Abstract
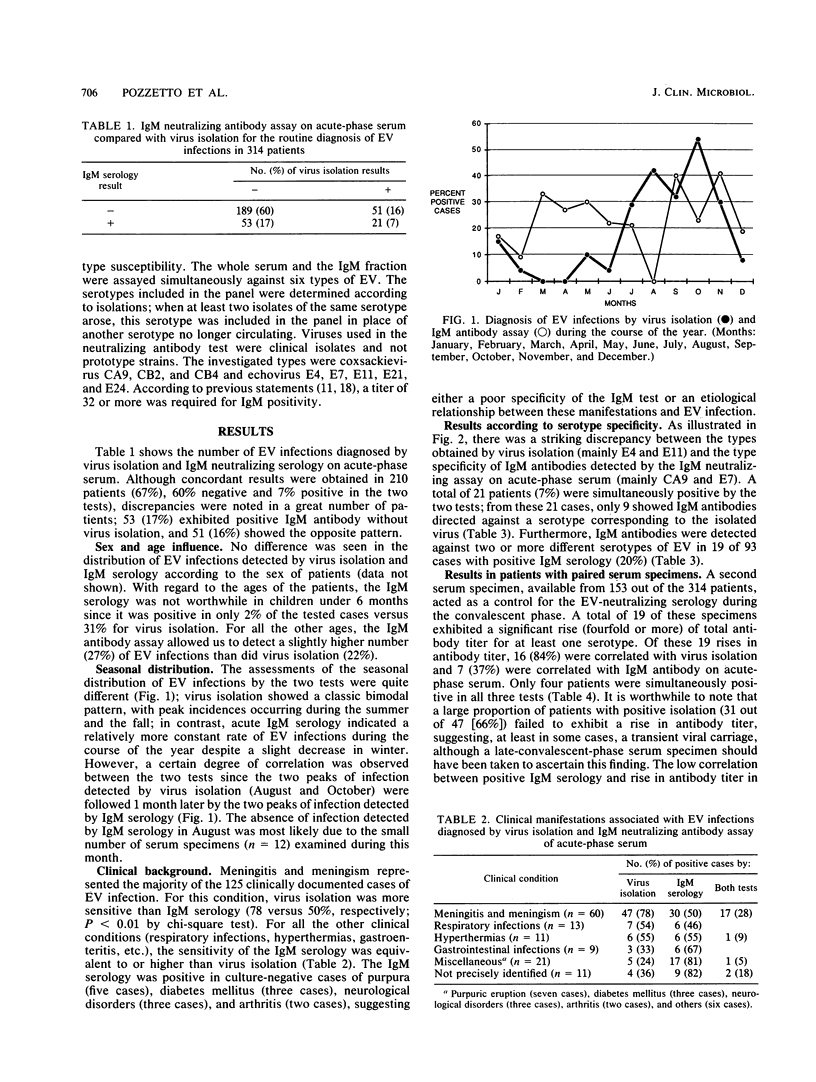
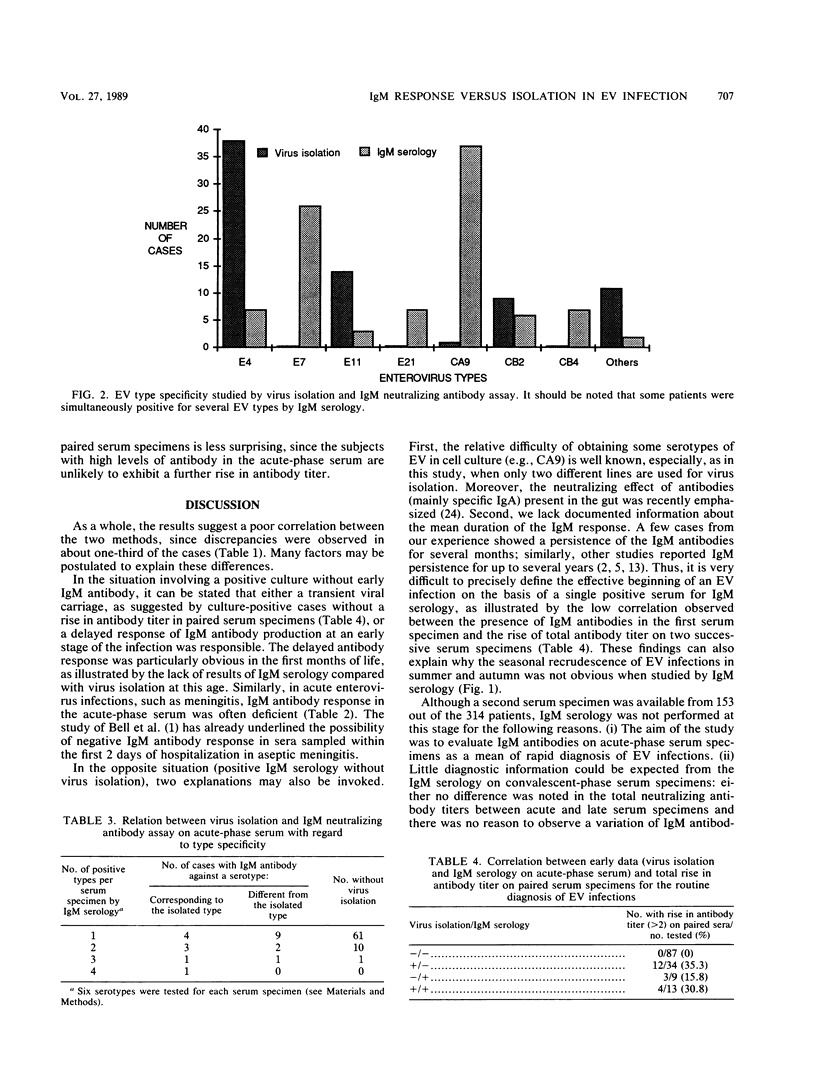
A total of 314 patients exhibiting symptoms consistent with a viral disease provided, during the early stage of hospitalization, at least one specimen from a peripheral site (throat or stools or both) and a serum specimen in order to evaluate the neutralizing immunoglobulin M (IgM) antibody response in acute-phase serum in comparison with virus isolation for the rapid diagnosis of enterovirus (EV) infection. IgM antibodies were fractionated by ion-exchange chromatography and tested by seroneutralization against the various types of EV that have been recently circulating. A total of 189 patients (60%) were negative, and 21 (7%) were positive by both methods; in 51 patients (16%), a virus was isolated without IgM antibody response; 53 patients (17%) showed the opposite pattern. In all age groups except for children under 6 months, the frequency of positive results was higher with IgM serology than with virus isolation (27 and 22%, respectively). Apart from meningitis, for which isolation was more efficient, the other clinical conditions were associated with similar percentages of positivity by both methods. Regarding the 21 cases with positive results by the two techniques, the same serotype was detected in 9 cases and different serotypes were detected in 12, suggesting crossreactivities. Thus, IgM neutralizing antibody response on acute-phase serum appears to be of limited value in the rapid diagnosis of acute EV infection but may prove useful for the investigation of the wide range of chronic diseases associated with EV.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banatvala J. E., Bryant J., Schernthaner G., Borkenstein M., Schober E., Brown D., De Silva L. M., Menser M. A., Silink M. Coxsackie B, mumps, rubella, and cytomegalovirus specific IgM responses in patients with juvenile-onset insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in Britain, Austria, and Australia. Lancet. 1985 Jun 22;1(8443):1409–1412. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91843-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell E. J., McCartney R. A., Basquill D., Chaudhuri A. K. Mu-antibody capture ELISA for the rapid diagnosis of enterovirus infections in patients with aseptic meningitis. J Med Virol. 1986 Jul;19(3):213–217. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890190303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calder B. D., Warnock P. J., McCartney R. A., Bell E. J. Coxsackie B viruses and the post-viral syndrome: a prospective study in general practice. J R Coll Gen Pract. 1987 Jan;37(294):11–14. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dörries R., ter Meulen V. Specificity of IgM antibodies in acute human coxsackievirus B infections, analysed by indirect solid phase enzyme immunoassay and immunoblot technique. J Gen Virol. 1983 Jan;64(Pt 1):159–167. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-1-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggers H. J., Mertens T. Persistence of Coxsackie B virus-specific IgM. Lancet. 1986 Aug 2;2(8501):284–284. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92102-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Hagrassy M. M., Banatvala J. E., Coltart D. J. Coxsackie-B-virus-specific IgM responses in patients with cardiac and other diseases. Lancet. 1980 Nov 29;2(8205):1160–1162. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)92595-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisk G., Fohlman J., Kobbah M., Ewald U., Tuvemo T., Diderholm H., Friman G. High frequency of Coxsackie-B-virus-specific IgM in children developing type I diabetes during a period of high diabetes morbidity. J Med Virol. 1985 Nov;17(3):219–227. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890170303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudin O. G., Berthoux F. C., Granouillet R., Genin C., Sabatier J. C. Infections persistantes à entérovirus non poliomyélitiques associées à des glomérulonéphrites. 9 observations. Nouv Presse Med. 1979 Oct 15;8(39):3143–3145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King M. L., Shaikh A., Bidwell D., Voller A., Banatvala J. E. Coxsackie-B-virus-specific IgM responses in children with insulin-dependent (juvenile-onset; type I) diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1983 Jun 25;1(8339):1397–1399. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92353-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIM K. A., BENYESH-MELNICK M. Typing of viruses by combinations of antiserum pools. Application to typing of enteroviruses (Coxsackie and ECHO). J Immunol. 1960 Mar;84:309–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau R. C. Coxsackie B virus-specific IgM responses in coronary care unit patients. J Med Virol. 1986 Feb;18(2):193–198. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890180211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner A. M., Wilson F. M. Virus myocardiopathy. Prog Med Virol. 1973;15:63–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCartney R. A., Banatvala J. E., Bell E. J. Routine use of mu-antibody-capture ELISA for the serological diagnosis of Coxsackie B virus infections. J Med Virol. 1986 Jul;19(3):205–212. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890190302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertens T., Pika U., Eggers H. J. Cross antigenicity among enteroviruses as revealed by immunoblot technique. Virology. 1983 Sep;129(2):431–442. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90181-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minor T. E., Helstrom P. B., Nelson D. B., D'Alessio D. J. Counterimmunoelectrophoresis test for immunoglobulin M antibodies to group B coxsackievirus. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Apr;9(4):503–506. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.4.503-506.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble G. R., Kaye H. S., Kendal A. P., Dowdle W. R. Age-related heterologous antibody responses to influenza virus vaccination. J Infect Dis. 1977 Dec;136 (Suppl):S686–S692. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement_3.s686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pozzetto B., Le Bihan J. C., Gaudin O. G. Rapid diagnosis of echovirus 33 infection by neutralizing specific IgM antibody. J Med Virol. 1986 Apr;18(4):361–367. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890180409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh S. F. Heterotypic reactions in a radioimmunoassay for coxsackie B virus specific IgM. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Apr;37(4):433–439. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.4.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reigel F., Burkhardt F., Schilt U. Reaction pattern of immunoglobulin M and G antibodies to echovirus 11 structural proteins. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jun;19(6):870–874. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.6.870-874.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt N. J., Lennette E. H., Dennis J. Characterization of antibodies produced in natural and experimental coxsackievirus infections. J Immunol. 1968 Jan;100(1):99–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt N. J., Magoffin R. L., Lennette E. H. Association of group B coxsackie viruses with cases of pericarditis, myocarditis, or pleurodynia by demonstration of immunoglobulin M antibody. Infect Immun. 1973 Sep;8(3):341–348. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.3.341-348.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torfason E. G., Frisk G., Diderholm H. Indirect and reverse radioimmunoassays and their apparent specificities in the detection of antibodies to enteroviruses in human sera. J Med Virol. 1984;13(1):13–31. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890130103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yousef G. E., Bell E. J., Mann G. F., Murugesan V., Smith D. G., McCartney R. A., Mowbray J. F. Chronic enterovirus infection in patients with postviral fatigue syndrome. Lancet. 1988 Jan 23;1(8578):146–150. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92722-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



