Abstract
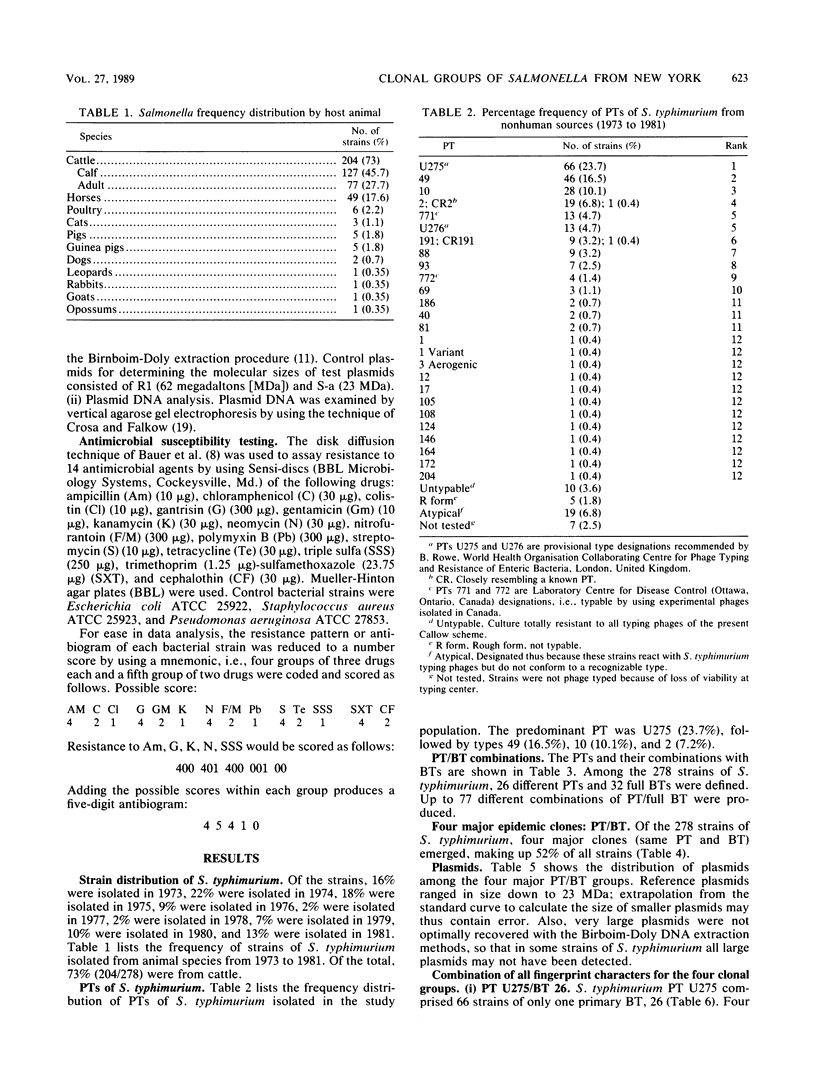
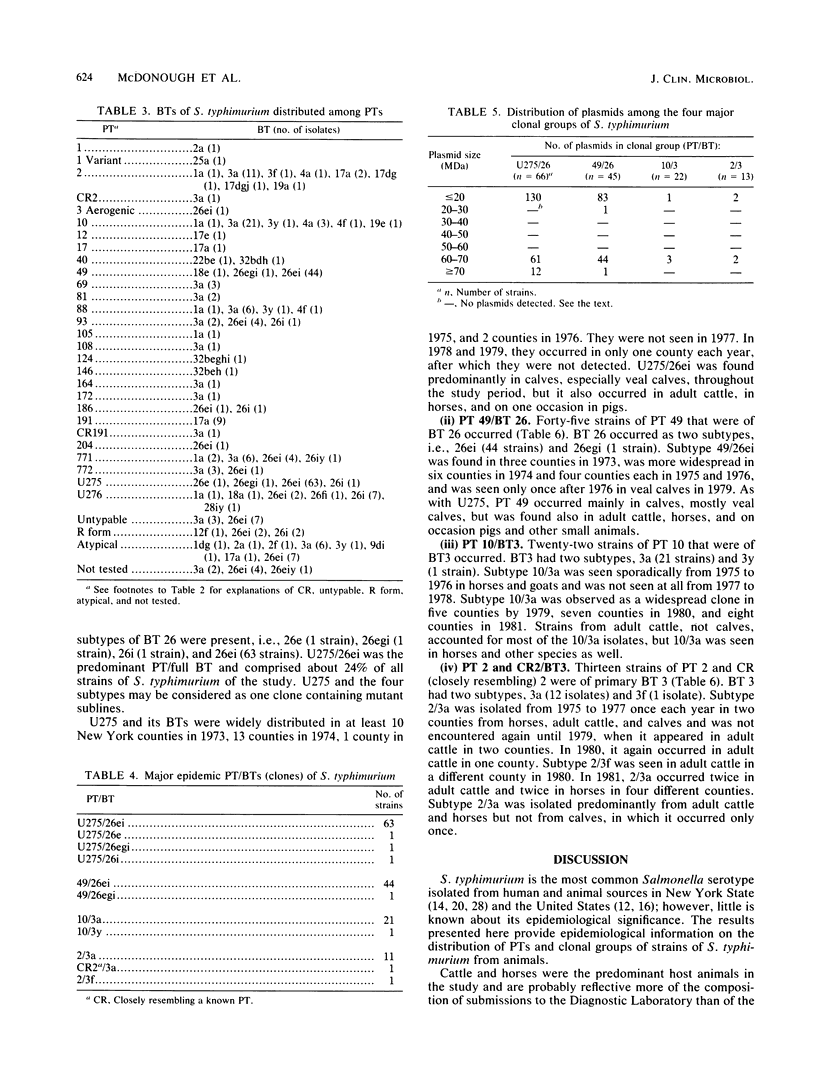
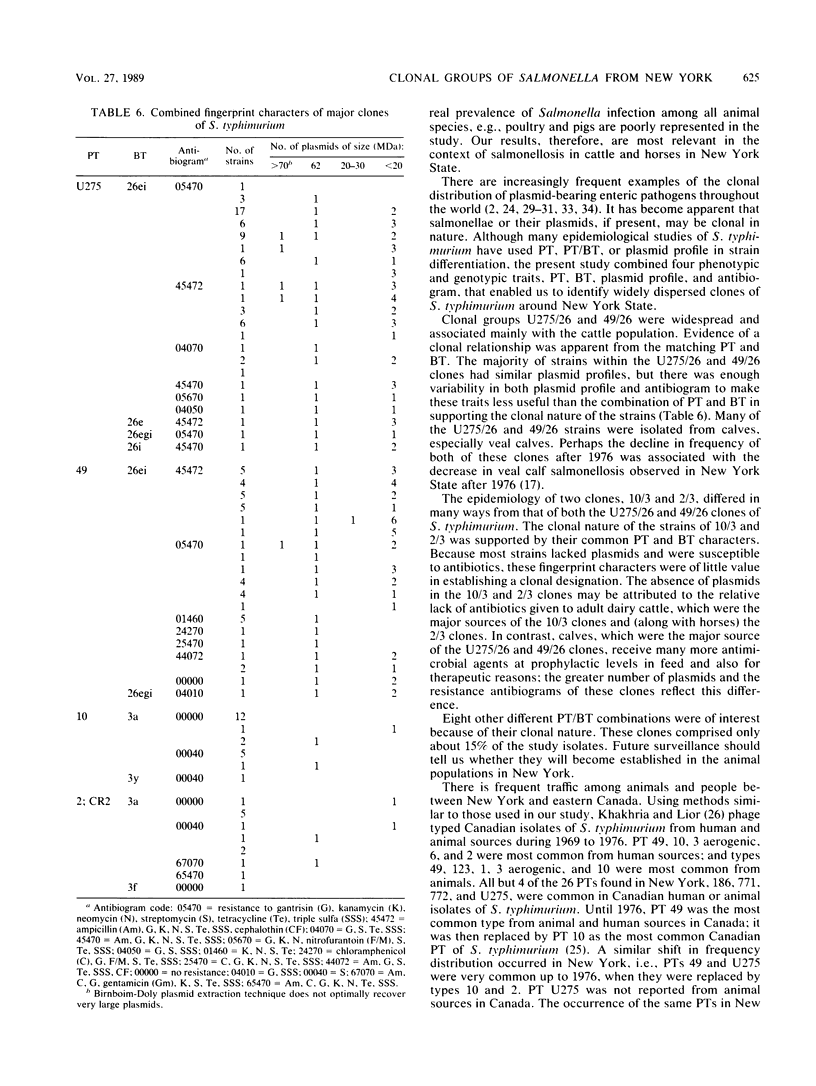
The epidemiology of 278 strains of Salmonella typhimurium isolated from 1973 to 1981 from animals in New York State was studied by using four "fingerprinting" techniques, bacteriophage type (B.R. Callow, J. Hyg. 57:346-359, 1959), biotype (J. P. Duguid, E. S. Anderson, G. A. Alfredsson, R. Barker, and D. C. Old, J. Med. Microbiol. 8:149-166, 1975), plasmid profile, and antibiogram. Phage type with biotype was the most useful marker for distinguishing clonal groups of S. typhimurium. Four clones of S. typhimurium predominated, i.e., phage type/biotypes U275/26, 49/26, 10/3, and 2/3. U275/26 and 49/26 were commonly found until 1976, but clones 10/3 and 2/3 were predominant after 1976. Comparison of results with data from Canada suggested a dissemination of strains of S. typhimurium between Canada and New York. Cattle were a common source of phage type 49, as has been observed in other countries.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alfredsson G. A., Barker R. M., Old D. C., Duguid J. P. Use of tartaric acid isomers and citric acid in the biotyping of Salmonella typhimurium. J Hyg (Lond) 1972 Dec;70(4):651–666. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400022518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson E. S., Threlfall E. J., Carr J. M., McConnell M. M., Smith H. R. Clonal distribution of resistance plasmid-carrying Salmonella typhimurium, mainly in the Middle East. J Hyg (Lond) 1977 Dec;79(3):425–448. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400053286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson E. S., Ward L. R., De Saxe M. J., Old D. C., Barker R., Duguid J. P. Correlation of phaga type, biotype and source in strains of Salmonella typhimurium. J Hyg (Lond) 1978 Oct;81(2):203–217. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400025031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson E. S., Ward L. R., Saxe M. J., de Sa J. D. Bacteriophage-typing designations of Salmonella typhimurium. J Hyg (Lond) 1977 Apr;78(2):297–300. