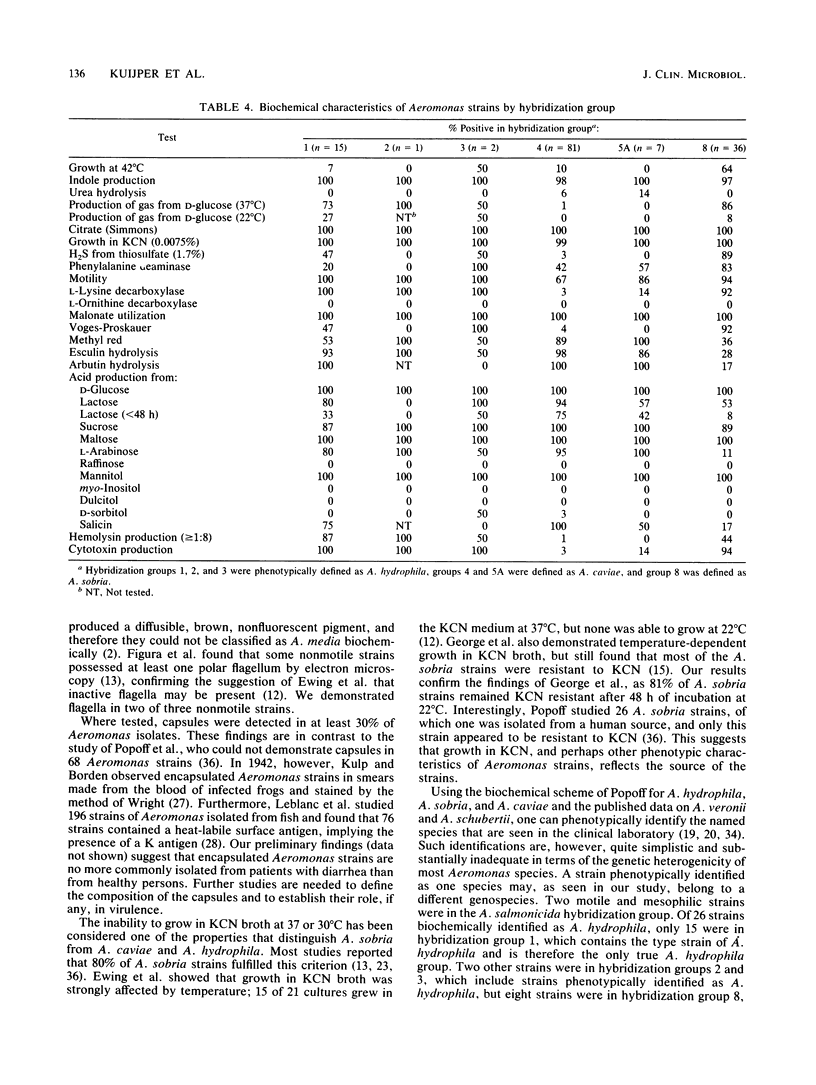
Phenotypic characteristics were used to identify 189 Aeromonas strains isolated from human feces. One hundred forty-two of these strains were placed in 11 DNA hybridization groups, and the genetic and phenotypic data were compared. According to the criteria of Popoff, 66% of the strains were identified as Aeromonas caviae, 18% were identified as A. sobria, and 16% were identified as A. hydrophila. Some biochemical characteristics differed from the criteria of Popoff; 19 of 40 (48%) of tested strains were encapsulated, 42 of 124 (34%) of A. caviae strains were nonmotile, and all A. sobria strains were resistant to KCN. Gas production from D-glucose was temperature dependent; 11 of 64 (17%) A. hydrophila and A. sobria strains produced gas only at 22 degrees C. Of 142 Aeromonas strains, 57% belonged to hybridization group 4, 25% belonged to group 8, 11% belonged to group 1, 4% belonged to group 5A, 2% belonged to group 3, and 1% belonged to group 2. Of 26 strains phenotypically identified as A. hydrophila, 8 (31%) were in hybridization group 8, which contains strains of the new species A. veronii. It therefore appears that our ability to identify Aeromonas strains phenotypically is not sufficiently specific. Either additional definitive biochemical markers must be found or phenotypic identification, at least for some Aeromonas groups, must be regarded as only presumptive.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agger W. A., McCormick J. D., Gurwith M. J. Clinical and microbiological features of Aeromonas hydrophila-associated diarrhea. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jun;21(6):909–913. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.6.909-913.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barer M. R., Millership S. E., Tabaqchali S. Relationship of toxin production to species in the genus Aeromonas. J Med Microbiol. 1986 Dec;22(4):303–309. doi: 10.1099/00222615-22-4-303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. J., McWhorter A. C., Knutson J. K., Steigerwalt A. G. Escherichia vulneris: a new species of Enterobacteriaceae associated with human wounds. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):1133–1140. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.1133-1140.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant T. N., Lee J. V., West P. A., Colwell R. R. A probability matrix for the identification of species of Vibrio and related genera. J Appl Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;61(5):469–480. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1986.tb04309.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant T. N., Lee J. V., West P. A., Colwell R. R. Numerical classification of species of Vibrio and related genera. J Appl Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;61(5):437–467. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1986.tb04308.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke V., Robinson J., Atkinson H. M., Gracey M. Biochemical characteristics of enterotoxigenic Aeromonas spp. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jan;15(1):48–52. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.1.48-52.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke V., Robinson J., Beaman J., Gracey M., Lesmana M., Rockhill R., Echeverria P., Janda J. M. Correlation of enterotoxicity with biotype in Aeromonas spp. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Nov;18(5):1196–1200. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.5.1196-1200.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumberbatch N., Gurwith M. J., Langston C., Sack R. B., Brunton J. L. Cytotoxic enterotoxin produced by Aeromonas hydrophila: relationship of toxigenic isolates to diarrheal disease. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):829–837. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.829-837.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figura N., Marri L., Verdiani S., Ceccherini C., Barberi A. Prevalence, species differentiation, and toxigenicity of Aeromonas strains in cases of childhood gastroenteritis and in controls. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Mar;23(3):595–599. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.3.595-599.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George W. L., Jones M. J., Nakata M. M. Phenotypic characteristics of Aeromonas species isolated from adult humans. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jun;23(6):1026–1029. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.6.1026-1029.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gracey M., Burke V. Characteristics of aeromonas species and their association with human diarrhoeal disease. J Diarrhoeal Dis Res. 1986 Jun;4(2):70–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gracey M., Burke V., Robinson J. Aeromonas-associated gastroenteritis. Lancet. 1982 Dec 11;2(8311):1304–1306. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91510-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazen T. C., Fliermans C. B., Hirsch R. P., Esch G. W. Prevalence and distribution of Aeromonas hydrophila in the United States. