Abstract
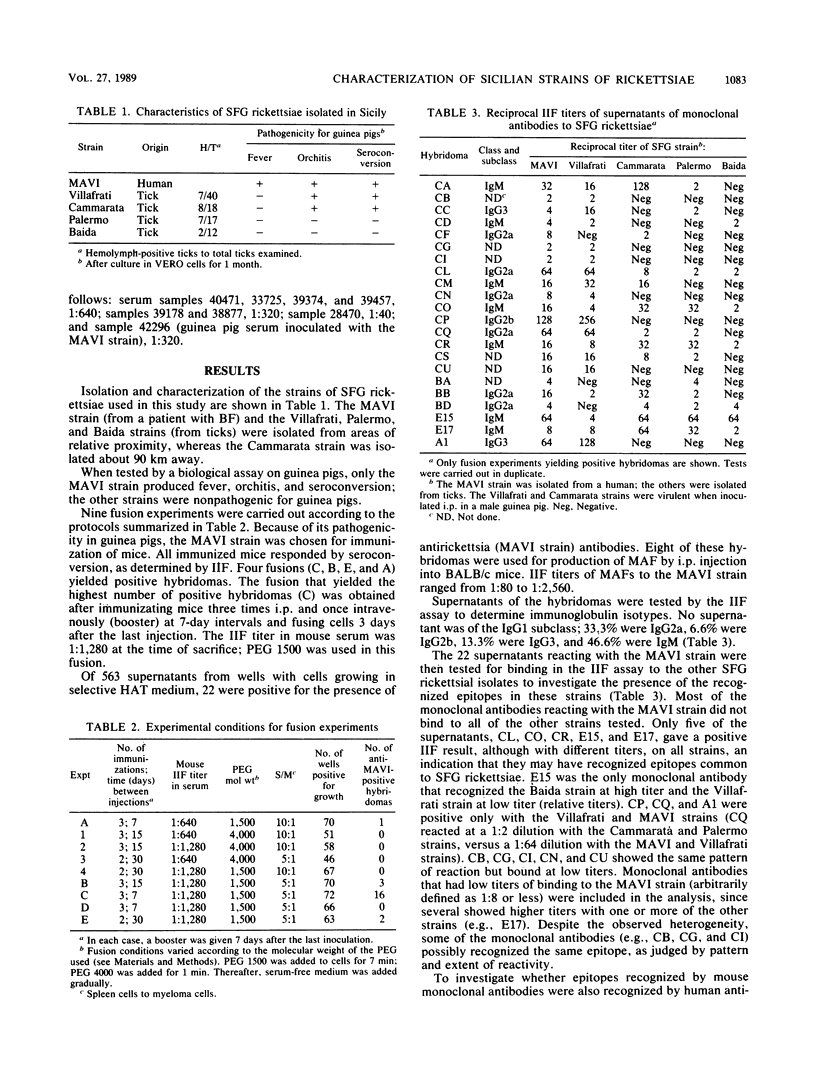
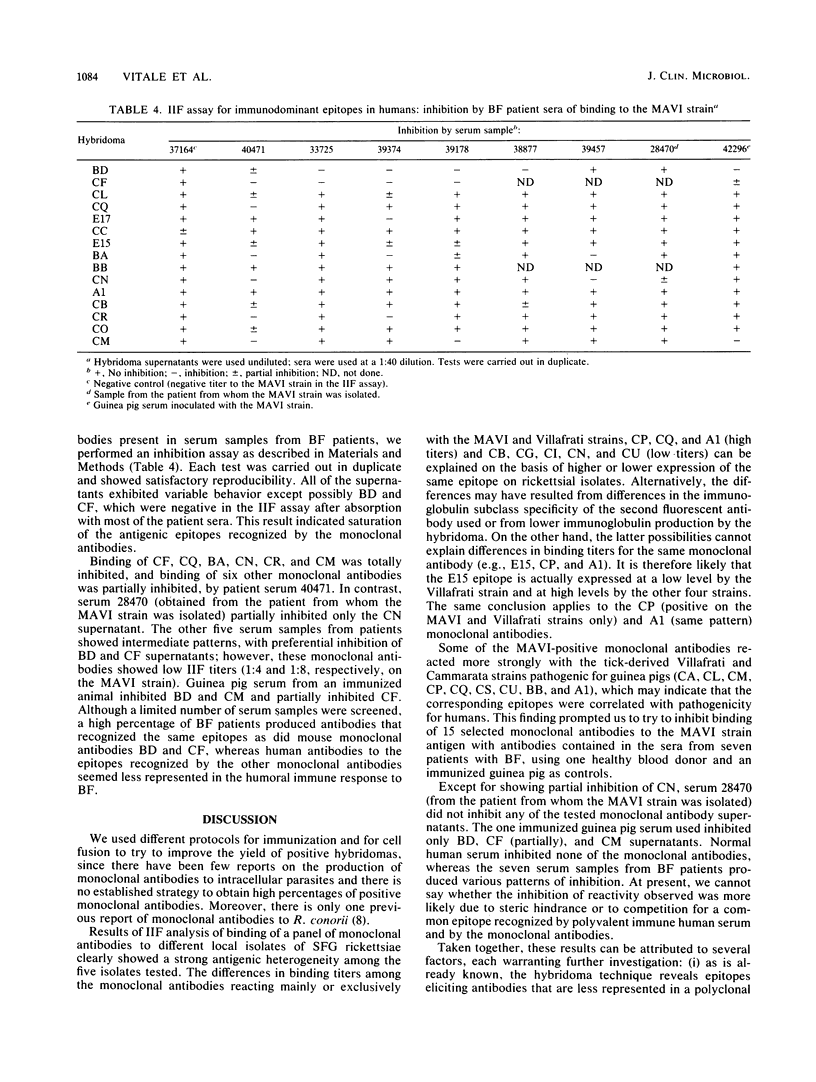
Twenty-two hybridomas producing anti-Rickettsia conorii monoclonal antibodies were obtained by nine fusion experiments. The strain chosen for immunization of mice was MAVI, an R. conorii strain isolated from a Sicilian patient with Boutonneuse fever. When tested for immunoglobulin isotype by an indirect immunofluorescence (IIF) assay, 46.6% of supernatants from the 22 hybridomas were immunoglobulin M. The supernatants were tested in the IIF assay for binding to the MAVI strain and four spotted fever group rickettsia strains isolated from Sicilian ticks (two virulent and two nonpathogenic when inoculated intraperitoneally in male guinea pigs). Only five of the supernatants showed a positive IIF result on all tested strains, although they produced different titers to the various strains, possibly an indication that they recognized an antigen common to spotted fever group rickettsiae. Immunodominant epitopes for humans were determined by using patient sera to analyze inhibition of binding to the MAVI strain. Although a limited number of serum samples were screened, a high percentage of Boutonneuse fever patients produced antibodies recognizing the same epitopes as were recognized by the mouse monoclonal antibodies. A striking heterogeneity was found both in the expression of mouse-recognized epitopes on the five rickettsial strains and in the serum antibody responses of Boutonneuse fever patients to these epitopes.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aeschlimann A., Burgdorfer W., Matile H., Peter O., Wyler R. Aspects nouveaux du rôle de vecteur joué par Ixodes ricinus L. en Suisse. Note préliminaire. Acta Trop. 1979 Jun;36(2):181–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BELL E. J., KOHLS G. M., STOENNER H. G., LACKMAN D. B. NONPATHOGENIC RICKETTSIAS RELATED TO THE SPOTTED FEVER GROUP ISOLATED FROM TICKS, DERMACENTOR VARIABILIS AND DERMACENTOR ANDERSONI FROM EASTERN MONTANA. J Immunol. 1963 May;90:770–781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W. Hemolymph test. A technique for detection of rickettsiae in ticks. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1970 Nov;19(6):1010–1014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cacciapuoti B., Rivosecchi L., Stella E., Ciceroni L., Khoury C. Osservazioni preliminari sulla prevalenza di Rickettsie del gruppo delle spotted fevers in Rhipicephalus sanguineus catturati in aree sub-urbane. Boll Ist Sieroter Milan. 