Abstract
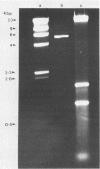
A nonradioactive dot blot hybridization assay for human parvovirus B19 DNA was set up by using a biotin-labeled DNA probe and streptavidin-alkaline phosphatase conjugate. The assay was used to examine 4,895 specimens referred for B19 virus diagnosis during 1987. Of 48 specimens that gave positive reactions for B19 DNA, 41 were confirmed virus positive by electron microscopy (n = 36), radioimmunoassay (n = 26), or counterimmunoelectrophoresis (n = 20). In 7 samples which were not confirmed and in 11 samples giving weak reactions for B19 DNA, there was serological or epidemiological evidence of recent B19 infection. A further 70 specimens gave weak, apparently false-positive reactions. By electron microscopy, 13 of 16 were contaminated by bacteria, and plasmid DNA was demonstrated in one specimen. Of 55 specimens tested, 52 reacted with streptavidin-alkaline phosphatase conjugate alone. These were probable sources of nonspecificity in an otherwise practical and economic screening method for B19 virus.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambinder R. F., Charache P., Staal S., Wright P., Forman M., Hayward S. D., Hayward G. S. The vector homology problem in diagnostic nucleic acid hybridization of clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jul;24(1):16–20. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.1.16-20.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson M. J., Davis L. R., Jones S. E., Pattison J. R., Serjeant G. R. The development and use of an antibody capture radioimmunoassay for specific IgM to a human parvovirus-like agent. J Hyg (Lond) 1982 Apr;88(2):309–324. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400070169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson M. J., Jones S. E., Fisher-Hoch S. P., Lewis E., Hall S. M., Bartlett C. L., Cohen B. J., Mortimer P. P., Pereira M. S. Human parvovirus, the cause of erythema infectiosum (fifth disease)? Lancet. 1983 Jun 18;1(8338):1378–1378. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92152-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson M. J., Jones S. E., Minson A. C. Diagnosis of human parvovirus infection by dot-blot hybridization using cloned viral DNA. J Med Virol. 1985 Feb;15(2):163–172. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890150209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson M. J., Khousam M. N., Maxwell D. J., Gould S. J., Happerfield L. C., Smith W. J. Human parvovirus B19 and hydrops fetalis. Lancet. 1988 Mar 5;1(8584):535–535. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91331-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T., Anand A., Ritchie L. D., Clewley J. P., Reid T. M. Intrauterine parvovirus infection associated with hydrops fetalis. Lancet. 1984 Nov 3;2(8410):1033–1034. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91126-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewley J. P. Detection of human parvovirus using a molecularly cloned probe. J Med Virol. 1985 Feb;15(2):173–181. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890150210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen B. J., Hewish R. A., Mortimer P. P. Comparison of radioimmunoassay and counter-immunoelectrophoresis for the detection of antibody to hepatitis B core antigen. J Virol Methods. 1981 Feb;2(3):181–192. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(81)90037-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen B. J., Mortimer P. P., Pereira M. S. Diagnostic assays with monoclonal antibodies for the human serum parvovirus-like virus (SPLV). J Hyg (Lond) 1983 Aug;91(1):113–130. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400060095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cossart Y. E., Field A. M., Cant B., Widdows D. Parvovirus-like particles in human sera. Lancet. 1975 Jan 11;1(7898):72–73. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91074-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham D. A., Pattison J. R., Craig R. K. Detection of parvovirus DNA in human serum using biotinylated RNA hybridisation probes. J Virol Methods. 1988 Mar-Apr;19(3-4):279–288. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(88)90022-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtzman G. J., Ozawa K., Cohen B., Hanson G., Oseas R., Young N. S. Chronic bone marrow failure due to persistent B19 parvovirus infection. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 30;317(5):287–294. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707303170506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori J., Beattie P., Melton D. W., Cohen B. J., Clewley J. P. Structure and mapping of the DNA of human parvovirus B19. J Gen Virol. 1987 Nov;68(Pt 11):2797–2806. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-11-2797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedobitek G., Finn T., Herbst H., Bornhöft G., Gerdes J., Stein H. Detection of viral DNA by in situ hybridization using bromodeoxyuridine-labeled DNA probes. Am J Pathol. 1988 Apr;131(1):1–4. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa K., Kurtzman G., Young N. Replication of the B19 parvovirus in human bone marrow cell cultures. Science. 1986 Aug 22;233(4766):883–886. doi: 10.1126/science.3738514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira H. G. Non-radioactive nucleic acid probes for the diagnosis of virus infections. Bioessays. 1986 Mar;4(3):110–113. doi: 10.1002/bies.950040305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter H. J., Khong T. Y., Evans M. F., Chan V. T., Fleming K. A. Parvovirus as a cause of hydrops fetalis: detection by in situ DNA hybridisation. J Clin Pathol. 1988 Apr;41(4):381–383. doi: 10.1136/jcp.41.4.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethabutr O., Hanchalay S., Echeverria P., Taylor D. N., Leksomboon U. A non-radioactive DNA probe to identify Shigella and enteroinvasive Escherichia coli in stools of children with diarrhoea. Lancet. 1985 Nov 16;2(8464):1095–1097. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90687-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabarés E. Detection of DNA viruses by radioactive and non radioactive DNA probes: application to African swine fever virus. Arch Virol. 1987;92(3-4):233–242. doi: 10.1007/BF01317480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. G., Woolf A. D., Mortimer P. P., Cohen B. J., Blake D. R., Bacon P. A. Human parvovirus arthropathy. Lancet. 1985 Feb 23;1(8426):419–421. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91145-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young N. Hematologic and hematopoietic consequences of B19 parvovirus infection. Semin Hematol. 1988 Apr;25(2):159–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]