Abstract
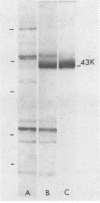
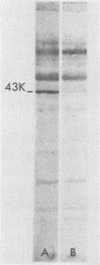
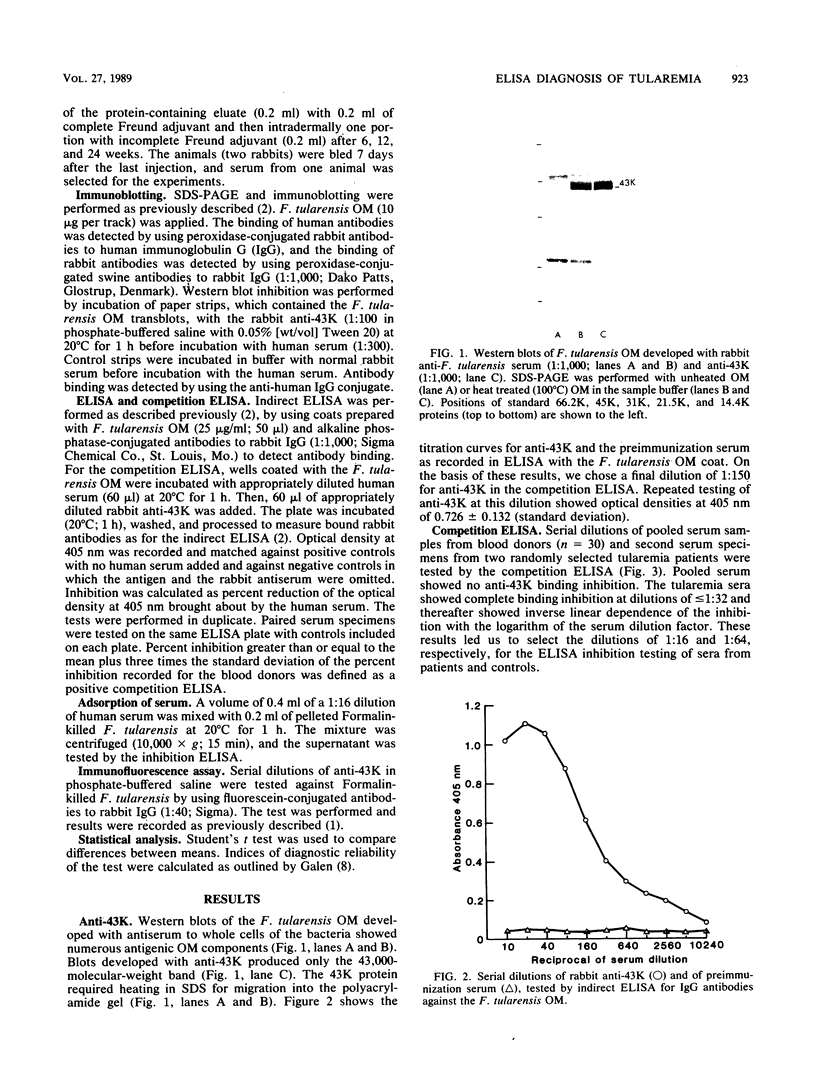
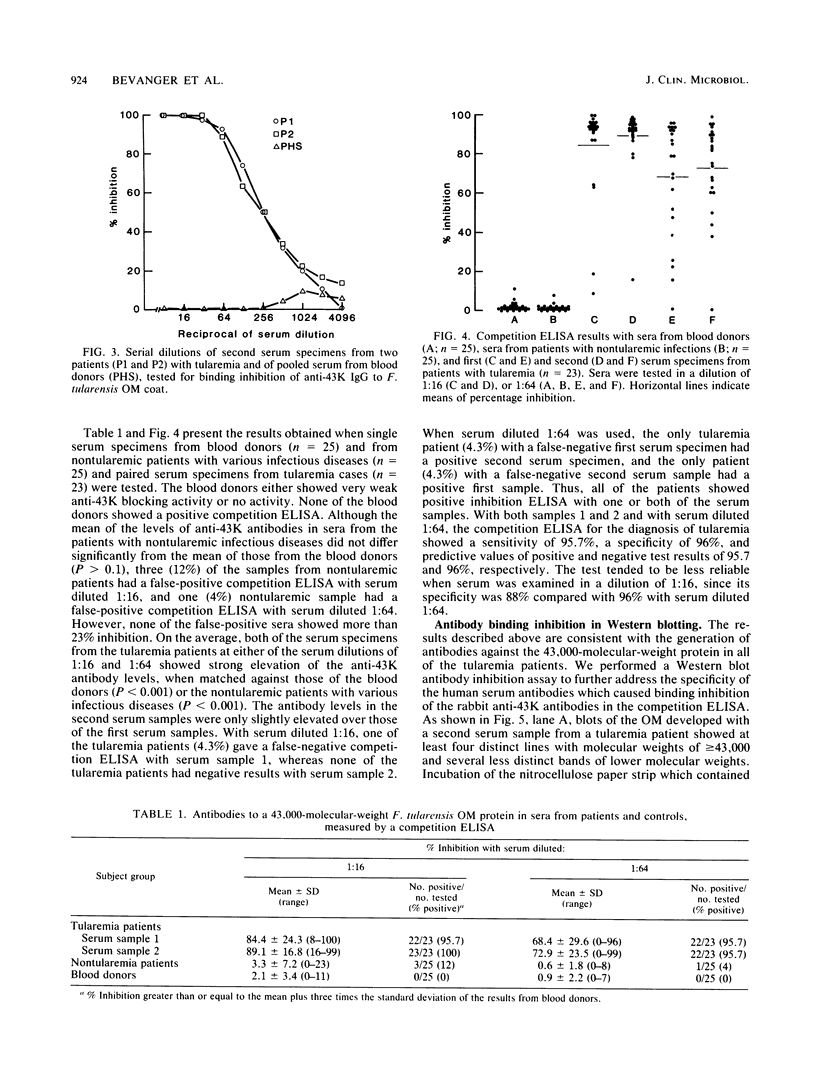
Antibodies against a 43,000-molecular-weight Francisella tularensis outer membrane (OM) protein (43K protein) were measured in paired serum specimens from 23 patients with tularemia and matched against antibodies in sera from 25 patients with nontularemic infectious diseases and from 25 blood donors. Antibodies were measured by a competition enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay which tested the ability of human serum to compete with rabbit anti-43K protein antibodies for its binding to the F. tularensis OM coat. The sera from nontularemic patients and from blood donors, in dilutions of 1:16 and 1:64, respectively, showed no or very low levels of antibodies. All of the tularemia patients showed positive tests with the first, the second, or both of the serum specimens examined. For instance, with serum diluted 1:64, each of the serum specimens showed a sensitivity of 95.7% and a specificity of 96%. When used for antibody competition in Western blotting (immunoblotting), the rabbit anti-43K selectivity blocked the binding of human serum antibodies to the 43,000-molecular-weight protein. This protein was immunoaccessible in Formalin-killed F. tularensis. These data indicate an important role of the 43,000-molecular-weight OM protein in the immunobiology of tularemia and emphasize its potential usefulness as an antigen in serodiagnostic tests.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bevanger L., Maeland J. A., Naess A. I. Agglutinins and antibodies to Francisella tularensis outer membrane antigens in the early diagnosis of disease during an outbreak of tularemia. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Mar;26(3):433–437. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.3.433-437.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevanger L., Maeland J. A. Type classification of group B streptococci by the fluorescent antibody test. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1977 Dec;85B(6):357–362. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1977.tb01990.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black J. R., Black W. J., Cannon J. G. Neisserial antigen H.8 is immunogenic in patients with disseminated gonococcal and meningococcal infections. J Infect Dis. 1985 Apr;151(4):650–657. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.4.650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. L., McKinney F. T., Klein G. C., Jones W. L. Evaluation of a safranin-O-stained antigen microagglutination test for francisella tularensis antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Feb;11(2):146–148. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.2.146-148.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson H. E., Lindberg A. A., Lindberg G., Hederstedt B., Karlsson K. A., Agell B. O. