Abstract
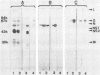
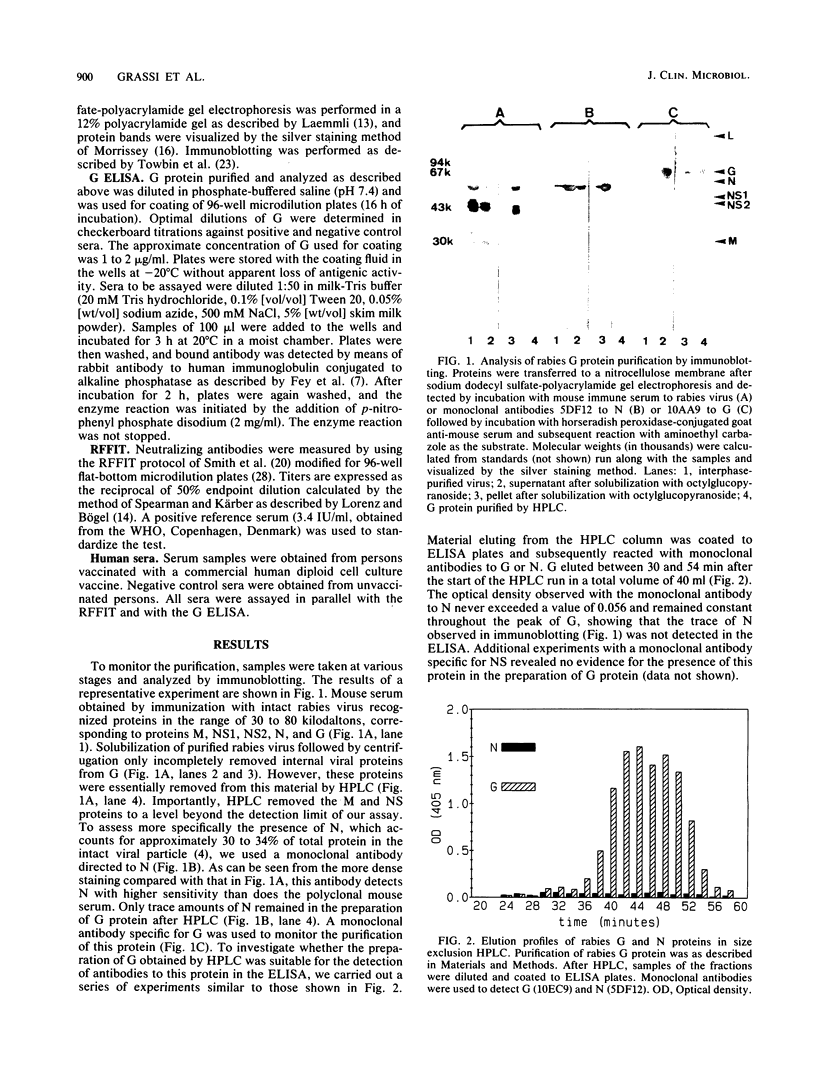
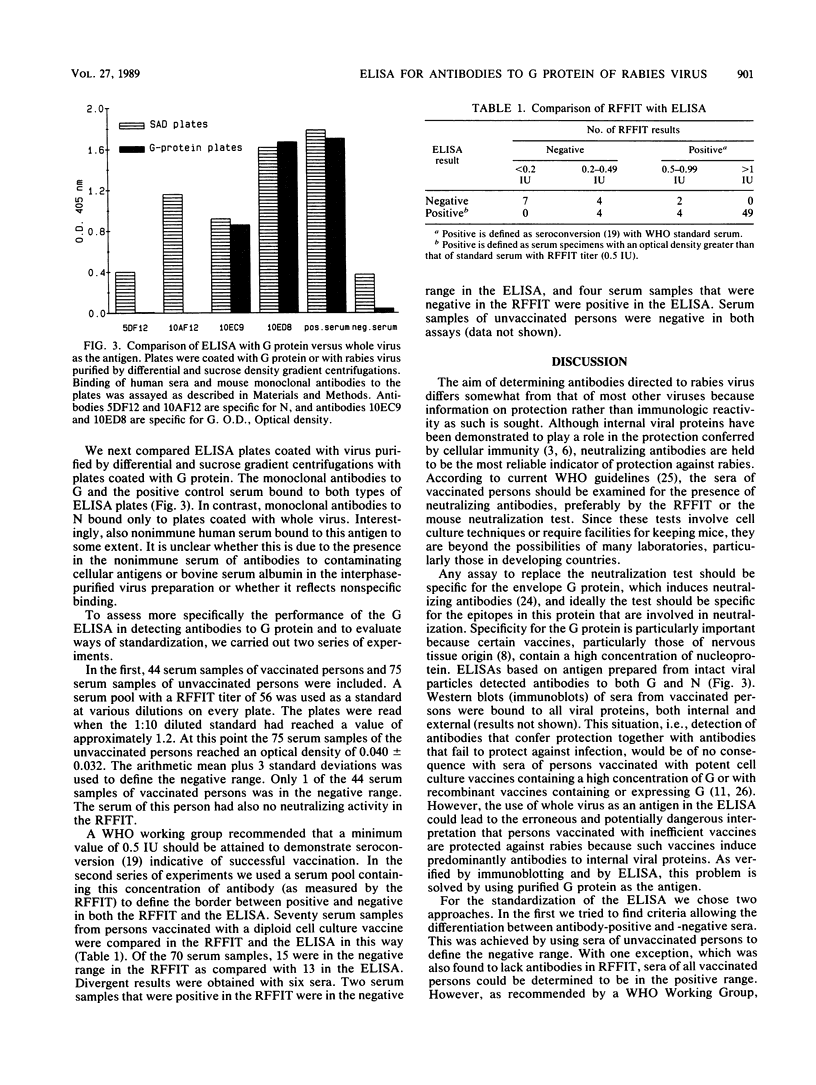
The envelope glycoprotein G of rabies virus induces neutralizing antibodies, which are important in protection against rabies. This protein was solubilized from purified virus and isolated by differential and sucrose density gradient centrifugation followed by high-performance liquid chromatography. Conditions for solubilization and purification of G were optimized by using immunoblotting and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay techniques. The reaction with conventional antisera and monoclonal antibodies indicated that purified G protein was essentially devoid of internal viral proteins. Microdilution plates were coated with purified G protein, and sera from humans vaccinated against rabies were tested for the presence of antibodies. Results were compared with those of the rapid fluorescent focus inhibition assay, which is the standard neutralization assay for antibodies to rabies virus. The results of this comparison indicate that the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for G is a reliable and simple alternative to the neutralization test.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atanasiu P., Savy V., Perrin P. Epreuve immunoenzymatique pour la détection rapide des anticorps antirabiques. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1977 May-Jun;128A(4):489–498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atanasiu P., Tsiang H., Perrin P., Favre S., Sisman J. Extraction d'un antigène soluble (glycoprotéine) par le Triton X100. A partir d'un vaccin antirabique de culture tissulaire de premier explant. Résultats d'immunisation et pouvoir protecteur. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1974 Dec;125(4):540–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celis E., Ou D., Dietzschold B., Koprowski H. Recognition of rabies and rabies-related viruses by T cells derived from human vaccine recipients. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3128–3134. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3128-3134.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J. H., Dietzschold B., Schneider L. G. Rabies virus glycoprotein. II. Biological and serological characterization. Infect Immun. 1977 Jun;16(3):754–759. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.3.754-759.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J. H. The structural proteins of rabies virus. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 1982;5(1-3):21–25. doi: 10.1016/0147-9571(82)90010-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietzschold B., Wang H. H., Rupprecht C. E., Celis E., Tollis M., Ertl H., Heber-Katz E., Koprowski H. Induction of protective immunity against rabies by immunization with rabies virus ribonucleoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9165–9169. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fey H., Pfister H., Rüegg O. Comparative evaluation of different enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay systems for the detection of staphylococcal enterotoxins A, B, C, and D. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jan;19(1):34–38. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.1.34-38.