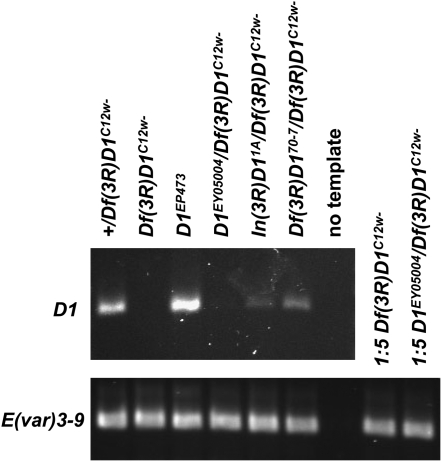
Figure 3.—
RT–PCR analysis of D1 mutant alleles. cDNA samples prepared from equivalent amounts of ovary RNA, for the indicated strains, were used as templates for PCR of the D1 mRNA (primers D1 1261F and D1 1803R) and control E(var)3-9 mRNA (primers E(var)3-9 2261F and E(var)3-9 2260R). Both primer sets spanned an intron, enabling products from potential contaminating genomic DNA to be distinguished. However, no genomic DNA products were observed. Where no (Df(3R)D1C12w−) or very little (D1EY05004/Df(3R)D1C12w−) D1 RT–PCR product was observed, the control E(var)3-9 PCR reaction was performed using fivefold diluted cDNA template, as a means to confirm the integrity of the cDNA template. E(var)3-9 mRNA has been quantified at ∼69% of the level of D1 mRNA in the ovary, using microarray analysis (Chintapalli et al. 2007).