Abstract
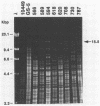
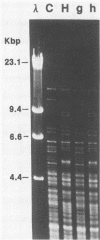
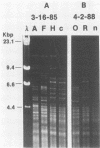
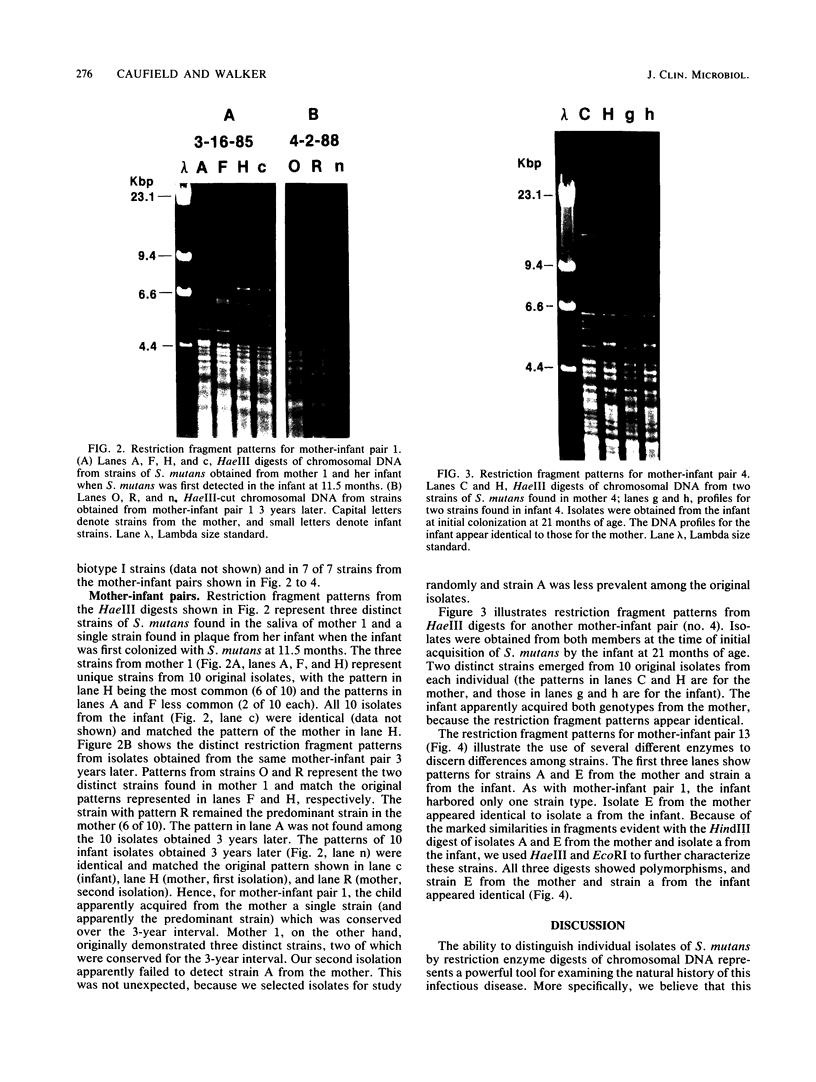
Attempts to study the acquisition, transmission, and other aspects of the natural history of Streptococcus mutans infections in humans have been hampered by limitations and inconsistencies in methods by which phenotypic characteristics of individual isolates are examined. Because most mutans streptococci associated with human dental caries fall within the biotype I (serotypes c and f) grouping, designated S. mutans, these typing methods are of little value in distinguishing individual isolates. Here we show that strains of S. mutans obtained from over 30 individuals demonstrate unique "fingerprints" of chromosomal DNA digested with restriction endonuclease HaeIII. To demonstrate that this polymorphism in restriction fragments can be used to study the acquisition and transmission of this organism, we examined isolates of S. mutans from three mother-infant pairs obtained at the time the infant first became colonized by this organism. Results indicate that strains of S. mutans found in infants exhibit restriction fragment profiles identical to those of their mothers, strongly supporting the notion that mothers transmit this organism to their infants. Also, we show that strains of S. mutans with the same restriction fragment profile were stably maintained over a 3-year interval in the one mother-infant pair studied. Moreover, we found that mothers and their infants harbored only a few individual strains, suggesting that transmission of this organism is probably confined within discrete family cohorts. Collectively, these findings demonstrate the potential utility of genomic fingerprinting in studying the natural history of S. mutans infections in humans.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caufield P. W., Childers N. K., Allen D. N., Hansen J. B. Distinct bacteriocin groups correlate with different groups of Streptococcus mutans plasmids. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):51–56. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.51-56.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caufield P. W., Ratanapridakul K., Allen D. N., Cutter G. R. Plasmid-containing strains of Streptococcus mutans cluster within family and racial cohorts: implications for natural transmission. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3216–3220. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3216-3220.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caufield P. W., Wannemuehler Y. M., Hansen J. B. Familial clustering of the Streptococcus mutans cryptic plasmid strain in a dental clinic population. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):785–787. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.785-787.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey A. L., Rogers A. H. Multiple types of the bacterium Streptococcus mutans in the human mouth and their intra-family transmission. Arch Oral Biol. 1984;29(6):453–460. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(84)90026-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmour M. N., Whittam T. S., Kilian M., Selander R. K. Genetic relationships among the oral streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5247–5257. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5247-5257.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold O. G., Jordan H. V., Van Houte J. A selective medium for Streptococcus mutans. Arch Oral Biol. 1973 Nov;18(11):1357–1364. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(73)90109-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuda N., Tsutsumi N., Sobue S., Hamada S. Longitudinal survey of the distribution of various serotypes of Streptococcus mutans in infants. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Oct;10(4):497–502. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.4.497-502.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers A. H. Evidence for the transmissibility of human dental caries. Aust Dent J. 1977 Feb;22(1):53–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1834-7819.1977.tb04444.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleifer K. H., Kilpper-Bälz R., Kraus J., Gehring F. Relatedness and classification of Streptococcus mutans and "mutans-like" streptococci. J Dent Res. 1984 Aug;63(8):1047–1050. doi: 10.1177/00220345840630080701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]