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häfliger U., Bichsel P., Wandeler A., Steck F. Zur oralen Immunisierung von Füchsen gegen Tollwut: Stabilisierung und Köderapplikation des Impfvirus. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1982 Sep;29(8):604–618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieny M. P., Lathe R., Drillien R., Spehner D., Skory S., Schmitt D., Wiktor T., Koprowski H., Lecocq J. P. Expression of rabies virus glycoprotein from a recombinant vaccinia virus. Nature. 1984 Nov 8;312(5990):163–166. doi: 10.1038/312163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurz J., Vogel I., Gerstl F., Dostal V. Comparative studies of two potency tests for antirabies serum: neutralization test in mice (MNT) and rapid fluorescent focus inhibition test (RFFIT). Dev Biol Stand. 1986;64:99–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz R. J., Bögel K. Laboratory techniques in rabies: methods of calculation. Monogr Ser World Health Organ. 1973;(23):321–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louie R. E., Dobkin M. B., Meyer P., Chin B., Roby R. E., Hammar A. H., Cabasso V. J. Measurement of rabies antibody: comparison of the mouse neutralization test (MNT) with the rapid fluorescent focus inhibition test (RFFIT). J Biol Stand. 1975;3(4):365–373. doi: 10.1016/0092-1157(75)90061-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson K. G., Prestage H. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay: a rapid reproducible test for the measurement of rabies antibody. J Med Virol. 1982;9(1):43–49. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890090107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrin P., Sureau P., Thibodeau L. Structural and immunogenic characteristics of rabies immunosomes. Dev Biol Stand. 1985;60:483–491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S., Yager P. A., Baer G. M. A rapid reproducible test for determining rabies neutralizing antibody. Bull World Health Organ. 1973 May;48(5):535–541. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sureau P., Rollin P. E., Zeller H. Corrélations entre l'epreuve immunoenzymatique, la séroneutralisation et la réduction de foyers fluorescents pour le titrage des anticorps rabiques. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 1982;5(1-3):143–150. doi: 10.1016/0147-9571(82)90028-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thraenhart O., Kuwert E. K. Enzyme immunoassay for demonstration of rabies-virus antibodies after immunisation. Lancet. 1977 Aug 20;2(8034):399–400. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90321-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiktor T. J., György E., Schlumberger D., Sokol F., Koprowski H. Antigenic properties of rabies virus components. J Immunol. 1973 Jan;110(1):269–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wunner W. H., Dietzschold B., Curtis P. J., Wiktor T. J. Rabies subunit vaccines. J Gen Virol. 1983 Aug;64(Pt 8):1649–1656. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-8-1649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalan E., Wilson C., Pukitis D. A microtest for the quantitation of rabies virus neutralizing antibodies. J Biol Stand. 1979 Jul;7(3):213–220. doi: 10.1016/s0092-1157(79)80024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]