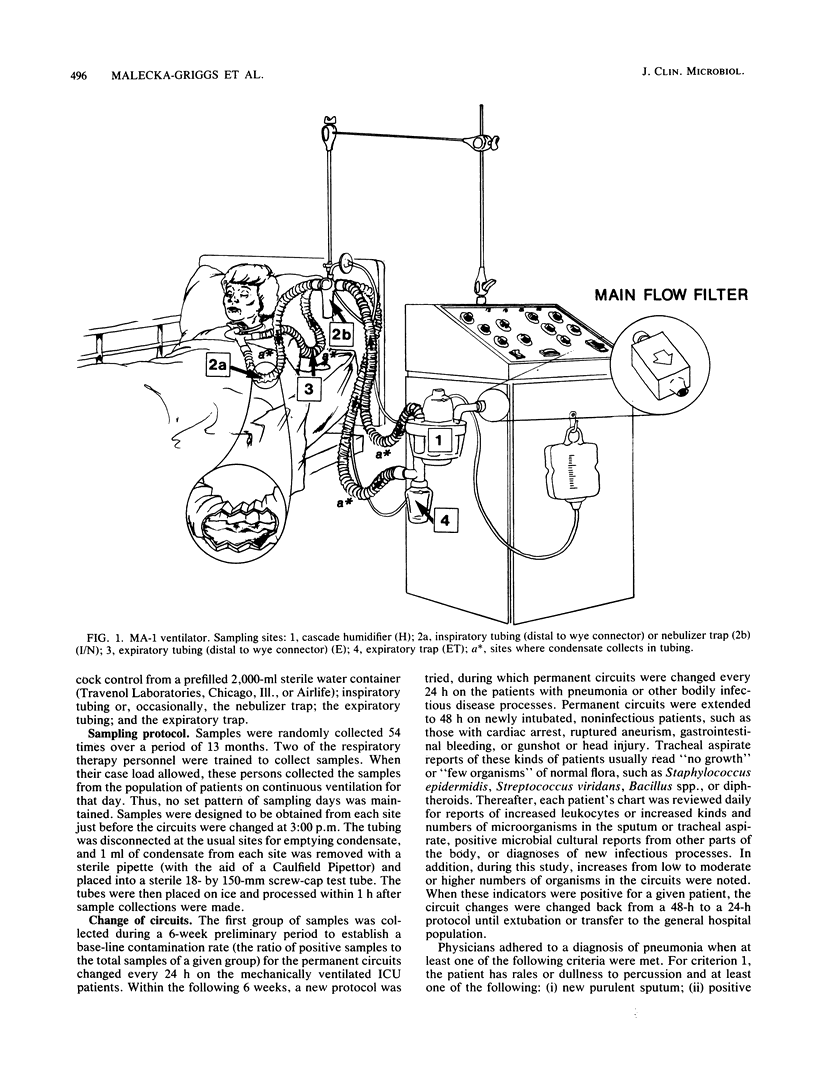
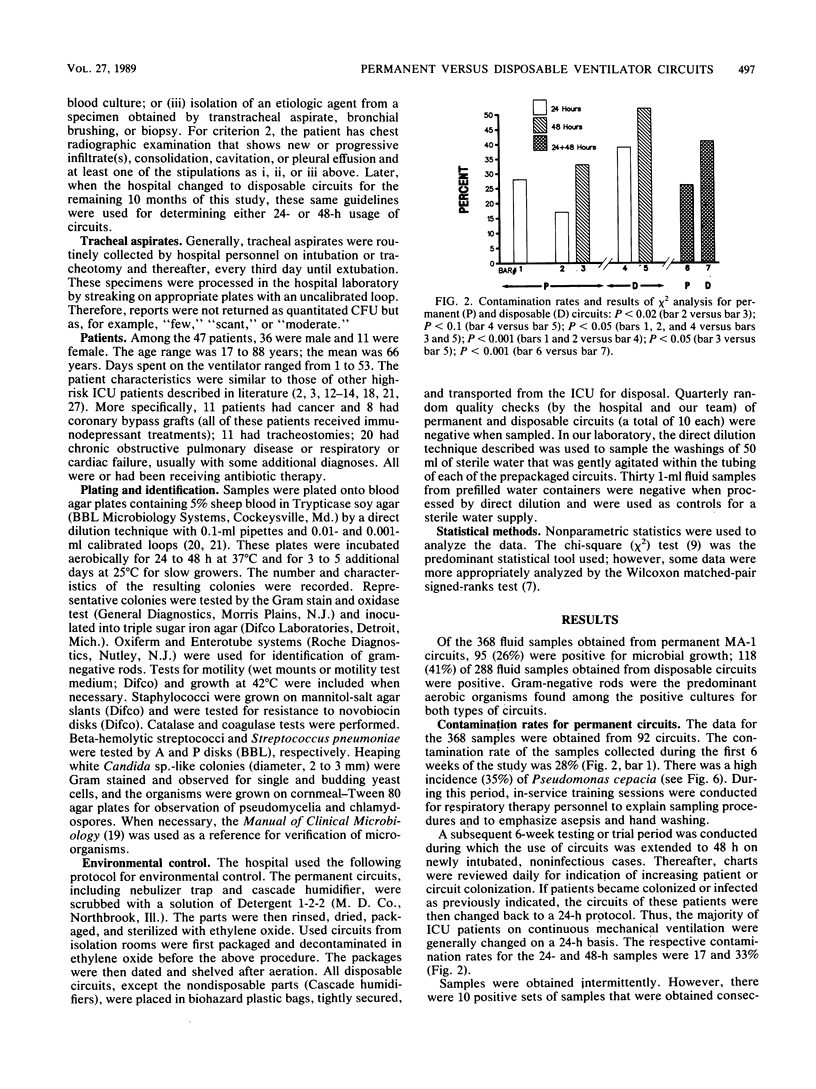
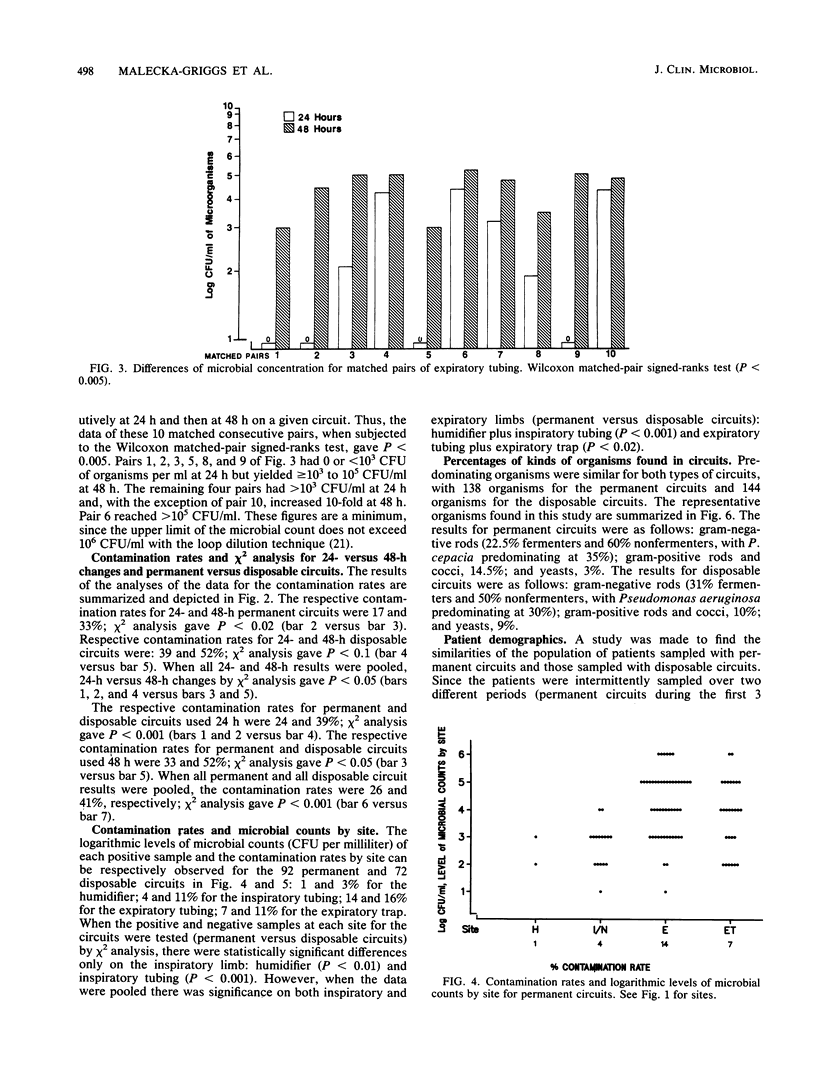
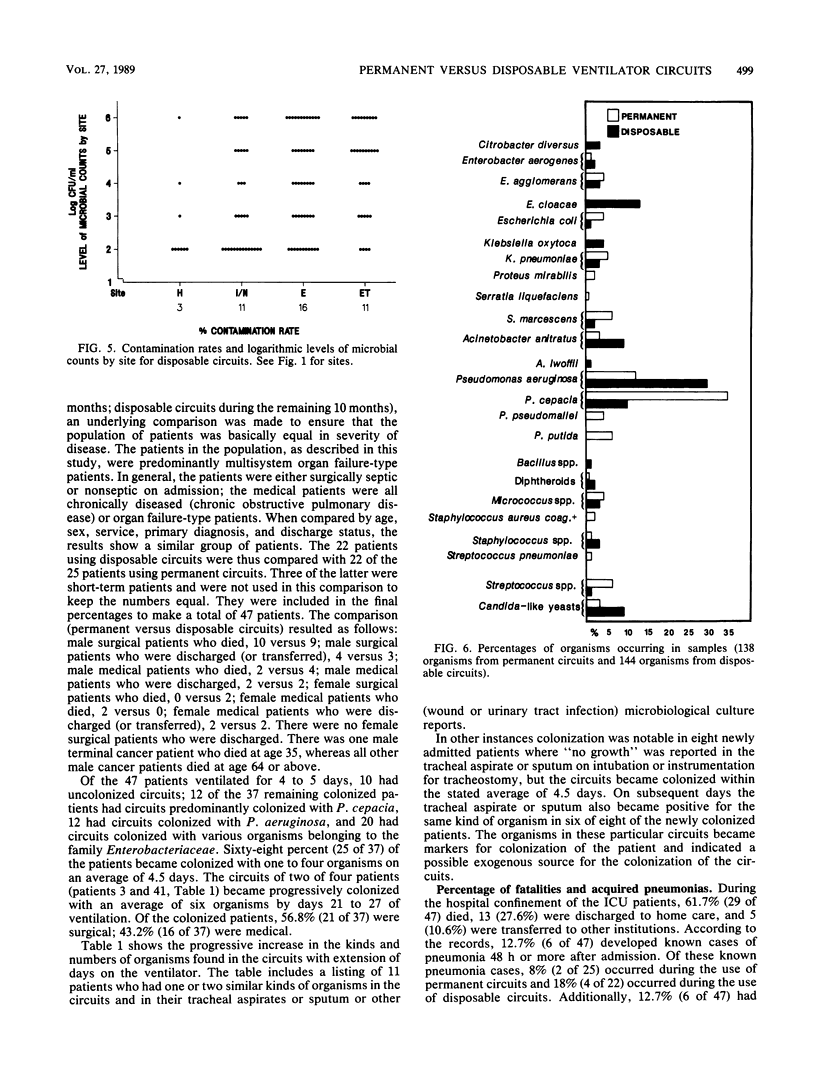
Abstract
One hospital sought to study the differences in using resterilizable permanent versus disposable ventilator circuits and changing the circuits on a 24-h versus a 48-h basis. Over a period of 13 months 656 condensate samples from 92 permanent and 72 disposable circuits were collected and plated by a loop dilution technique. Two samples were collected from the inspiratory limb (humidifier; tubing or nebulizer), and two were collected from the expiratory limb (tubing and trap) of each circuit. Contamination rates were higher for disposable circuits than for permanent circuits and for 48-h changes than for 24-h changes. Results of chi 2 testing by site indicated there was more contamination on the inspiratory and expiratory limbs each with use of disposable circuits than with the use of permanent circuits. The total results (chi 2 analysis) showed significantly greater microbial growth with the use of disposable circuits (permanent versus disposable, P less than 0.001) and extension of time to 48-h changes (24 h versus 48 h, P less than 0.05). In the experience of this hospital permanent circuits proved more advantageous from the standpoint of contamination risk and cost.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bryan C. S., Reynolds K. L. Bacteremic nosocomial pneumonia. Analysis of 172 episodes from a single metropolitan area. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 May;129(5):668–671. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.129.5.668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celis R., Torres A., Gatell J. M., Almela M., Rodríguez-Roisin R., Agustí-Vidal A. Nosocomial pneumonia. A multivariate analysis of risk and prognosis. Chest. 