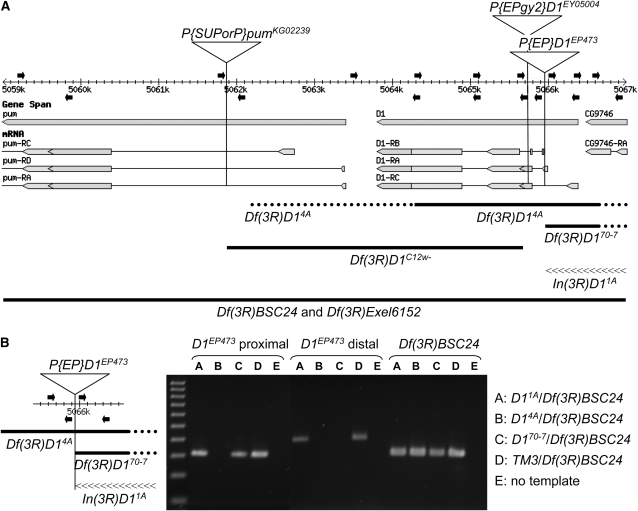
Figure 5.—
A map of D1-mutant alleles. (A) The D1 gene and portions of the flanking pumilio and CG9746 genes and their transcripts are illustrated as they map to the 3R genomic sequence (adapted from FlyBase Release 5.1, http://www.flybase.org). Proximal is to the left and distal is to the right. The insertion sites of the three P elements utilized in this study are indicated by vertical lines on the map. Both the pumKG02239 and the D1EY05004 P insertions are oriented with the 5′-P end proximal and the 3′-P end distal. The D1EP473 insertion is oriented with the 3′-P end proximal and the 5′-P end distal. Primers used for PCR analyses of D1 mutants isolated in this study are shown above (forward primers) and below (reverse primers) the map as solid arrows. The precise locations are listed in Table 2. The extents of the deletions are shown below as thick solid lines, with the dotted portions reflecting the uncertainty of the endpoints. The Df(3R)BSC24 (3R:4,757,601-5,220,293) and Df(3R)Exel6152 (3R:4,983,798-5,073,203) deletions extend well beyond this ∼8-kb region. The inverted region of In(3R)D11A (distal breakpoint at position 5,067,087) is illustrated by a linear array of “<” symbols. (B) The PCR data for two primer sets, which amplify genomic segments immediately proximal and distal to the D1EP473 insertion as illustrated at left, is shown for the three D1EP473 excision alleles associated with chromosome rearrangements that were isolated in this study. Genomic DNA was isolated from single first instar larvae of genotypes In(3R)D11A/Df(3R)BSC24, Df(3R)14A/Df(3R)BSC24, and Df(3R)D170-7/Df(3R)BSC24, as hemizygous adults were inviable. A sibling TM3/Df(3R)BSC24 larva served as a positive control for the PCR reaction. A third PCR primer set that hybridized to the P element marking the Df(3R)BSC24 deficiency and the flanking genomic DNA, thus specific for the Df(3R)BSC24 chromosome, was used to confirm the integrity of the DNA preparation, as well as the genotypes. A 100-bp ladder (100–1000 bp) is shown in the first lane.