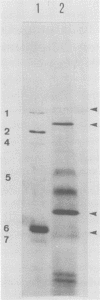
Abstract
Three monoclonal antibodies (MAbs)--B5C9, B5E4, and B10G10--to human group B rotavirus, an agent implicated in epidemic outbreaks of diarrhea in the People's Republic of China, primarily in adults, were prepared. MAb reactivity was decreased when virus preparations were treated with EDTA, suggesting reactivity with the outer-capsid protein(s). Competition experiments suggested that these MAbs recognize overlapping epitopes within a single antigenic site. A simple antigen detection enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) specific for the human group B rotavirus was established by using these MAbs as capture antibodies. Fifteen clinical samples obtained from three epidemic areas in the People's Republic of China and previously shown by Chinese scientists to contain group B virus were all positive in the MAb capture antigen detection ELISA, whereas none of the 57 samples lacking the group B virus reacted in the test. The results suggest that this MAb capture antigen detection ELISA will be useful to identify outbreaks caused by the human group B rotavirus and to monitor possible spread of the virus.
Full text
PDF
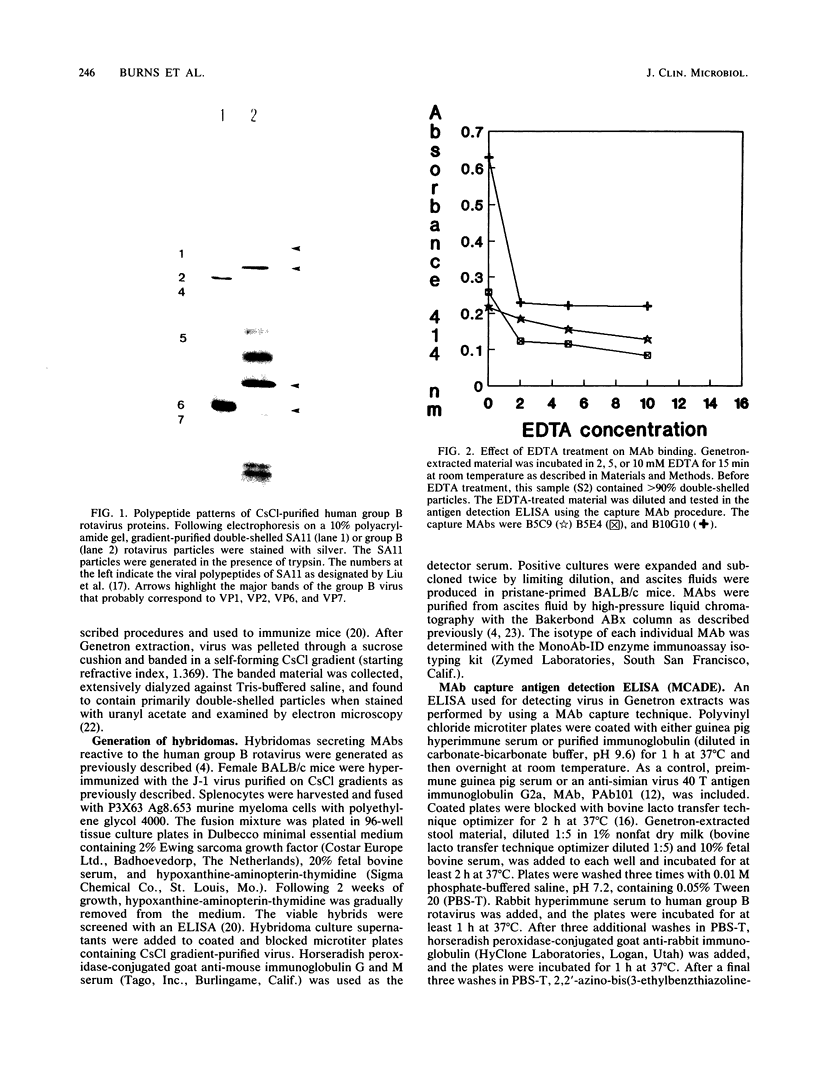
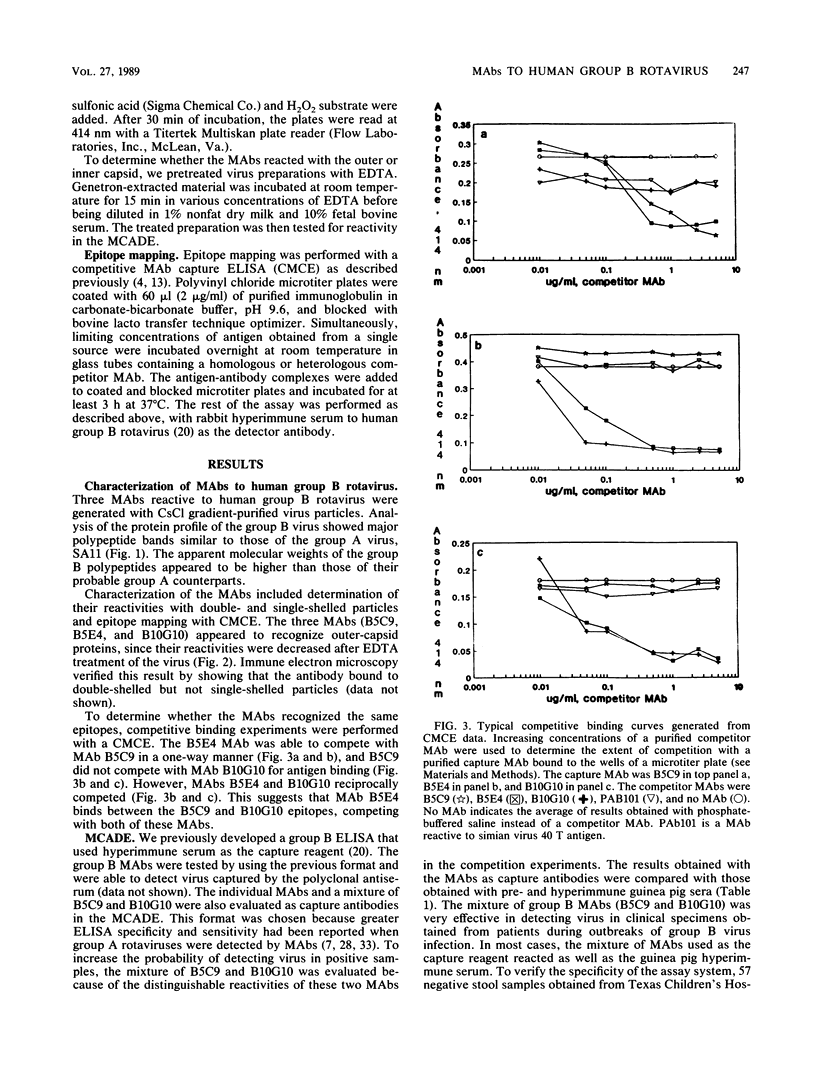


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bridger J. C. Novel rotaviruses in animals and man. Ciba Found Symp. 1987;128:5–23. doi: 10.1002/9780470513460.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridger J. C., Pedley S., McCrae M. A. Group C rotaviruses in humans. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Apr;23(4):760–763. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.4.760-763.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. W., Beards G. M., Chen G. M., Flewett T. H. Prevalence of antibody to group B (atypical) rotavirus in humans and animals. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Feb;25(2):316–319. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.2.316-319.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns J. W., Greenberg H. B., Shaw R. D., Estes M. K. Functional and topographical analyses of epitopes on the hemagglutinin (VP4) of the simian rotavirus SA11. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2164–2172. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2164-2172.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasey D., Banks J. The commonest rotaviruses from neonatal lamb diarrhoea in England and Wales have atypical electropherotypes. Vet Rec. 1984 Sep 29;115(13):326–327. doi: 10.1136/vr.115.13.326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. M., Hung T., Bridger J. C., McCrae M. A. Chinese adult rotavirus is a group B rotavirus. Lancet. 1985 Nov 16;2(8464):1123–1124. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90710-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cukor G., Perron D. M., Hudson R., Blacklow N. R. Detection of rotavirus in human stools by using monoclonal antibody. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jun;19(6):888–892. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.6.888-892.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dai G. Z., Sun M. S., Liu S. Q., Ding X. F., Chen Y. D., Wang L. C., Du D. P., Zhao G., Su Y., Li J. First report of an epidemic of diarrhoea in human neonates involving the new rotavirus and biological characteristics of the epidemic virus strain (KMB/R85). J Med Virol. 1987 Aug;22(4):365–373. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890220409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desselberger U., Hung T., Follett E. A. Genome analysis of human rotaviruses by oligonucleotide mapping of isolated RNA segments. Virus Res. 1986 Jun;4(4):357–368. