Abstract
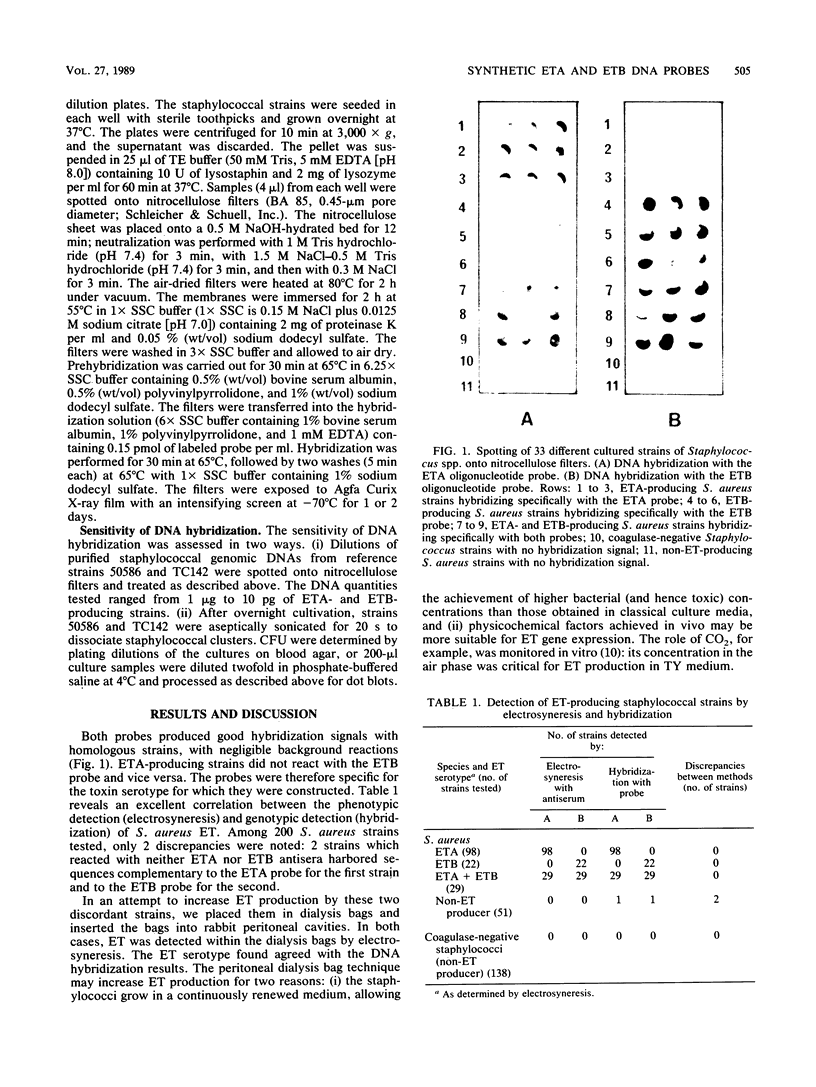
Two methods for the detection of exfoliative toxin (ET) from Staphylococcus aureus were compared: (i) a phenotypic assay, electrosyneresis, and (ii) a genotypic assay, staphylococcal DNA hybridization with oligodeoxynucleotide probes. The probes were chosen from the previously determined sequences of serotype A and B of ET, one probe for serotype A and another for serotype B. Strains exhibiting ET production in electrosyneresis always possessed the ET gene(s). Conversely, some strains not exhibiting ET production in electrosyneresis harbored the ET gene(s). The latter strains produced levels of ET. ET-negative phage group 2 strains of S. aureus as well as tested coagulase-negative staphylococci did not possess the ET gene(s). The sensitivity of the DNA hybridization technique was 10(6) bacteria or 100 ng of genomic DNA.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anthony B. F., Giuliano D. M., Oh W. Nursery outbreak of staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome. Rapid identification of the epidemic bacterial strain. Am J Dis Child. 1972 Jul;124(1):41–44. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1972.02110130043006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arbuthnott J. P., Billcliffe B. Qualitative and quantitative methods for detecting staphylococcal epidermolytic toxin. J Med Microbiol. 1976 May;9(2):191–201. doi: 10.1099/00222615-9-2-191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker D. H., Wuepper K. D., Rasmussen J. E. Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome: detection of antibody to epidermolytic toxin by a primary binding assay. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1978 Mar;3(1):17–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2230.1978.tb01453.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleurette J., Ritter J. Prévalence des souches de Staphylococcus aureus productrices d'exfoliatine dans le groupe bactériophagique II. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1980 Sep-Oct;131B(2):175–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapral F. A., Miller M. M. Product of Staphylococcus aureus responsible for the scalded-skin syndrome. Infect Immun. 1971 Nov;4(5):541–545. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.5.541-545.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. Y., Schmidt J. J., Johnson-Winegar A. D., Spero L., Iandolo J. J. Sequence determination and comparison of the exfoliative toxin A and toxin B genes from Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):3904–3909. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.3904-3909.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Toole P. W., Foster T. J. Nucleotide sequence of the epidermolytic toxin A gene of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):3910–3915. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.3910-3915.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piémont Y., Haubensack M., Monteil H. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for Staphylococcus aureus exfoliative toxins A and B and some applications. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Dec;20(6):1114–1121. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.6.1114-1121.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piémont Y., Monteil H. Mise en évidence par électrosynérèse des deux sérotypes d'exfoliatine produits par Staphylococcus aureus. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1983 Mar-Apr;134A(2):169–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogolsky M. Nonenteric toxins of Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Sep;43(3):320–360. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.3.320-360.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willard D., Monteil H., Piemont Y., Assi R., Messer J., Lavillaureix J., Minck R., Gandar R. L'exfoliatine dans les staphylococcies néonatales. Nouv Presse Med. 1982 Dec 18;11(51):3769–3771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuepper K. D., Baker D. H., Dimond R. L. Measurement of the staphylococcal epidermolytic toxin: a comparison of bioassay, radial immunodiffusion, and radioimmunoassay. J Invest Dermatol. 1976 Oct;67(4):526–531. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12664548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]