Abstract
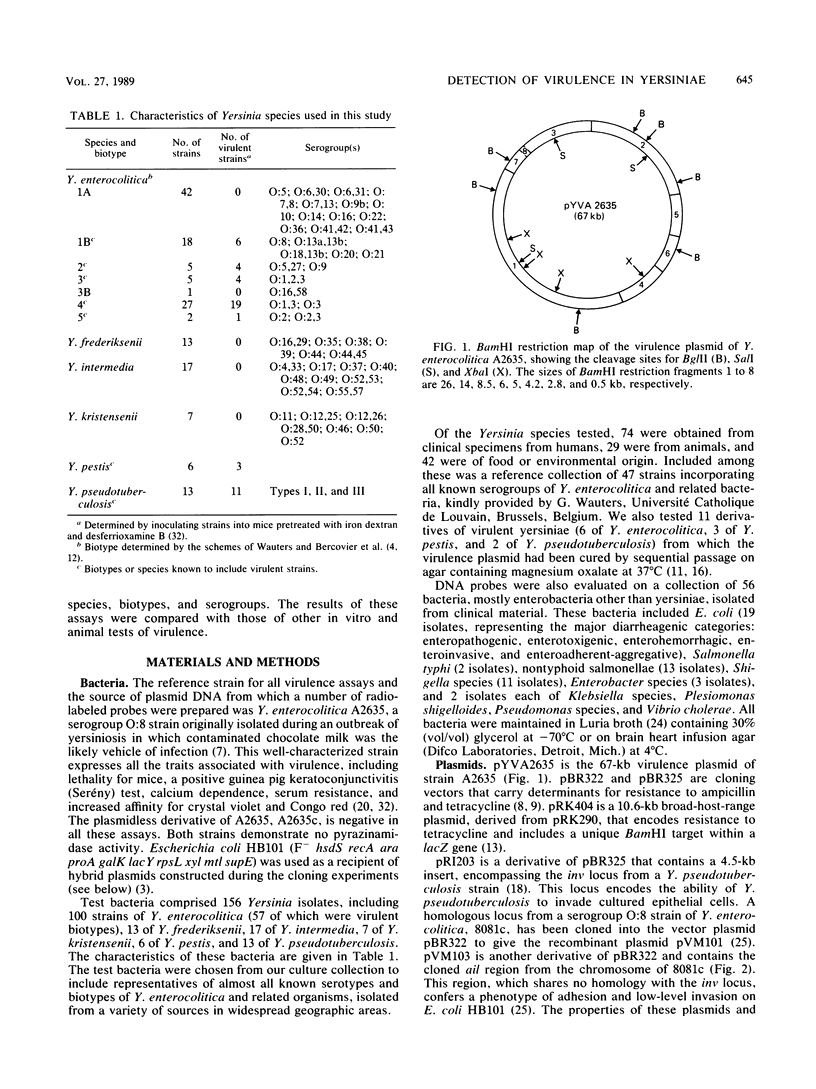
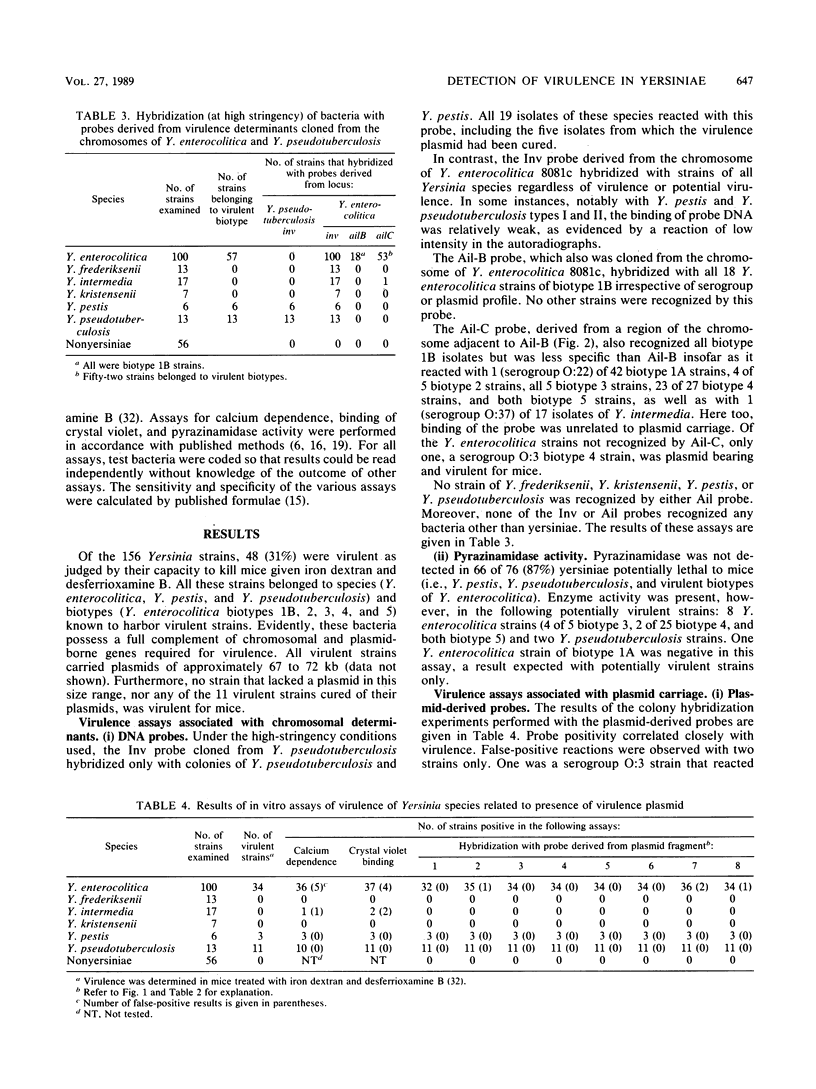
The virulence of yersiniae varies according to (i) species and biotype and (ii) possession of a 67- to 72-kilobase virulence plasmid. Y. pestis, Y. pseudotuberculosis, and biotypes 1B, 2, 3, 4, and 5 of Y. enterocolitica are inherently virulent but express full virulence only when in possession of a virulence plasmid. Other Yersinia species and biotypes 1A and 3B of Y. enterocolitica are seldom implicated in disease. In this study, we prepared DNA probes from eight nonoverlapping regions of the virulence plasmid of a strain of Y. enterocolitica and from the inv and ail chromosomal loci responsible for the invasive capacity of Y. enterocolitica and Y. pseudotuberculosis. The probes were used in colony hybridization experiments to investigate 156 yersiniae of various species and biotypes and of differing virulence. Probes prepared from the inv gene of Y. pseudotuberculosis hybridized with Y. pseudotuberculosis and Y. pestis only, whereas an analogous probe prepared from Y. enterocolitica hybridized with all species and biotypes of yersiniae (but not with other bacteria) regardless of virulence or potential virulence. Probes prepared from the ail region of Y. enterocolitica reacted almost exclusively with Y. enterocolitica strains of pathogenic biotypes. Probes prepared from the virulence plasmid of a serogroup O:8, biotype 1B isolate of Y. enterocolitica identified virulent yersiniae in all species with a high degree of sensitivity and specificity. These probes did not react with yersiniae of avirulent biotypes or species. Of the other assays of virulence evaluated (calcium dependence, binding of crystal violet, and pyrazinamidase activity), binding of crystal violet provided a simple means for identifying plasmid-bearing strains.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aho K. Yersinia reactive arthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1983 Nov;22(4 Suppl 2):41–45. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/xxii.suppl_2.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann B. J. Pedigrees of some mutant strains of Escherichia coli K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):525–557. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.525-557.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhaduri S., Conway L. K., Lachica R. V. Assay of crystal violet binding for rapid identification of virulent plasmid-bearing clones of Yersinia enterocolitica. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jun;25(6):1039–1042. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.6.1039-1042.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black R. E., Jackson R. J., Tsai T., Medvesky M., Shayegani M., Feeley J. C., MacLeod K. I., Wakelee A. M. Epidemic Yersinia enterocolitica infection due to contaminated chocolate milk. N Engl J Med. 1978 Jan 12;298(2):76–79. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197801122980204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. III. Derivatives of plasmid pBR322 carrying unique Eco RI sites for selection of Eco RI generated recombinant DNA molecules. Gene. 1978 Oct;4(2):121–136. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(78)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottone E. J. Yersinia enterocolitica: a panoramic view of a charismatic microorganism. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol. 1977;5(2):211–241. doi: 10.3109/10408417709102312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang M. T., Schink J., Shimaoka J., Doyle M. P. Comparison of three tests for virulent Yersinia enterocolitica. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Sep;20(3):589–591. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.3.589-591.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelis G., Laroche Y., Balligand G., Sory M. P., Wauters G. Yersinia enterocolitica, a primary model for bacterial invasiveness. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jan-Feb;9(1):64–87. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Schmidhauser T., Yakobson E., Lu P., Liang X. W., Finlay D. R., Guiney D., Helinski D. R. Plasmids related to the broad host range vector, pRK290, useful for gene cloning and for monitoring gene expression. Plasmid. 1985 Mar;13(2):149–153. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Sodd M. A., Neill R. J., Seguin M. C., Williams J. E. Cloning and use of Vwa plasmid DNA as gene probes for virulent Yersiniae. Contrib Microbiol Immunol. 1987;9:296–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIGUCHI K., SMITH J. L. Studies on the nutrition and physiology of Pasteurella pestis. VI. A differential plating medium for the estimation of the mutation rate to avirulence. J Bacteriol. 1961 Apr;81:605–608. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.4.605-608.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill W. E., Payne W. L., Aulisio C. C. Detection and enumeration of virulent Yersinia enterocolitica in food by DNA colony hybridization. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Sep;46(3):636–641. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.3.636-641.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Falkow S. A single genetic locus encoded by Yersinia pseudotuberculosis permits invasion of cultured animal cells by Escherichia coli K-12. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):262–264. doi: 10.1038/317262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandolo K., Wauters G. Pyrazinamidase activity in Yersinia enterocolitica and related organisms. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jun;21(6):980–982. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.6.980-982.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay B. A., Wachsmuth K., Gemski P., Feeley J. C., Quan T. J., Brenner D. J. Virulence and phenotypic characterization of Yersinia enterocolitica isolated from humans in the United States. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jan;17(1):128–138. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.1.128-138.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen J. H. Yersinia enterocolitica infections and rheumatic diseases. Scand J Rheumatol. 1980;9(3):129–137. doi: 10.3109/03009748009098143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Falkow S. Evidence for two genetic loci in Yersinia enterocolitica that can promote invasion of epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1242–1248. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1242-1248.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Farmer J. J., 3rd, Hill W. E., Falkow S. The ail locus is found uniquely in Yersinia enterocolitica serotypes commonly associated with disease. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):121–131. