Abstract
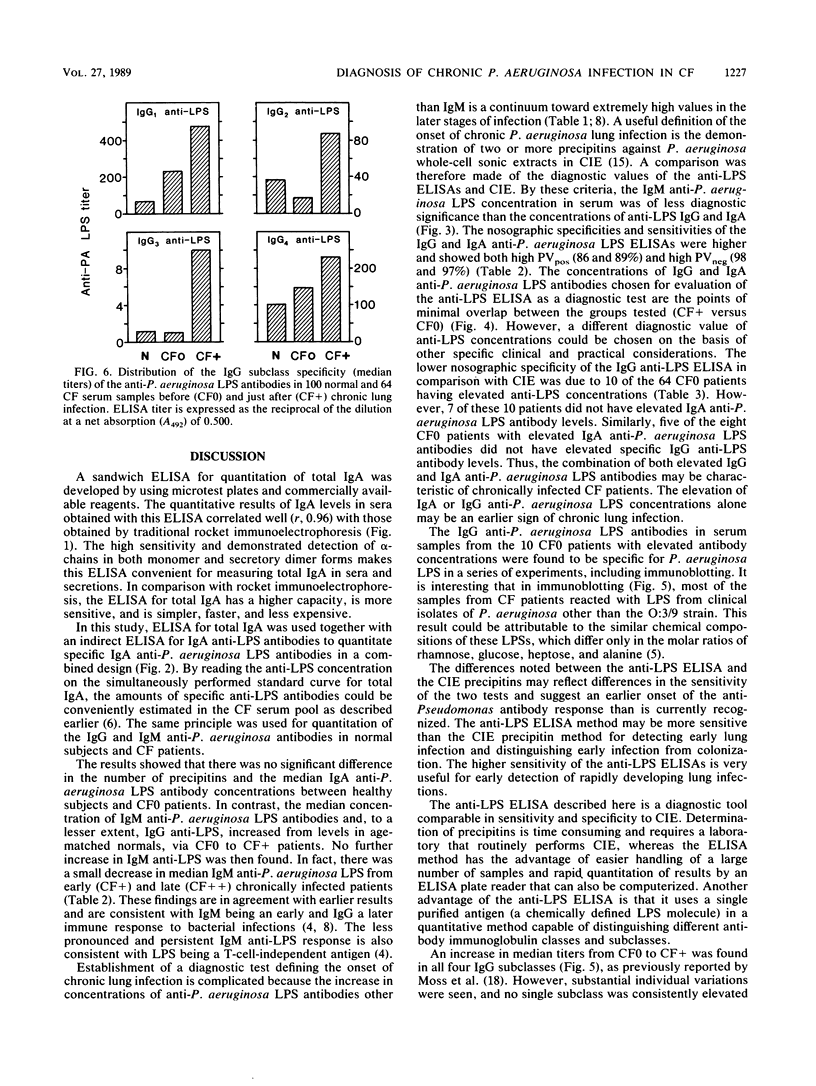
Chronic lung infection in cystic fibrosis is characteristically associated with polyagglutinable, serum-sensitive, mucoid strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) methods for standard-free quantitation of immunoglobulin G (IgG) and IgM antibodies to P. aeruginosa lipopolysaccharides (LPSs) have been developed. We now report the development of assays for quantitation of monomer and dimer total IgA and IgA anti-LPS antibodies. Use of these methods in diagnosis of early chronic P. aeruginosa lung infection was assessed. IgG and IgA anti-LPS levels increased significantly at the onset of chronic infection and continued to increase to very high levels in the later stages of infection. IgM anti-LPS levels also rose at the onset of chronic infection but did not increase further. The function of true- and false-positive rates was illustrated by using various concentrations of IgG, IgA, and IgM anti-LPS for discrimination of patients. Values that gave optimum separations were used for statistical evaluation of the diagnostic sensitivities and specificities of anti-LPS antibody concentrations. The results obtained in these assays were compared with a diagnosis, based on the number of precipitins in crossed immunoelectrophoresis, of serum samples from cystic fibrosis patients. In 64 paired serum samples taken before and immediately after the onset of chronic infection, as defined by crossed immunoelectrophoresis precipitins, the predictive values of a positive ELISA were 86% for IgG and 89% for IgA. The predictive values for a negative ELISA were 98% for IgG and 97% for IgA. Results of the IgM anti-LPS ELISA had a lower predictive value. Immunoblotting and absorption studies showed that IgG anti-LPS antibodies were directed specifically against LPS of P. aeuruginosa. ELISAs were developed to determine the specific IgG sublclasses involved. The increase in IgG anti-LPS involved all four subclasses. Highest anti-LPS titers were seen with IgG1 and IgG4, but the largest relative increases were seen with IgG2 and IgG3.