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for immunological diagnosis of human tularemia. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Nov;10(5):615–621. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.5.615-621.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eigelsbach H. T., Hunter D. H., Janssen W. A., Dangerfield H. G., Rabinowitz S. G. Murine model for study of cell-mediated immunity: protection against death from fully virulent Francisella tularensis infection. Infect Immun. 1975 Nov;12(5):999–1005. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.5.999-1005.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabay J. E., Blake M., Niles W. D., Horwitz M. A. Purification of Legionella pneumophila major outer membrane protein and demonstration that it is a porin. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):85–91. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.85-91.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilleland H. E., Jr, Gilleland L. B., Matthews-Greer J. M. Outer membrane protein F preparation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa as a vaccine against chronic pulmonary infection with heterologous immunotype strains in a rat model. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1017–1022. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1017-1022.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilleland H. E., Jr, Parker M. G., Matthews J. M., Berg R. D. Use of a purified outer membrane protein F (porin) preparation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa as a protective vaccine in mice. Infect Immun. 1984 Apr;44(1):49–54. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.1.49-54.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewitt J., Coates A. R., Mitchison D. A., Ivanyi J. The use of murine monoclonal antibodies without purification of antigen in the serodiagnosis of tuberculosis. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Dec 17;55(2):205–211. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90032-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner K. A., Warren K. A., Tam M., Frank M. M. Monoclonal antibodies directed against gonococcal protein I vary in bactericidal activity. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3411–3419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koskela P., Salminen A. Humoral immunity against Francisella tularensis after natural infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Dec;22(6):973–979. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.6.973-979.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocca L. F., Frasch C. E. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel typing system for characterization of Neisseria meningitidis isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Aug;16(2):240–244. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.2.240-244.