1988 Feb;93(2):318–324. doi: 10.1378/chest.93.2.318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven D. E., Connolly M. G., Jr, Lichtenberg D. A., Primeau P. J., McCabe W. R. Contamination of mechanical ventilators with tubing changes every 24 or 48 hours. N Engl J Med. 1982 Jun 24;306(25):1505–1509. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198206243062501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven D. E., Kunches L. M., Kilinsky V., Lichtenberg D. A., Make B. J., McCabe W. R. Risk factors for pneumonia and fatality in patients receiving continuous mechanical ventilation. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 May;133(5):792–796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donowitz L. G., Wenzel R. P., Hoyt J. W. High risk of hospital-acquired infection in the ICU patient. Crit Care Med. 1982 Jun;10(6):355–357. doi: 10.1097/00003246-198206000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favero M. S., Carson L. A., Bond W. W., Petersen N. J. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: growth in distilled water from hospitals. Science. 1971 Aug 27;173(3999):836–838. doi: 10.1126/science.173.3999.836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favero M. S., Petersen N. J., Carson L. A., Bond W. W., Hindman S. H. Gram-negative water bacteria in hemodialysis systems. Health Lab Sci. 1975 Oct;12(4):321–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross P. A., Neu H. C., Aswapokee P., Van Antwerpen C., Aswapokee N. Deaths from nosocomial infections: experience in a university hospital and a community hospital. Am J Med. 1980 Feb;68(2):219–223. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90357-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross P. A., Van Antwerpen C. Nosocomial infections and hospital deaths. A case-control study. Am J Med. 1983 Oct;75(4):658–662. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)90453-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haley R. W., Hooton T. M., Culver D. H., Stanley R. C., Emori T. G., Hardison C. D., Quade D., Shachtman R. H., Schaberg D. R., Shah B. V. Nosocomial infections in U.S. hospitals, 1975-1976: estimated frequency by selected characteristics of patients. Am J Med. 1981 Apr;70(4):947–959. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90561-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johanson W. G., Jr, Pierce A. K., Sanford J. P., Thomas G. D. Nosocomial respiratory infections with gram-negative bacilli. The significance of colonization of the respiratory tract. Ann Intern Med. 1972 Nov;77(5):701–706. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-77-5-701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johanson W. G., Pierce A. K., Sanford J. P. Changing pharyngeal bacterial flora of hospitalized patients. Emergence of gram-negative bacilli. N Engl J Med. 1969 Nov 20;281(21):1137–1140. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196911202812101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malecka-Griggs B. Microbiological assessment of 24- and 48-h changes and management of semiclosed circuits from ventilators in a neonatal intensive care unit. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Feb;23(2):322–328. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.2.322-328.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malecka-Griggs B., Reinhardt D. J. Direct dilution sampling, quantitation, and microbial assessment of open-system ventilation circuits in intensive care units. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 May;17(5):870–877. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.5.870-877.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manship L., McMillin R. D., Brown J. J. The influence of sepsis and multisystem and organ failure on mortality in the surgical intensive care unit. Am Surg. 1984 Feb;50(2):94–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer D. L. Microbiology of pneumonia in the patient at risk. Am J Med. 1984 May 15;76(5A):53–60. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90244-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheth N. K., Franson T. R., Rose H. D., Buckmire F. L., Cooper J. A., Sohnle P. G. Colonization of bacteria on polyvinyl chloride and Teflon intravascular catheters in hospitalized patients. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Nov;18(5):1061–1063. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.5.1061-1063.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons B. P., Wong E. S. Guideline for prevention of nosocomial pneumonia. Infect Control. 1982 Jul-Aug;3(4):327–333. doi: 10.1017/s0195941700056423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton J. R. A new controversy in respiratory equipment management: reusables versus disposed disposables versus reused disposables. Respir Care. 1986 Mar;31(3):213–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenzel R. P., Thompson R. L., Landry S. M., Russell B. S., Miller P. J., Ponce de Leon S., Miller G. B., Jr Hospital-acquired infections in intensive care unit patients: an overview with emphasis on epidemics. Infect Control. 1983 Sep-Oct;4(5):371–375. doi: 10.1017/s0195941700059774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