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(86)90082-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrov D. H., Estes M. K., Rangelova S. M., Shindarov L. M., Melnick J. L., Graham D. Y. Detection of antigenically distinct rotaviruses from infants. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):523–526. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.523-526.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrov D. H., Graham D. Y., Lopez J., Muchinik G., Velasco G., Stenback W. A., Estes M. K. RNA electropherotypes of human rotaviruses from North and South America. Bull World Health Organ. 1984;62(2):321–329. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurney E. G., Tamowski S., Deppert W. Antigenic binding sites of monoclonal antibodies specific for simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):1168–1172. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.1168-1172.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendry R. M., Fernie B. F., Anderson L. J., Godfrey E., McIntosh K. Monoclonal capture antibody ELISA for respiratory syncytial virus: detection of individual viral antigens and determination of monoclonal antibody specificities. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Mar 18;77(2):247–258. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90037-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hung T., Chen G. M., Wang C. G., Yao H. L., Fang Z. Y., Chao T. X., Chou Z. Y., Ye W., Chang X. J., Den S. S. Waterborne outbreak of rotavirus diarrhoea in adults in China caused by a novel rotavirus. Lancet. 1984 May 26;1(8387):1139–1142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu M., Offit P. A., Estes M. K. Identification of the simian rotavirus SA11 genome segment 3 product. Virology. 1988 Mar;163(1):26–32. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90230-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNulty M. S., Allan G. M., Todd D., McFerran J. B., McCracken R. M. Isolation from chickens of a rotavirus lacking the rotavirus group antigen. J Gen Virol. 1981 Aug;55(Pt 2):405–413. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-55-2-405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita Y., Taniguchi K., Urasawa T., Urasawa S. Analysis of serotype-specific neutralization epitopes on VP7 of human rotavirus by the use of neutralizing monoclonal antibodies and antigenic variants. J Gen Virol. 1988 Feb;69(Pt 2):451–458. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-2-451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakata S., Estes M. K., Graham D. Y., Loosle R., Tao H., Wang S. H., Saif L. J., Melnick J. L. Antigenic characterization and ELISA detection of adult diarrhea rotaviruses. J Infect Dis. 1986 Sep;154(3):448–455. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.3.448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakata S., Estes M. K., Graham D. Y., Wang S. S., Gary G. W., Melnick J. L. Detection of antibody to group B adult diarrhea rotaviruses in humans. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 May;25(5):812–818. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.5.812-818.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakata S., Petrie B. L., Calomeni E. P., Estes M. K. Electron microscopy procedure influences detection of rotaviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Oct;25(10):1902–1906. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.10.1902-1906.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedley S., Bridger J. C., Brown J. F., McCrae M. A. Molecular characterization of rotaviruses with distinct group antigens. J Gen Virol. 