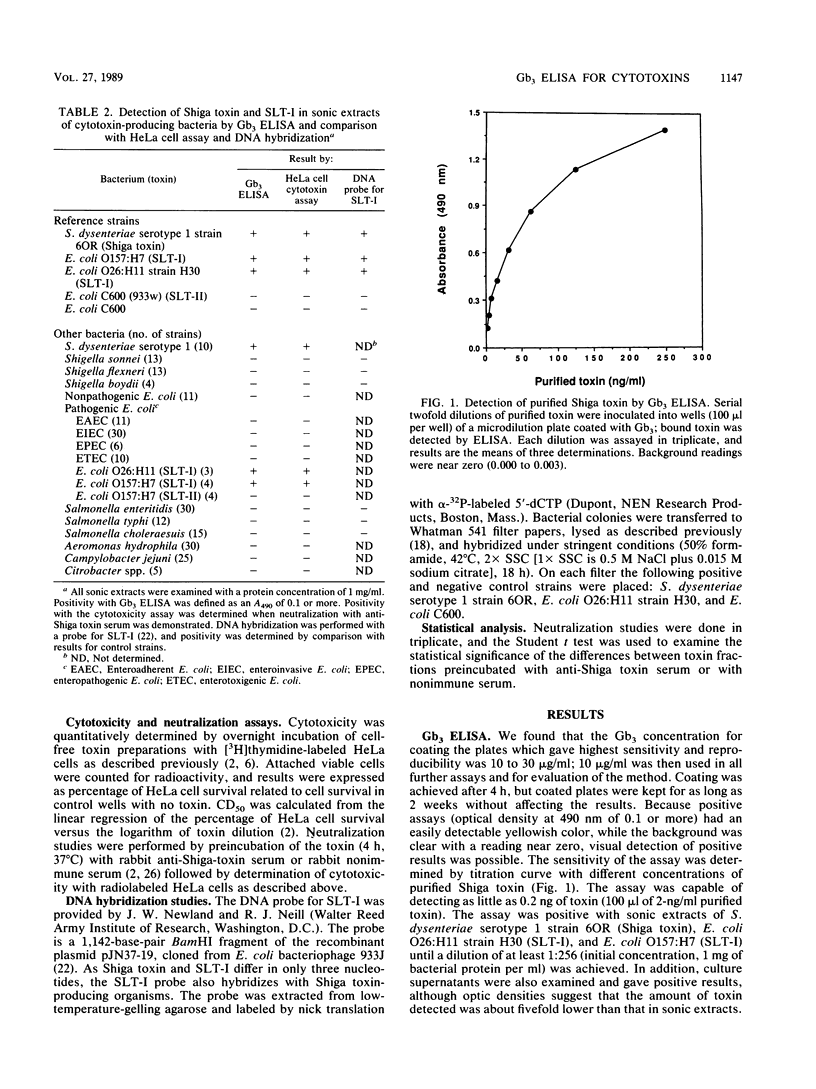
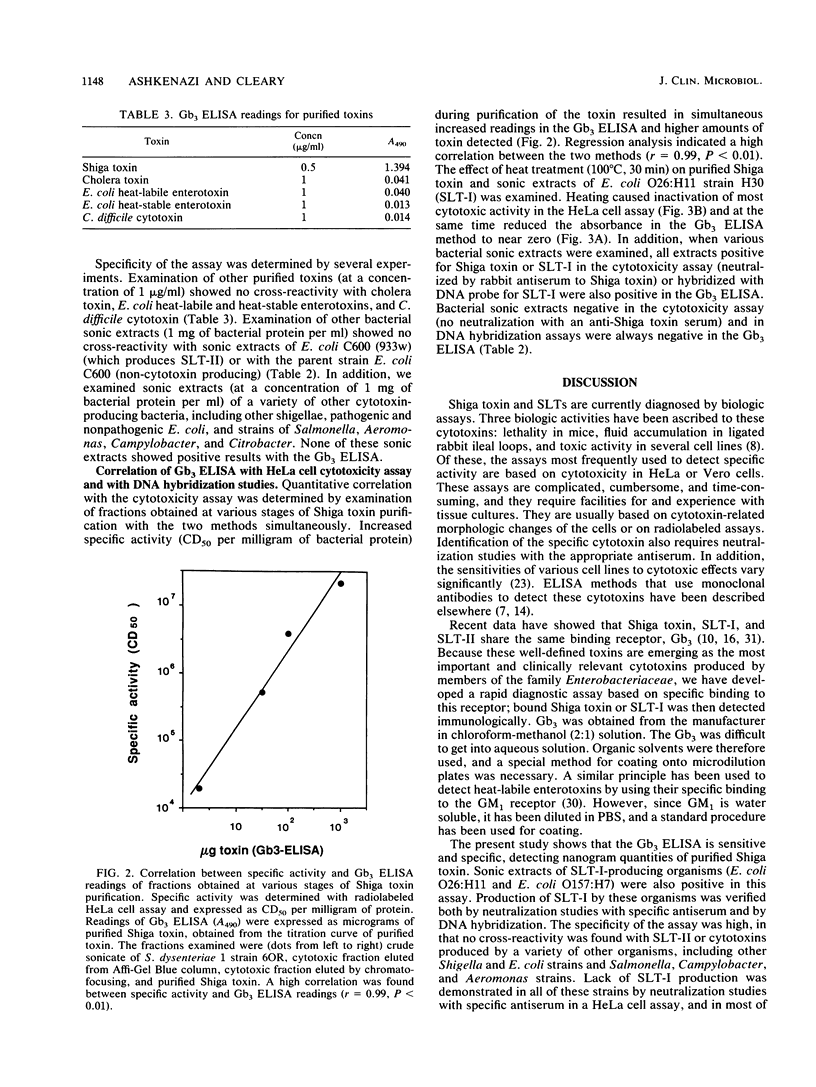
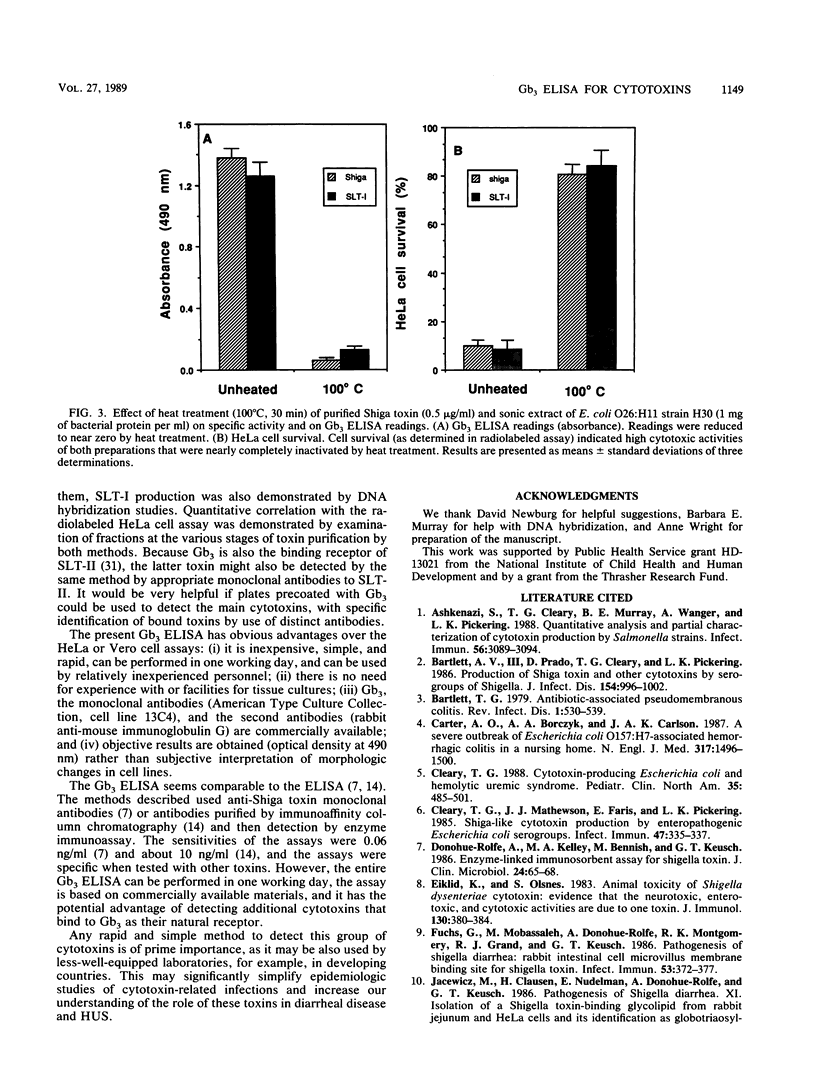
Abstract
Shiga toxin and the closely related Shiga-like toxins produced by Escherichia coli represent a group of very similar cytotoxins that may play an important role in diarrheal disease and hemolytic uremic syndrome. These toxins have the same biologic activities and according to recent studies also share the same binding receptor, globotriosyl ceramide (Gb3). They are currently detected, on the basis of their ability to damage several cell lines, by using expensive and tedious assays that require facilities for and experience with tissue cultures and are therefore most suitable for research laboratories. We have developed a rapid method to detect Shiga toxin and Shiga-like toxin I based on specific binding to their Gb3 natural receptor, which was coated onto microdilution plates. Bound toxin was then detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) with monoclonal antibodies. The sensitivity of the Gb3 ELISA was 0.2 ng (2 ng/ml) of purified toxin. The assay was positive with sonic extracts of Shigella dysenteriae serotype 1 strain 6OR (a Shiga toxin producer), E. coli serotype O26:H11 strain H30, and E. coli serotype O157:H7 (both Shiga-like toxin I producers). The assay was very specific in that no cross-reactivity was noted with purified cholera toxin, E. coli heat-labile and heat-stable enterotoxins, and Clostridium difficile cytotoxin, or sonic extracts of other cytotoxin-producing organisms, such as other shigellae, pathogenic and nonpathogenic E. coli, Salmonella spp., Campylobacter spp., and Aeromonas spp. These results were in complete agreement with a [3H]thymidine-labeled HeLa cell cytotoxicity assay and with detection of the structural genes by DNA hybridization studies with a Shiga-like toxin I probe. Quantitative analysis showed a high correlation between Gb3 ELISA and HeLa cell assay when fractions obtained at various stages of toxin purification were examined by both methods (r = 0.99, P < 0.01). This rapid Gb3 ELISA is sensitive and specific and may be diagnostically useful in cytotoxin-related infections.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashkenazi S., Cleary T. G., Murray B. E., Wanger A., Pickering L. K. Quantitative analysis and partial characterization of cytotoxin production by Salmonella strains. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3089–3094. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3089-3094.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett A. V., 3rd, Prado D., Cleary T. G., Pickering L. K. Production of Shiga toxin and other cytotoxins by serogroups of Shigella. J Infect Dis. 1986 Dec;154(6):996–1002. