Abstract
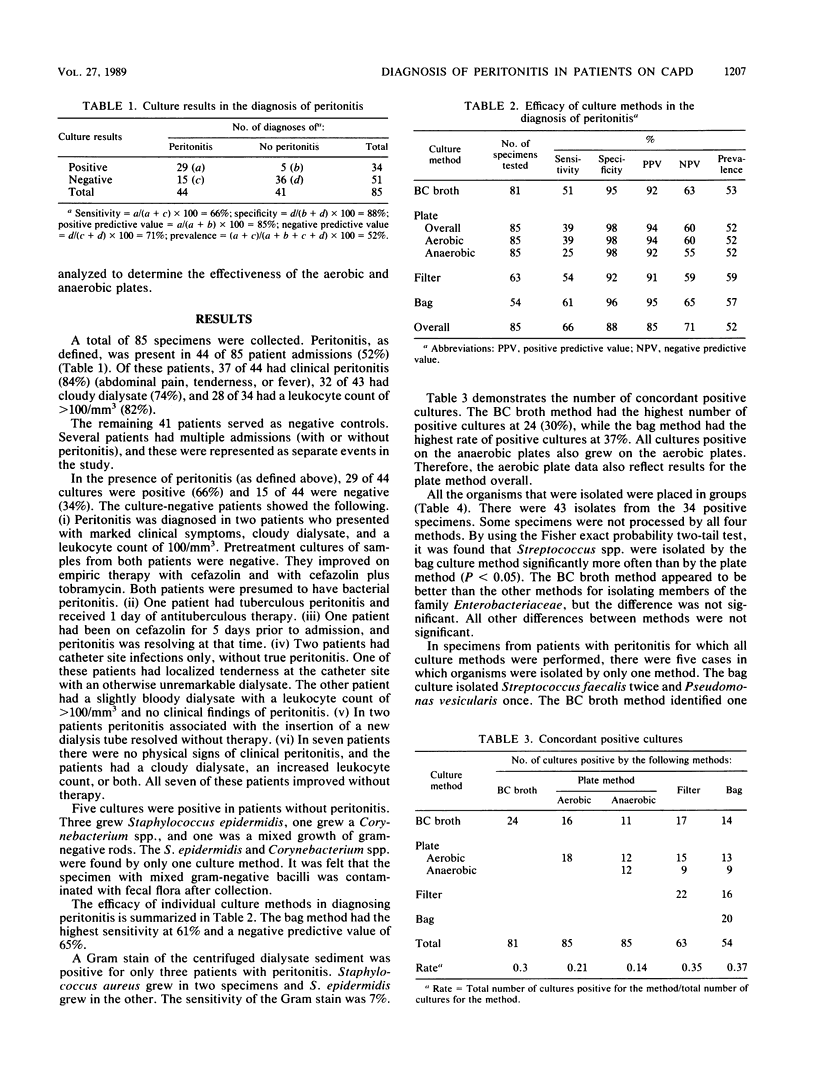
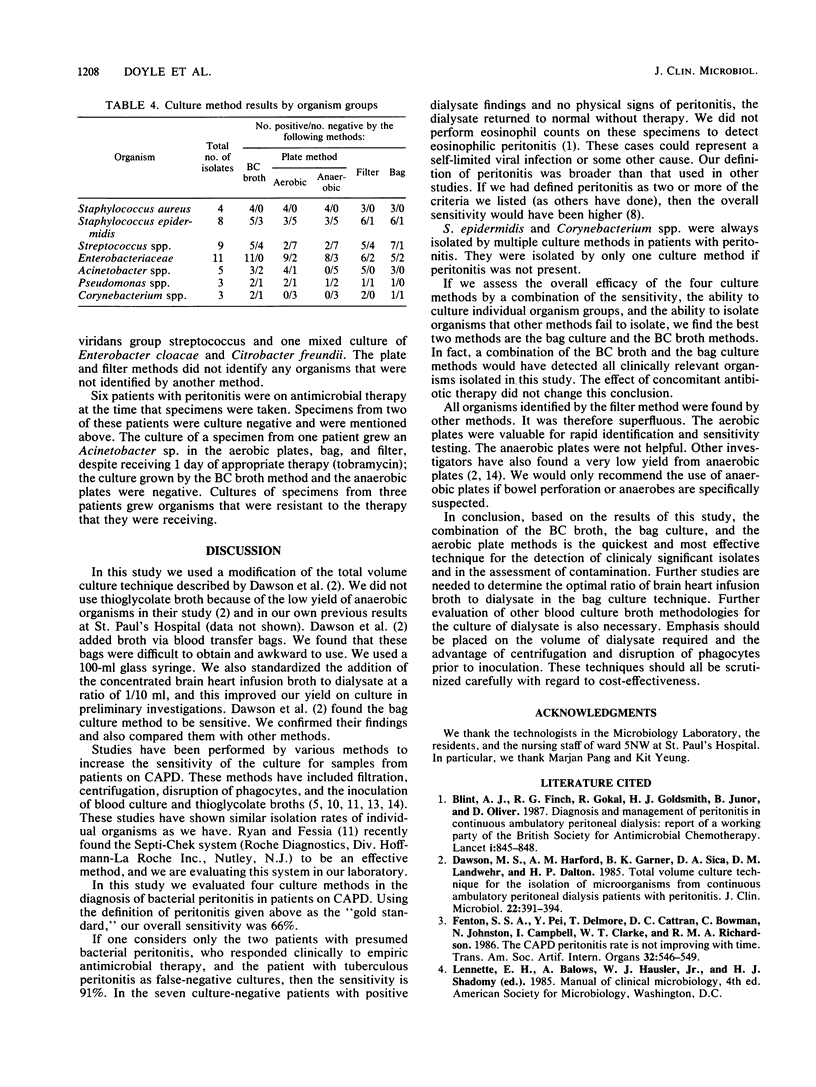
A prospective study was performed to evaluate four culture methods for the diagnosis of bacterial peritonitis in patients on continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Peritonitis was present in 44 of 85 patient admissions (52%). The overall sensitivity of the culture methods in detecting peritonitis was 66%. The sensitivities of the individual methods were as follows: bag culture method, 61%; blood culture broth method, 51%; filter method, 54%; and plate method, 39%. Our broad definition of peritonitis resulted in lower sensitivities. A combination of the bag and blood culture broth methods detected all positive cultures.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dawson M. S., Harford A. M., Garner B. K., Sica D. A., Landwehr D. M., Dalton H. P. Total volume culture technique for the isolation of microorganisms from continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients with peritonitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Sep;22(3):391–394. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.3.391-394.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diagnosis and management of peritonitis in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Report of a working party of the British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. Lancet. 1987 Apr 11;1(8537):845–849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton S. S., Pei Y., Delmore T., Cattran D. C., Bowman C., Johnston N., Campbell I., Clarke W. T., Richardson R. M. The CAPD peritonitis rate is not improving with time. ASAIO Trans. 1986 Jul-Sep;32(1):546–549. doi: 10.1097/00002480-198609000-00034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Males B. M., Walshe J. J., Garringer L., Koscinski D., Amsterdam D. Addi-Chek filtration, BACTEC, and 10-ml culture methods for recovery of microorganisms from dialysis effluent during episodes of peritonitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Feb;23(2):350–353. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.2.350-353.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncrief J. W., Nolph K. D., Rubin J., Popovich R. P. Additional experience with continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD). Trans Am Soc Artif Intern Organs. 