1983 Oct;64(Pt 10):2093–2101. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-10-2093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedley S., Bridger J. C., Chasey D., McCrae M. A. Definition of two new groups of atypical rotaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1986 Jan;67(Pt 1):131–137. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-1-131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qiu F. X., Tian Y., Liu J. C., Zhang X. S., Hao Y. P. Antibody against adult diarrhoea rotavirus among healthy adult population in China. J Virol Methods. 1986 Sep;14(2):127–132. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(86)90043-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saif L. J., Bohl E. H., Theil K. W., Cross R. F., House J. A. Rotavirus-like, calicivirus-like, and 23-nm virus-like particles associated with diarrhea in young pigs. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jul;12(1):105–111. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.1.105-111.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw R. D., Stoner-Ma D. L., Estes M. K., Greenberg H. B. Specific enzyme-linked immunoassay for rotavirus serotypes 1 and 3. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Aug;22(2):286–291. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.2.286-291.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw R. D., Vo P. T., Offit P. A., Coulson B. S., Greenberg H. B. Antigenic mapping of the surface proteins of rhesus rotavirus. Virology. 1986 Dec;155(2):434–451. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90205-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass D. R., Herring A. J., Campbell I., Inglis J. M., Hargreaves F. D. Comparison of atypical rotaviruses from calves, piglets, lambs and man. J Gen Virol. 1984 May;65(Pt 5):909–914. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-5-909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su C. Q., Wu Y. L., Shen H. K., Wang D. B., Chen Y. H., Wu D. M., He L. N., Yang Z. L. An outbreak of epidemic diarrhoea in adults caused by a new rotavirus in Anhui Province of China in the summer of 1983. J Med Virol. 1986 Jun;19(2):167–173. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890190210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi K., Urasawa T., Morita Y., Greenberg H. B., Urasawa S. Direct serotyping of human rotavirus in stools by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using serotype 1-, 2-, 3-, and 4-specific monoclonal antibodies to VP7. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jun;155(6):1159–1166. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.6.1159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theil K. W., Saif L. J., Moorhead P. D., Whitmoyer R. E. Porcine rotavirus-like virus (group B rotavirus): characterization and pathogenicity for gnotobiotic pigs. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Mar;21(3):340–345. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.3.340-345.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vonderfecht S. L., Huber A. C., Eiden J., Mader L. C., Yolken R. H. Infectious diarrhea of infant rats produced by a rotavirus-like agent. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):94–98. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.94-98.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. S., Cai R. F., Chen J., Li R. J., Jiang R. S. Etiologic studies of the 1983 and 1984 outbreaks of epidemic diarrhea in Guangxi. Intervirology. 1985;24(3):140–146. doi: 10.1159/000149633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]