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.6.996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett J. G. Antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis. Rev Infect Dis. 1979 May-Jun;1(3):530–539. doi: 10.1093/clinids/1.3.530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter A. O., Borczyk A. A., Carlson J. A., Harvey B., Hockin J. C., Karmali M. A., Krishnan C., Korn D. A., Lior H. A severe outbreak of Escherichia coli O157:H7--associated hemorrhagic colitis in a nursing home. N Engl J Med. 1987 Dec 10;317(24):1496–1500. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198712103172403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleary T. G. Cytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli and the hemolytic uremic syndrome. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1988 Jun;35(3):485–501. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)36467-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleary T. G., Mathewson J. J., Faris E., Pickering L. K. Shiga-like cytotoxin production by enteropathogenic Escherichia coli serogroups. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):335–337. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.335-337.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donohue-Rolfe A., Kelley M. A., Bennish M., Keusch G. T. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for shigella toxin. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jul;24(1):65–68. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.1.65-68.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiklid K., Olsnes S. Animal toxicity of Shigella dysenteriae cytotoxin: evidence that the neurotoxic, enterotoxic, and cytotoxic activities are due to one toxin. J Immunol. 1983 Jan;130(1):380–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs G., Mobassaleh M., Donohue-Rolfe A., Montgomery R. K., Grand R. J., Keusch G. T. Pathogenesis of Shigella diarrhea: rabbit intestinal cell microvillus membrane binding site for Shigella toxin. Infect Immun. 1986 Aug;53(2):372–377. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.2.372-377.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. P., Newland J. W., Holmes R. K., O'Brien A. D. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the structural genes for Shiga-like toxin I encoded by bacteriophage 933J from Escherichia coli. Microb Pathog. 1987 Feb;2(2):147–153. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90106-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., Petric M., Lim C., Fleming P. C., Arbus G. S., Lior H. The association between idiopathic hemolytic uremic syndrome and infection by verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1985 May;151(5):775–782. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.5.775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindschuh M., Pickering L. K., Cleary T. G., Ruiz-Palacios G. Clinical and biochemical significance of toxin production by Aeromonas hydrophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 May;25(5):916–921. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.5.916-921.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kongmuang U., Honda T., Miwatani T. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to detect Shiga toxin of Shigella dysenteriae and related toxins. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jan;25(1):115–118. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.1.115-118.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konowalchuk J., Speirs J. I., Stavric S. Vero response to a cytotoxin of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):775–779. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.775-779.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg A. A., Brown J. E., Strömberg N., Westling-Ryd M., Schultz J. E., Karlsson K. A. Identification of the carbohydrate receptor for Shiga toxin produced by Shigella dysenteriae type 1. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1779–1785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingwood C. A., Law H., Richardson S., Petric M., Brunton J. L., De Grandis S., Karmali M. Glycolipid binding of purified and recombinant Escherichia coli produced verotoxin in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8834–8839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maas R. An improved colony hybridization method with significantly increased sensitivity for detection of single genes. Plasmid. 1983 Nov;10(3):296–298. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(83)90045-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marques L. R., Moore M. A., Wells J. G., Wachsmuth I. K., O'Brien A. D. Production of Shiga-like toxin by Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1986 Aug;154(2):338–341. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.2.338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neill M. A., Tarr P. I., Clausen C. R., Christie D. L., Hickman R. O. Escherichia coli O157:H7 as the predominant pathogen associated with the hemolytic uremic syndrome: a prospective study in the Pacific Northwest. Pediatrics. 1987 Jul;80(1):37–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newland J. W., Neill R. J. DNA probes for Shiga-like toxins I and II and for toxin-converting bacteriophages. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jul;26(7):1292–1297. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.7.1292-1297.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newland J. W., Strockbine N. A., Miller S. F., O'Brien A. D., Holmes R. K. Cloning of Shiga-like toxin structural genes from a toxin converting phage of Escherichia coli. Science. 1985 Oct 11;230(4722):179–181. doi: 10.1126/science.2994228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Holmes R. K. Shiga and Shiga-like toxins. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):206–220. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.206-220.