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400056187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker R. M., Old D. C. Biotypes of strains of Salmonella typhimurium of phage types 49, 204 and 193. J Med Microbiol. 1980 May;13(2):369–371. doi: 10.1099/00222615-13-2-369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker R., Old D. C. Biotyping and colicine typing of Salmonella typhimurium strains of phage type 141 isolated in Scotland. J Med Microbiol. 1979 Aug;12(3):265–276. doi: 10.1099/00222615-12-3-265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker R., Old D. C., Sharp J. C. Phage type/biotype groups of Salmonella typhimurium in Scotland 1974-6: variation during spread of epidemic clones. J Hyg (Lond) 1980 Feb;84(1):115–125. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400026607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezanson G. S., Khakhria R., Bollegraaf E. Nosocomial outbreak caused by antibiotic-resistant strain of Salmonella typhimurium acquired from dairy cattle. Can Med Assoc J. 1983 Feb 15;128(4):426–427. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezanson G. S., Pauzé M., Lior H. Antibiotic resistance and R-plasmids in food chain Salmonella: evidence of plasmid relatedness. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Mar;41(3):585–592. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.3.585-592.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn B. O., Harrington R., Jr Salmonella and Arizona serotypes from animals and related sources reported during fiscal year 1978. Proc Annu Meet U S Anim Health Assoc. 1979;(83):394–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandis H., Posch J., Oberhoffer G., Andries L., Lehmacher U. Beitrag zur Epidemiologie von Salmonella typhimurium, dargestellt anhand der Ergebnisse der Lysotypie aus den Jahren 1969--1978. Offentl Gesundheitswes. 1980 Sep 20;42 (Suppl 2):75–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruner D. W. Salmonella cultures typed during the years 1950-1971 for the service laboratories of the New York State Veterinary College at Cornell University. Cornell Vet. 1973 Jan;63(1):138–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CALLOW B. R. A new phage-typing scheme for Salmonella typhi-murium. J Hyg (Lond) 1959 Sep;57:346–359. