Abstract
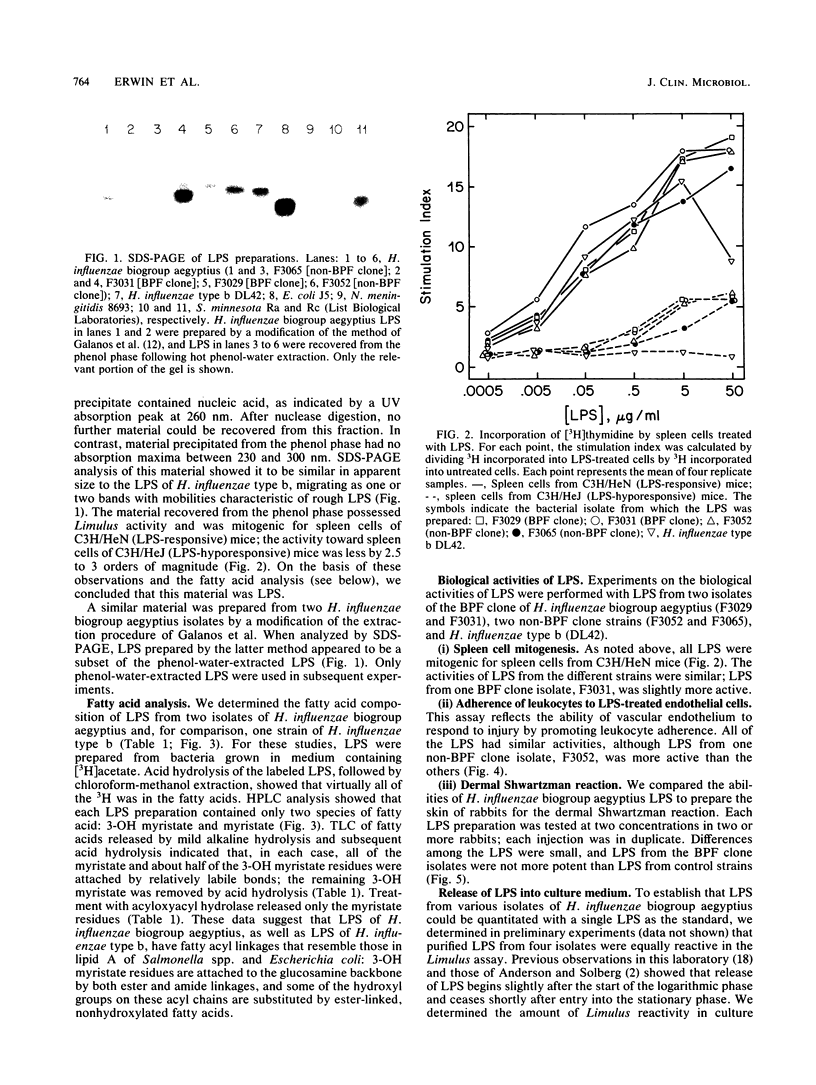
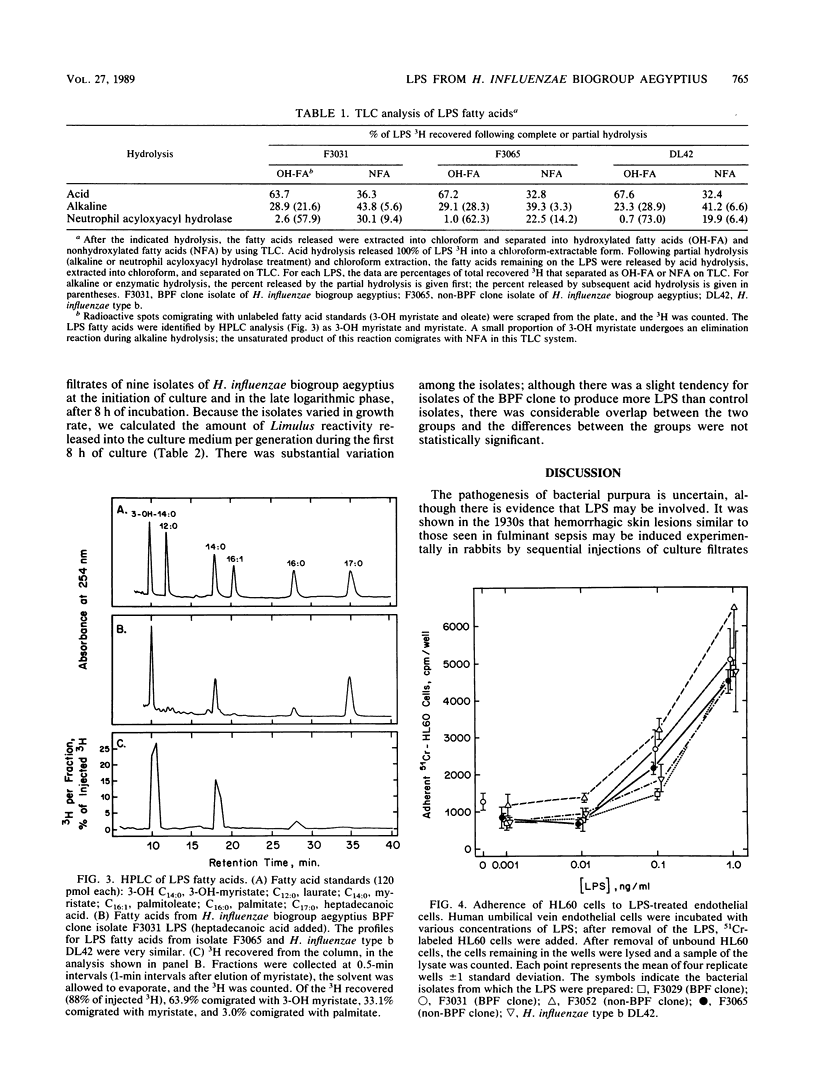
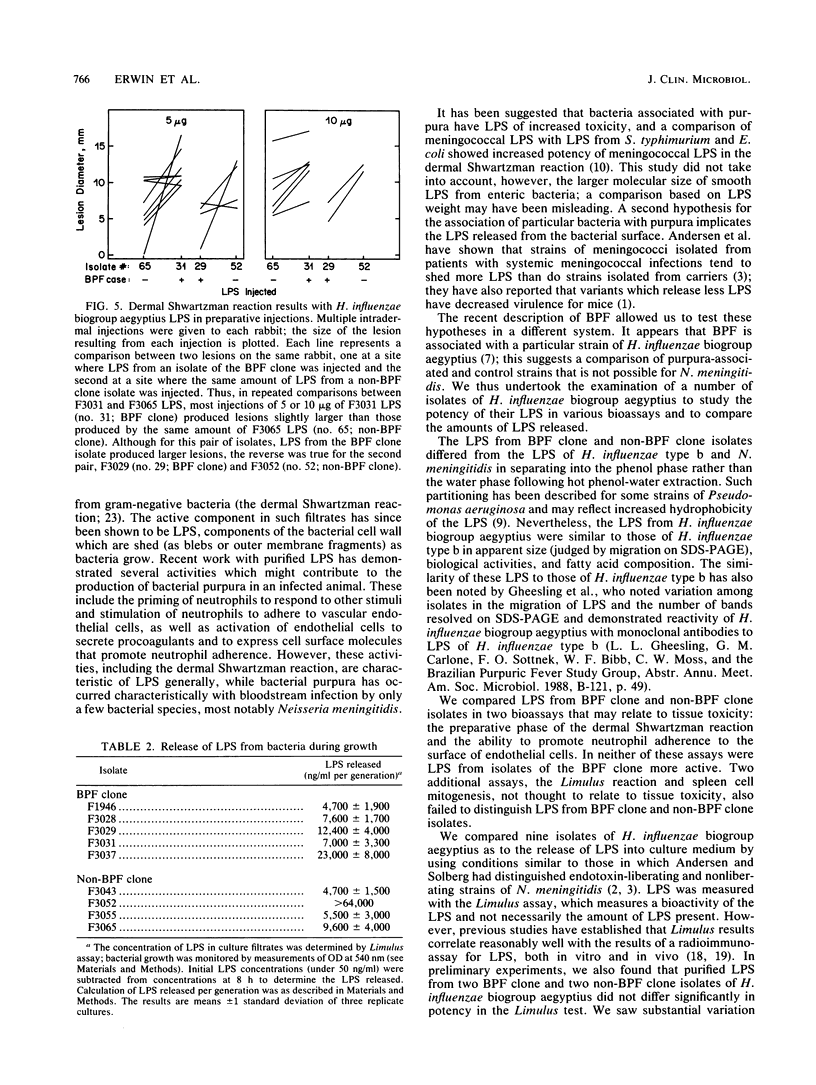
Haemophilus influenzae biogroup aegyptius (H. aegyptius) has been identified as the etiologic agent of the recently described disease Brazilian purpuric fever (BPF). Although there is heterogeneity among the strains associated with conjunctivitis, isolates from patients with BPF appear to be derived from a single clone. The clinical presentation of BPF suggests that bacterial lipopolysaccharides (LPS) are involved in its pathogenesis. We prepared LPS from H. influenzae biogroup aegyptius and found them to be similar to H. influenzae type b LPS in apparent size (by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis), biological activities, and fatty acid composition. We compared LPS from BPF clone isolates with LPS from non-BPF clone isolates in tests of Limulus lysate activation, spleen cell mitogenesis, promotion of neutrophil adherence to LPS-treated endothelial cells, and the dermal Shwartzman reaction. In none of these activities were LPS from the BPF clone isolates more potent. Because LPS shed from growing bacteria may be involved in the pathogenesis of purpura, we also measured the rate at which LPS were released into culture medium during bacterial growth and found no significant difference between BPF clone and non-BPF clone isolates.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen B. M., Solberg O., Bryn K., Frøholm L. O., Gaustad P., Høiby E. A., Kristiansen B. E., Bøvre K. Endotoxin liberation from Neisseria meningitidis isolated from carriers and clinical cases. Scand J Infect Dis. 1987;19(4):409–419. doi: 10.3109/00365548709021673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen B. M., Solberg O. Endotoxin liberation associated with growth, encapsulation and virulence of Neisseria meningitidis. Scand J Infect Dis. 1988;20(1):21–31. doi: 