1985;64(1):77–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damiani G., Biano A., Beltrame A., Vismara D., Mezzopreti M. F., Colizzi V., Young D. B., Bloom B. R. Generation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to 28-, 35-, and 65-kilodalton proteins of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1281–1287. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1281-1287.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng H. M., Walker D. H., Wang J. G. Analysis of T-cell-dependent and -independent antigens of Rickettsia conorii with monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):7–15. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.7-15.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange J. V., Walker D. H. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to Rickettsia rickettsii. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):289–294. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.289-294.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansueto S., Tringali G., Walker D. H. Widespread, simultaneous increase in the incidence of spotted fever group rickettsioses. J Infect Dis. 1986 Sep;154(3):539–540. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.3.539-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansueto S., Vitale G., Tringali G., Pintagro C., Occhino C., Miceli M. D. Studi sieroimmunologici nella Febbre Bottonosa. I. Valutazione di un kit del commercio per micro-immunofluorescenza nella diagnostica sierologica della Febbre Bottonosa. Quad Sclavo Diagn. 1983 Jun;19(2):262–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehácek J., Pospísil V., Ciampor F. First record of bacillary rickettsia-like organisms in European tick Dermacentor marginatus (Sulzer). Folia Parasitol (Praha) 1976;23(4):301–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sexton D. J., Burgdorfer W., Thomas L., Norment B. R. Rocky Mountain spotted fever in Mississippi: survey for spotted fever antibodies in dogs and for spotted fever group reckettsiae in dog ticks. Am J Epidemiol. 1976 Feb;103(2):192–197. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tringali G., Intonazzo V., Perna A. M., Mansueto S., Vitale G., Walker D. H. Epidemiology of boutonneuse fever in western Sicily. Distribution and prevalence of spotted fever group rickettsial infection in dog ticks (Rhipicephalus sanguineus). Am J Epidemiol. 1986 Apr;123(4):721–727. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de StGroth S. F., Scheidegger D. Production of monoclonal antibodies: strategy and tactics. J Immunol Methods. 1980;35(1-2):1–21. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90146-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