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Bartos L. C. Purification and analysis with monoclonal antibodies of P2, the major outer membrane protein of nontypable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1084–1089. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1084-1089.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbusch J. P. Characterization of the major envelope protein from Escherichia coli. Regular arrangement on the peptidoglycan and unusual dodecyl sulfate binding. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 25;249(24):8019–8029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandström G., Tärnvik A., Wolf-Watz H. Immunospecific T-lymphocyte stimulation by membrane proteins from Francisella tularensis. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Apr;25(4):641–644. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.4.641-644.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarafian S. K., Tam M. R., Morse S. A. Gonococcal protein I-specific opsonic IgG in normal human serum. J Infect Dis. 1983 Dec;148(6):1025–1032. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.6.1025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saukkonen K., Abdillahi H., Poolman J. T., Leinonen M. Protective efficacy of monoclonal antibodies to class 1 and class 3 outer membrane proteins of Neisseria meningitidis B:15:P1.16 in infant rat infection model: new prospects for vaccine development. Microb Pathog. 1987 Oct;3(4):261–267. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syrjälä H., Koskela P., Ripatti T., Salminen A., Herva E. Agglutination and ELISA methods in the diagnosis of tularemia in different clinical forms and severities of the disease. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jan;153(1):142–145. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.1.142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twining S. S., Lehmann H., Atassi M. Z. The antibody response to myoglobin is independent of the immunized species. Analysis in terms of replacements in the antigenic sites and in environmental residues of the cross-reactions of fifteen myoglobins with sperm-whale myoglobin antisera raised in different species. Biochem J. 1980 Dec 1;191(3):681–697. doi: 10.1042/bj1910681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tärnvik A., Sandström G., Löfgren S. Time of lymphocyte response after onset of tularemia and after tularemia vaccination. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Dec;10(6):854–860. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.6.854-860.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viljanen M. K., Nurmi T., Salminen A. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) with bacterial sonicate antigen for IgM, IgA, and IgG antibodies to Francisella tularensis: comparison with bacterial agglutination test and ELISA with lipopolysaccharide antigen. J Infect Dis. 1983 Oct;148(4):715–720. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.4.715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]