Abstract
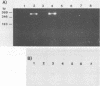
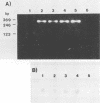
The direct identification of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli from clinical specimens was examined by using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for amplifying the heat-labile toxin (LT) gene. Two synthetic primers, each of which was 20 bases in length, were used with the thermostable DNA polymerase from Thermus aquaticus to amplify the LT gene. The amplified PCR products were detected by either gel electrophoresis or hybridization to a 24-base synthetic oligonucleotide probe conjugated to alkaline phosphatase. The PCR method detected LT-positive bacteria but did not react with E. coli producing the heat-stable toxin, enteroinvasive E. coli, Salmonella typhi, Salmonella typhimurium, or Shigella dysenteriae. By the PCR method, a single bacterium could be detected following 30 cycles of amplification. The T. aquaticus DNA polymerase was inhibited by more than 10(3) organisms in the amplification reaction mixture. A group of 40 clinical specimens consisting of 16 LT bioassay-positive and 24 LT bioassay-negative stool specimens were tested by PCR for the presence of toxigenic E. coli. The total DNA from 100 microliters of stool specimen was extracted and partially purified with a commercially available ion-exchange column. All 16 of the bioassay-positive stool specimens were positive by PCR. In addition, one stool specimen which was bioassay negative for LT but positive for LT in a previous hybridization assay with a different LT probe was also positive by PCR. This may indicate that the LT gene is present but either is not expressed or is expressed below detectable levels. Amplification of specific DNA sequences by PCR provides a highly sensitive and specific tool for the detection of pathogenic microorganisms directly from clinical specimens without the need for prior isolation. This technique may find wide application in the detection of other organisms in addition to enterotoxigenic E.coli.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bialkowska-Hobrzanska H. Detection of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli by dot blot hybridization with biotinylated DNA probes. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Feb;25(2):338–343. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.2.338-343.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boileau C. R., d'Hauteville H. M., Sansonetti P. J. DNA hybridization technique to detect Shigella species and enteroinvasive escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Nov;20(5):959–961. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.5.959-961.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean A. G., Ching Y. C., Williams R. G., Harden L. B. Test for Escherichia coli enterotoxin using infant mice: application in a study of diarrhea in children in Honolulu. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):407–411. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duggan D. B., Ehrlich G. D., Davey F. P., Kwok S., Sninsky J., Goldberg J., Baltrucki L., Poiesz B. J. HTLV-I-induced lymphoma mimicking Hodgkin's disease. Diagnosis by polymerase chain reaction amplification of specific HTLV-I sequences in tumor DNA. Blood. 1988 Apr;71(4):1027–1032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitts R., Diamond M., Hamilton C., Neri M. DNA-DNA hybridization assay for detection of Salmonella spp. in foods. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Nov;46(5):1146–1151. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.5.1146-1151.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jablonski E., Moomaw E. W., Tullis R. H., Ruth J. L. Preparation of oligodeoxynucleotide-alkaline phosphatase conjugates and their use as hybridization probes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 11;14(15):6115–6128. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.15.6115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer P. R., Waldrop A. A., Ward D. C. Enzymatic synthesis of biotin-labeled polynucleotides: novel nucleic acid affinity probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6633–6637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong J., Vinal A. C., Dallas W. S. Nucleotide sequence comparison between heat-labile toxin B-subunit cistrons from Escherichia coli of human and porcine origin. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):73–77. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.73-77.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley S. L., Huq I., Alim A. R., So M., Samadpour-Motalebi M., Falkow S. Detection of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli by DNA colony hybridization. J Infect Dis. 1980 Dec;142(6):892–898. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.6.892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olive D. M., Atta A. I., Setti S. K. Detection of toxigenic Escherichia coli using biotin-labelled DNA probes following enzymatic amplification of the heat labile toxin gene. Mol Cell Probes. 1988 Mar;2(1):47–57. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(88)90043-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olive D. M., Khalik D. A., Sethi S. K. Identification of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli using alkaline phosphatase-labeled synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotide probes. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;7(2):167–171. doi: 10.1007/BF01963071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack D. A., Sack R. B. Test for enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli using Y-1 adrenal cells in miniculture. Infect Immun. 1975 Feb;11(2):334–336. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.2.334-336.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Bugawan T. L., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Analysis of enzymatically amplified beta-globin and HLA-DQ alpha DNA with allele-specific oligonucleotide probes. Nature. 1986 Nov 13;324(6093):163–166. doi: 10.1038/324163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seriwatana J., Echeverria P., Taylor D. N., Sakuldaipeara T., Changchawalit S., Chivoratanond O. Identification of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli with synthetic alkaline phosphatase-conjugated oligonucleotide DNA probes. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;25(8):1438–1441. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.8.1438-1441.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Shaffer J., Murphy R. F., Bonner J., Hirose T., Itakura K. Hybridization of synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotides to phi chi 174 DNA: the effect of single base pair mismatch. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 10;6(11):3543–3557. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.11.3543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Yokota T. Sequence of heat-labile enterotoxin of Escherichia coli pathogenic for humans. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):728–733. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.728-733.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]