1978;24:476–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolph K. D., Cutler S. J., Steinberg S. M., Novak J. W. Continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis in the United States: a three-year study. Kidney Int. 1985 Aug;28(2):198–205. doi: 10.1038/ki.1985.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oreopoulos D. G., Khanna R., Williams P., Vas S. I. Continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis - 1981. Nephron. 1982;30(4):293–303. doi: 10.1159/000182504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oreopoulos D. G., Robson M., Izatt S., Clayton S., deVeber G. A. A simple and safe technique for continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD). Trans Am Soc Artif Intern Organs. 1978;24:484–489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole-Warren L. A., Taylor P. C., Farrell P. C. Laboratory diagnosis of peritonitis in patients treated with continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Pathology. 1986 Apr;18(2):237–239. doi: 10.3109/00313028609059466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan S., Fessia S. Improved method for recovery of peritonitis-causing microorganisms from peritoneal dialysate. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Feb;25(2):383–384. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.2.383-384.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter M. T., Sheps S. B. Diagnostic testing revisited: pathways through uncertainty. Can Med Assoc J. 1985 Apr 1;132(7):755–760. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. C., Poole-Warren L. A., Grundy R. E. Increased microbial yield from continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis peritonitis effluent after chemical or physical disruption of phagocytes. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Mar;25(3):580–583. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.3.580-583.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vas S. I., Law L. Microbiological diagnosis of peritonitis in patients on continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Apr;21(4):522–523. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.4.522-523.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