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.121-131.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Martinez R. J. Role of a plasmid in the pathogenicity of Yersinia species. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;118:29–51. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70586-1_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Moseley S. L., Falkow S. Characterization of plasmids and plasmid-associated determinants of Yersinia enterocolitica pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):775–782. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.775-782.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Wolf-Watz H., Bolin I., Beeder A. B., Falkow S. Characterization of common virulence plasmids in Yersinia species and their role in the expression of outer membrane proteins. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):108–114. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.108-114.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prpic J. K., Robins-Browne R. M., Davey R. B. In vitro assessment of virulence in Yersinia enterocolitica and related species. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jul;22(1):105–110. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.1.105-110.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins-Browne R. M., Prpic J. K. Effects of iron and desferrioxamine on infections with Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):774–779. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.774-779.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins-Browne R. M., Tzipori S., Gonis G., Hayes J., Withers M., Prpic J. K. The pathogenesis of Yersinia enterocolitica infection in gnotobiotic piglets. J Med Microbiol. 1985 Jun;19(3):297–308. doi: 10.1099/00222615-19-3-297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiemann D. A., Devenish J. A. Relationship of HeLa cell infectivity to biochemical, serological, and virulence characteristics of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):497–506. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.497-506.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shayegani M., DeForge I., McGlynn D. M., Root T. Characteristics of Yersinia enterocolitica and related species isolated from human, animal, and environmental sources. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Sep;14(3):304–312. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.3.304-312.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tacket C. O., Davis B. R., Carter G. P., Randolph J. F., Cohen M. L. Yersinia enterocolitica pharyngitis. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Jul;99(1):40–42. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-1-40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Une T. Studies on the pathogenicity of Yersinia enterocolitica. II. Interaction with cultured cells in vitro. Microbiol Immunol. 1977;21(7):365–377. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1977.tb00301.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachsmuth K., Kay B. A., Birkness K. A. Diagnostic value of plasmid analyses and assays for virulence in Yersinia enterocolitica. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1984 Jun;2(3):219–228. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(84)90034-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]