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Nov;36(5):731–738. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.5.731-738.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman-Brenner F. W., Fanning G. R., Arduino M. J., Brenner D. J., Farmer J. J., 3rd Aeromonas schubertii, a new mannitol-negative species found in human clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Aug;26(8):1561–1564. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.8.1561-1564.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman-Brenner F. W., MacDonald K. L., Steigerwalt A. G., Fanning G. R., Brenner D. J., Farmer J. J., 3rd Aeromonas veronii, a new ornithine decarboxylase-positive species that may cause diarrhea. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 May;25(5):900–906. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.5.900-906.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg S. D., Schell W. L., Fanning G. R., Wachsmuth I. K., Hickman-Brenner F. W., Blake P. A., Brenner D. J., Farmer J. J., 3rd Aeromonas intestinal infections in the United States. Ann Intern Med. 1986 Nov;105(5):683–689. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-105-5-683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janda J. M., Bottone E. J., Skinner C. V., Calcaterra D. Phenotypic markers associated with gastrointestinal Aeromonas hydrophila isolates from symptomatic children. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Apr;17(4):588–591. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.4.588-591.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janda J. M., Reitano M., Bottone E. J. Biotyping of Aeromonas isolates as a correlate to delineating a species-associated disease spectrum. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jan;19(1):44–47. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.1.44-47.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keusch G. T., Donta S. T. Classification of enterotoxins on the basis of activity in cell culture. J Infect Dis. 1975 Jan;131(1):58–63. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.1.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuijper E. J., Peeters M. F. De betekenis van verschillende Aeromonas-soorten in de faeces van patiënten met en zonder diarree. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 1986 Feb 15;130(7):302–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuijper E. J., Zanen H. C., Peeters M. F. Aeromonas-associated diarrhea in the Netherlands. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Apr;106(4):640–641. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-106-4-640_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulp W. L., Borden D. G. Further Studies on Proteus hydrophilus, the Etiological Agent in "Red Leg" Disease of Frogs. J Bacteriol. 1942 Dec;44(6):673–685. doi: 10.1128/jb.44.6.673-685.1942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leblanc D., Mittal K. R., Olivier G., Lallier R. Serogrouping of motile Aeromonas species isolated from healthy and moribund fish. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jul;42(1):56–60. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.1.56-60.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millership S. E., Barer M. R., Tabaqchali S. Toxin production by Aeromonas spp. from different sources. J Med Microbiol. 1986 Dec;22(4):311–314. doi: 10.1099/00222615-22-4-311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overman T. L., Kessler J. F., Seabolt J. P. Comparison of API 20E, API rapid E, and API rapid NFT for identification of members of the family Vibrionaceae. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Nov;22(5):778–781. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.5.778-781.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popoff M., Véron M. A taxonomic study of the Aeromonas hydrophila-Aeromonas punctata group. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 May;94(1):11–22. doi: 10.1099/00221287-94-1-11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toranzo A. E., Santos Y., Nieto T. P., Barja J. L. Evaluation of different assay systems for identification of environmental Aeromonas strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Mar;51(3):652–656. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.3.652-656.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull P. C., Lee J. V., Miliotis M. D., Van de Walle S., Koornhof H. J., Jeffery L., Bryant T. N. Enterotoxin production in relation to taxonomic grouping and source of isolation of Aeromonas species. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):175–180. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.175-180.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Graevenitz A., Mensch A. H. The genus aeromonas in human bacteriology report of 30 cases and review of the literature. N Engl J Med. 1968 Feb 1;278(5):245–249. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196802012780504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]