Abstract
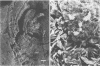
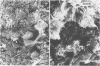
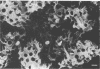
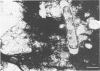
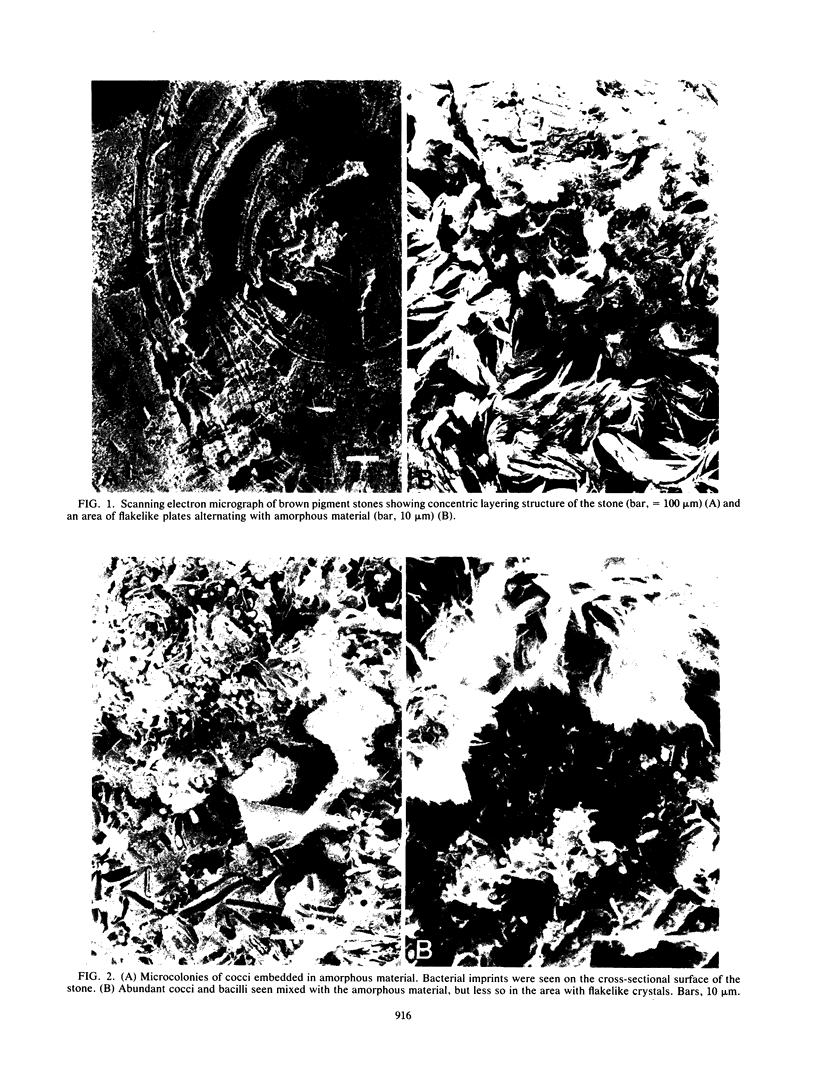
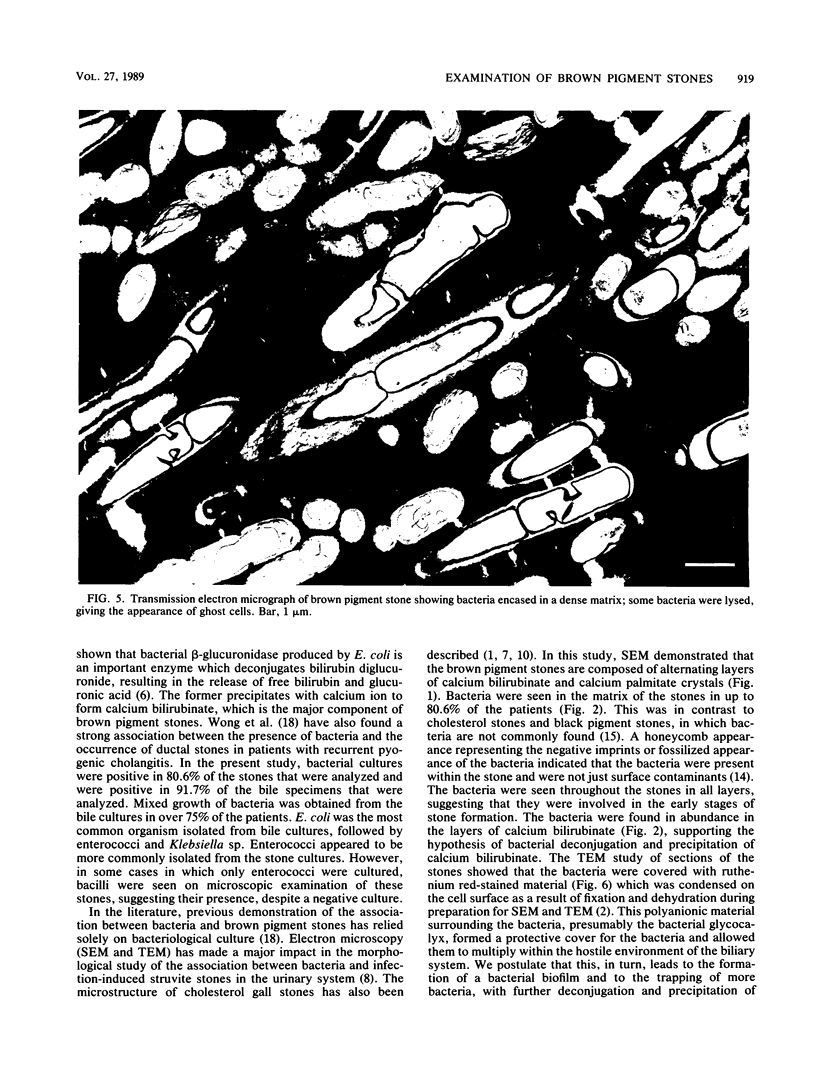
Bacteriological and morphological studies of 38 brown pigment common duct stones were performed. Stone cultures were positive for bacteria in 80.5% of those studied. Enterococci were the most common organisms that were isolated. Scanning electron microscopy showed the presence of bacteria in 84.2% of the stones. The bacteria were seen embedded within an amorphous matrix in alternating layers of flakelike crystals. Transmission electron microscopy showed the presence of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria surrounded by a ruthenium red-stained exopolysaccharide material. Results of the bacteriological and morphological studies confirmed the close relationship between the presence of bacteria and the development of brown pigment stones.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Been J. M., Bills P. M., Lewis D. Microstructure of gallstones. Gastroenterology. 1979 Mar;76(3):548–555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Irvin R. T., Cheng K. J. The bacterial glycocalyx in nature and disease. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:299–324. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.001503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung J. W., Ling T. K., Kung J. L., Vallance-Owen J. The role of bacteria in the blockage of biliary stents. Gastrointest Endosc. 1988 Jan-Feb;34(1):19–22. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(88)71223-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li A. K., Chung S. C., Leung J. W., Mok S. D. Recurrent pyogenic cholangitis: an update. Trop Gastroenterol. 1985 Jul-Sep;6(3):119–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maki T. Pathogenesis of calcium bilirubinate gallstone: role of E. coli, beta-glucuronidase and coagulation by inorganic ions, polyelectrolytes and agitation. Ann Surg. 1966 Jul;164(1):90–100. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196607000-00010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malet P. F., Takabayashi A., Trotman B. W., Soloway R. D., Weston N. E. Black and brown pigment gallstones differ in microstructure and microcomposition. Hepatology. 1984 Mar-Apr;4(2):227–234. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840040210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean R. J., Nickel J. C., Noakes V. C., Costerton J. W. An in vitro ultrastructural study of infectious kidney stone genesis. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):805–811. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.805-811.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagase M., Tanimura H., Setoyama M., Hikasa Y. Present features of gallstones in Japan. A collective review of 2,144 cases. Am J Surg. 1978 Jun;135(6):788–790. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(78)90165-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osuga T., Mitamura K., Miyagawa S., Sato N., Kintaka S., Portman O. W. A scanning electron microscopic study of gallstone development in man. Lab Invest. 1974 Dec;31(6):696–704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speer A. G., Cotton P. B., Rode J., Seddon A. M., Neal C. R., Holton J., Costerton J. W. Biliary stent blockage with bacterial biofilm. A light and electron microscopy study. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Apr;108(4):546–553. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-108-4-546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart L., Smith A. L., Pellegrini C. A., Motson R. W., Way L. W. Pigment gallstones form as a composite of bacterial microcolonies and pigment solids. Ann Surg. 1987 Sep;206(3):242–250. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198709000-00002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabata M., Nakayama F. Bacteria and gallstones. Etiological significance. Dig Dis Sci. 1981 Mar;26(3):218–224. doi: 10.1007/BF01391633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trotman B. W., Ostrow J. D., Soloway R. D. Pigment vs cholesterol cholelithiasis: comparison of stone and bile composition. Am J Dig Dis. 1974 Jul;19(7):585–590. doi: 10.1007/BF01073011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trotman B. W., Soloway R. D. Pigment gallstone disease: Summary of the National Institutes of Health--international workshop. Hepatology. 1982 Nov-Dec;2(6):879–884. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840020624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong W. T., Teoh-Chan C. H., Huang C. T., Cheng F. C., Ong G. B. The bacteriology of recurrent pyogenic cholangitis and associated diseases. J Hyg (Lond) 1981 Dec;87(3):407–412. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400069643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wosiewitz U. Scanning electron microscopy in gallstone research. Scan Electron Microsc. 1983;(Pt 1):419–430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]