10.3109/00365548809117213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen B. M., Solberg O. The virulence in mice of Neisseria meningitidis variants differing in free endotoxin activities and cell envelope properties. NIPH Ann. 1984 Dec;7(2):47–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Pober J. S., Wheeler M. E., Cotran R. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Interleukin 1 acts on cultured human vascular endothelium to increase the adhesion of polymorphonuclear leukocytes, monocytes, and related leukocyte cell lines. J Clin Invest. 1985 Nov;76(5):2003–2011. doi: 10.1172/JCI112200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlone G. M., Gorelkin L., Gheesling L. L., Erwin A. L., Hoiseth S. K., Mulks M. H., O'Connor S. P., Weyant R. S., Myrick J., Rubin L. Potential virulence-associated factors in Brazilian purpuric fever. Brazilian Purpuric Fever Study Group. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Apr;27(4):609–614. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.4.609-614.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryz S. J., Jr, Pitt T. L., Fürer E., Germanier R. Role of lipopolysaccharide in virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):508–513. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.508-513.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. E., Arnold K. Role of meningococcal endotoxin in meningococcal purpura. J Exp Med. 1974 Jul 1;140(1):159–171. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.1.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durst H. D., Milano M., Kikta E. J., Jr, Connelly S. A., Grushka E. Phenacyl esters of fatty acids via crown ether catalysts for enhanced ultraviolet detection in liquid chromatography. Anal Chem. 1975 Sep;47(11):1797–1801. doi: 10.1021/ac60361a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. L., Munford R. S. Enzymatic deacylation of the lipid A moiety of Salmonella typhimurium lipopolysaccharides by human neutrophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6671–6675. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. G., Perry M. B. Improved techniques for the preparation of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Jan;22(1):29–34. doi: 10.1139/m76-004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura A., Gulig P. A., McCracken G. H., Jr, Loftus T. A., Hansen E. J. A minor high-molecular-weight outer membrane protein of Haemophilus influenzae type b is a protective antigen. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):253–259. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.253-259.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munford R. S., Hall C. L. A comparison of two quantitative assays for bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1987;231:93–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munford R. S., Hall C. L. Detoxification of bacterial lipopolysaccharides (endotoxins) by a human neutrophil enzyme. Science. 1986 Oct 10;234(4773):203–205. doi: 10.1126/science.3529396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munford R. S., Hall C. L., Grimm L. Detection of free endotoxin in cerebrospinal fluid by the Limulus lysate test. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):531–533. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.531-533.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PITTMAN M., DAVIS D. J. Identification of the Koch-Weeks bacillus (Hemophilus aegyptius). J Bacteriol. 1950 Mar;59(3):413–426. doi: 10.1128/jb.59.3.413-426.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohlman T. H., Munford R. S., Harlan J. M. Deacylated lipopolysaccharide inhibits neutrophil adherence to endothelium induced by lipopolysaccharide in vitro. J Exp Med. 1987 May 1;165(5):1393–1402. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.5.1393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