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Newland J. W., Miller S. F., Holmes R. K., Smith H. W., Formal S. B. Shiga-like toxin-converting phages from Escherichia coli strains that cause hemorrhagic colitis or infantile diarrhea. Science. 1984 Nov 9;226(4675):694–696. doi: 10.1126/science.6387911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perera L. P., Marques L. R., O'Brien A. D. Isolation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to Shiga-like toxin II of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli and use of the monoclonal antibodies in a colony enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Oct;26(10):2127–2131. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.10.2127-2131.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prado D., Cleary T. G., Pickering L. K., Ericsson C. D., Bartlett A. V., 3rd, DuPont H. L., Johnson P. C. The relation between production of cytotoxin and clinical features in shigellosis. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jul;154(1):149–155. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.1.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley L. W., Remis R. S., Helgerson S. D., McGee H. B., Wells J. G., Davis B. R., Hebert R. J., Olcott E. S., Johnson L. M., Hargrett N. T. Hemorrhagic colitis associated with a rare Escherichia coli serotype. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 24;308(12):681–685. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303243081203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strockbine N. A., Marques L. R., Holmes R. K., O'Brien A. D. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies against Shiga-like toxin from Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):695–700. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.695-700.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strockbine N. A., Marques L. R., Newland J. W., Smith H. W., Holmes R. K., O'Brien A. D. Two toxin-converting phages from Escherichia coli O157:H7 strain 933 encode antigenically distinct toxins with similar biologic activities. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):135–140. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.135-140.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svennerholm A. M., Wiklund G. Rapid GM1-enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with visual reading for identification of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Apr;17(4):596–600. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.4.596-600.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waddell T., Head S., Petric M., Cohen A., Lingwood C. Globotriosyl ceramide is specifically recognized by the Escherichia coli verocytotoxin 2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Apr 29;152(2):674–679. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80091-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