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400020209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherubin C. E., Timoney J. F., Sierra M. F., Ma P., Marr J., Shin S. A sudden decline in ampicillin resistance in Salmonella typhimurium. JAMA. 1980 Feb 1;243(5):439–442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crichton P. B., Old D. C. Biotyping of Escherichia coli. J Med Microbiol. 1979 Nov;12(4):473–486. doi: 10.1099/00222615-12-4-473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dondero N. C., Thomas C. T., Khare M., Timoney J. F., Fukui G. M. Salmonella in surface waters of central New York state. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Apr;33(4):791–801. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.4.791-801.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duguid J. P., Anderson E. S., Alfredsson G. A., Barker R., Old D. C. A new biotyping scheme for Salmonella typhimurium and its phylogenetic significance. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Feb;8(1):149–166. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-1-149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg S. D., Wachsmuth I. K., Hickman-Brenner F. W., Cohen M. L. Comparison of plasmid profile analysis, phage typing, and antimicrobial susceptibility testing in characterizing Salmonella typhimurium isolates from outbreaks. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):100–104. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.100-104.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khakhria R., Bezanson G., Duck D., Lior H. The epidemic spread of Salmonella typhimurium phage type 10 in Canada (1970-1979). Can J Microbiol. 1983 Nov;29(11):1583–1588. doi: 10.1139/m83-241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis M. J., Stocker B. A. A biochemical subdivision of one phage type of Salmonella typhimurium. J Hyg (Lond) 1971 Dec;69(4):683–691. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400021951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonough P. L., Shin S. J., Timoney J. F. Salmonella serotypes from animals in New York State, 1978-1983. Cornell Vet. 1986 Jan;76(1):30–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov F., Orskov I. From the national institutes of health. Summary of a workshop on the clone concept in the epidemiology, taxonomy, and evolution of the enterobacteriaceae and other bacteria. J Infect Dis. 1983 Aug;148(2):346–357. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.2.346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe B., Frost J. A., Threlfall E. J., Ward L. R. Spread of a multiresistant clone of Salmonella typhimurium phage type 66/122 in South-East Asia and the Middle East. Lancet. 1980 May 17;1(8177):1070–1071. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91509-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe B., Threlfall E. J., Ward L. R., Ashley A. S. International spread of multiresistent strains of Salmonella typhimurium phage types 204 and 193 from Britain to Europe. Vet Rec. 1979 Nov 17;105(20):468–469. doi: 10.1136/vr.105.20.468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. N., Wachsmuth I. K., Shangkuan Y. H., Schmidt E. V., Barrett T. J., Schrader J. S., Scherach C. S., McGee H. B., Feldman R. A., Brenner D. J. Salmonellosis associated with marijuana: a multistate outbreak traced by plasmid fingerprinting. N Engl J Med. 1982 May 27;306(21):1249–1253. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198205273062101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Threlfall E. J., Ward L. R., Rowe B. Epidermic spread of a chloramphenicol-resistant strain of Salmonella typhimurium phage type 204 in bovine animals in Britain. Vet Rec. 1978 Nov 11;103(20):438–440. doi: 10.1136/vr.103.20.438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Threlfall E. J., Ward L. R., Rowe B. Spread of multiresistant strains of Salmonella typhimurium phage types 204 and 193 in Britain. Br Med J. 1978 Oct 7;2(6143):997–997. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6143.997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timoney J. F. The epidemiology and genetics of antibiotic resistance of Salmonella typhimurium isolated from diseases animals in New York. J Infect Dis. 1978 Jan;137(1):67–73. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