Full text
PDF

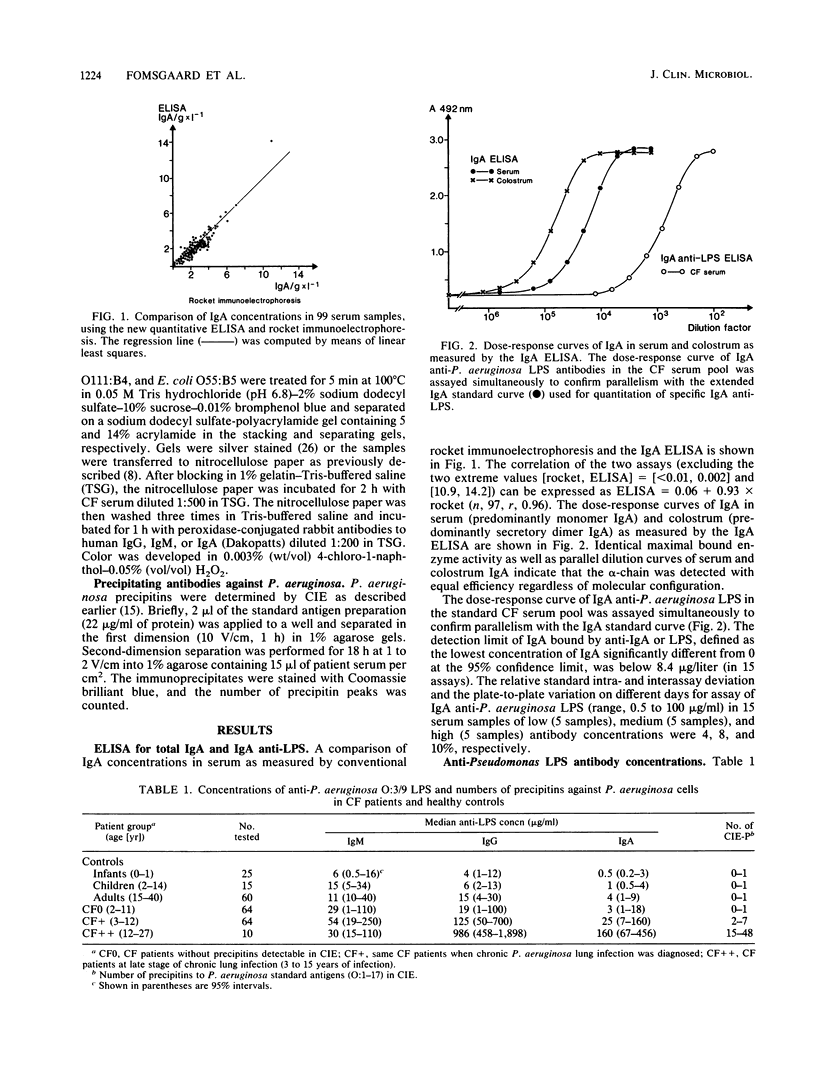
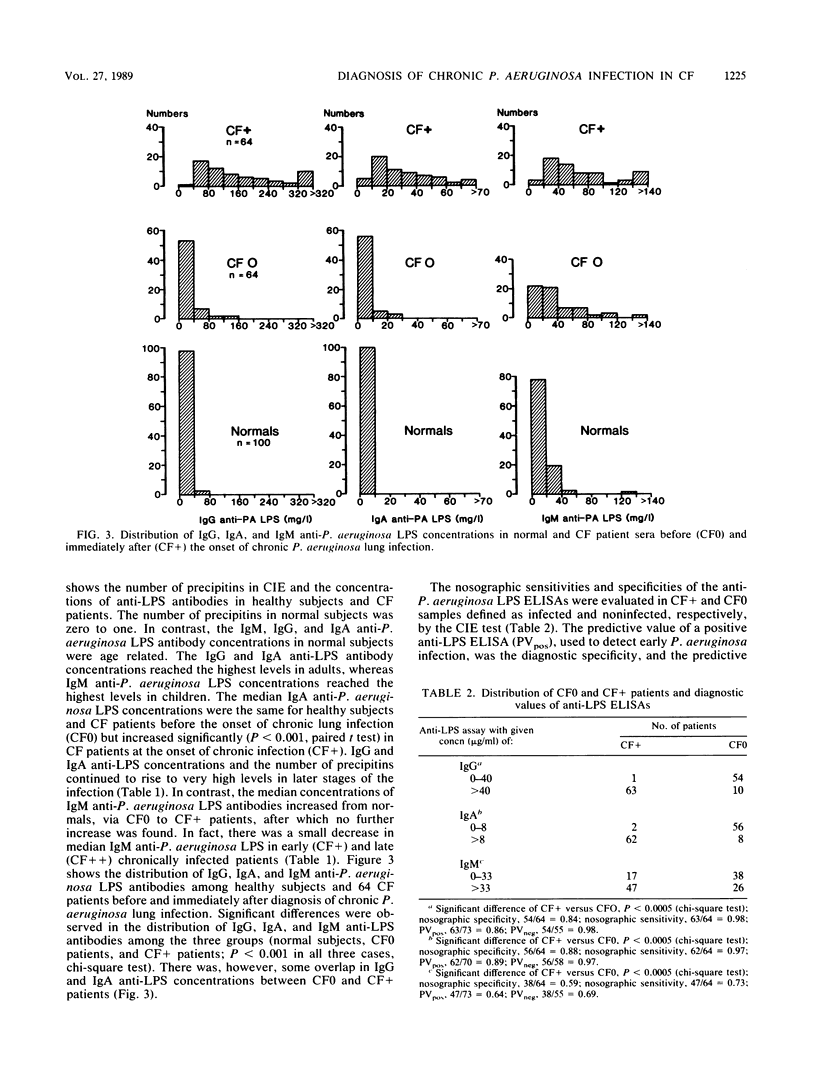
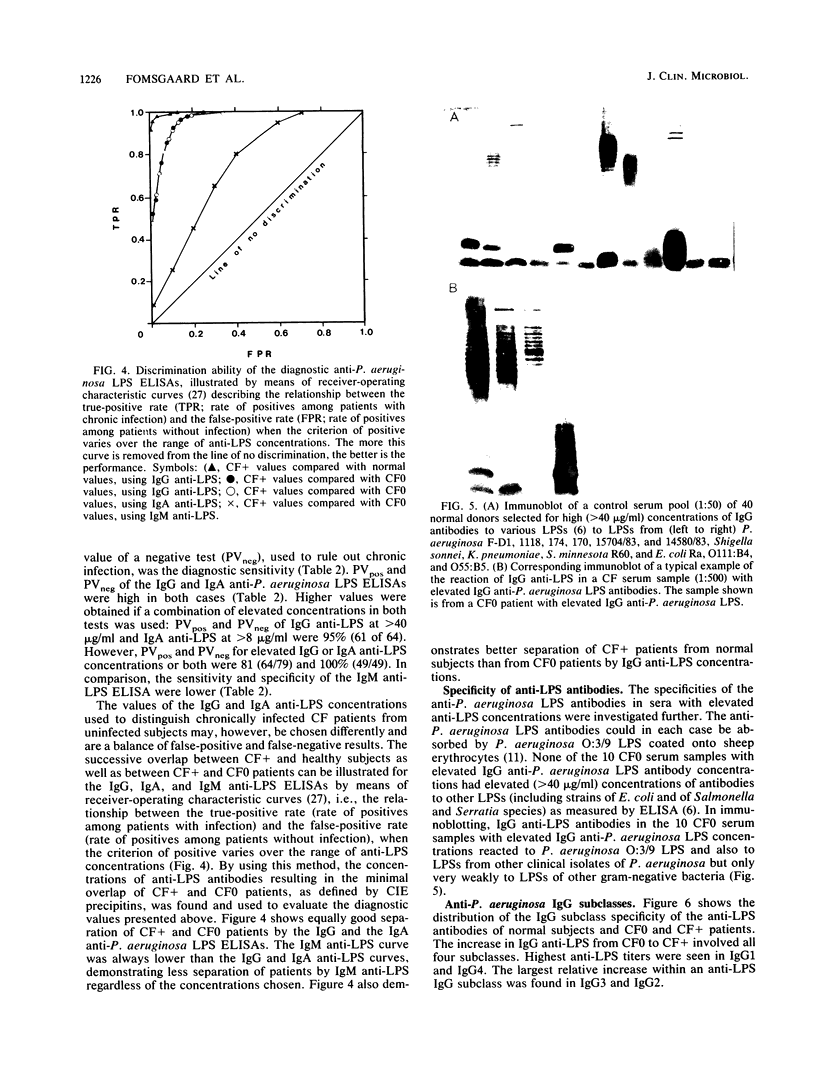


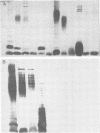
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borowski R. S., Stock L. M., Schiller N. L. Development of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for studying Pseudomonas aeruginosa cell surface antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jun;19(6):736–741. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.6.736-741.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brett M. M., Ghoneim A. T., Littlewood J. M. Serum antibodies to Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis. Arch Dis Child. 1986 Nov;61(11):1114–1120. doi: 10.1136/adc.61.11.1114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fomsgaard A., Conrad R. S., Galanos C., Shand G. H., Høiby N. Comparative immunochemistry of lipopolysaccharides from typable and polyagglutinable Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from patients with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 May;26(5):821–826. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.5.821-826.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fomsgaard A., Dinesen B. ELISA for human IgG and IgM anti-lipopolysaccharide antibodies with indirect standardization. J Immunoassay. 1987;8(4):333–350. doi: 10.1080/15321818708057032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fomsgaard A., Feldt-Rasmussen B., Deckert M., Dinesen B. Micro-ELISA for the quantitation of human urinary IgG. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1987 Apr;47(2):195–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fomsgaard A., Høiby N., Shand G. H., Conrad R. S., Galanos C. Longitudinal study of antibody response to lipopolysaccharides during chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infection in cystic fibrosis. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2270–2278. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2270-2278.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O. Electrodialysis of lipopolysaccharides and their conversion to uniform salt forms. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jun;54(2):603–610. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04172.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. Preparation and properties of antisera against the lipid-A component of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Dec 22;24(1):116–122. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb19661.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granström M., Ericsson A., Strandvik B., Wretlind B., Pavlovskis O. R., Berka R., Vasil M. L. Relation between antibody response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoproteins and colonization/infection in patients with cystic fibrosis. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1984 Nov;73(6):772–777. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1984.tb17774.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarström L., Insel R. A., Persson M. A., Smith C. I. The IgG1 subclass preference of selected, naturally occurring antipolysaccharide antibodies. Monogr Allergy. 1988;23:18–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Mutharia L. M., Chan L., Darveau R. P., Speert D. P., Pier G. B. Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from patients with cystic fibrosis: a class of serum-sensitive, nontypable strains deficient in lipopolysaccharide O side chains. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):170–177. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.170-177.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Høiby N., Hertz J. B., Sompolinsky D. Antibody response in patients with Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection to a 'common antigen' from P. aeruginosa analysed by means of quantitative immunoelectrophoretic methods. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1980 Jun;88(3):149–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1980.tb00088.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Quantitative estimation of proteins by electrophoresis in agarose gel containing antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss R. B., Hsu Y. P., Sullivan M. M., Lewiston N. J. Altered antibody isotype in cystic fibrosis: possible role in opsonic deficiency. Pediatr Res. 1986 May;20(5):453–459. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198605000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen S. S., Espersen F., Høiby N. Diagnosis of chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in cystic fibrosis by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Oct;25(10):1830–1836. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.10.1830-1836.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen S. S., Jensen T., Pressler T., Høiby N., Rosendal K. Does centralized treatment of cystic fibrosis increase the risk of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection? Acta Paediatr Scand. 1986 Sep;75(5):840–845. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1986.tb10299.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitt T. L., Todd H. C., Mackintosh C. A., Im S. W. Evaluation of three serological tests for detection of antibody to Pseudomonas aeruginosa in human sera. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Apr;4(2):190–196. doi: 10.1007/BF02013596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shand G. H., Pedersen S. S., Tilling R., Brown M. R., Høiby N. Use of immunoblot detection of serum antibodies in the diagnosis of chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infection in cystic fibrosis. J Med Microbiol. 1988 Nov;27(3):169–177. doi: 10.1099/00222615-27-3-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shryock T. R., Mollé J. S., Klinger J. D., Thomassen M. J. Association with phagocytic inhibition of anti-Pseudomonas aeruginosa immunoglobulin G antibody subclass levels in serum from patients with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Mar;23(3):513–516. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.3.513-516.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siber G. R., Schur P. H., Aisenberg A. C., Weitzman S. A., Schiffman G. Correlation between serum IgG-2 concentrations and the antibody response to bacterial polysaccharide antigens. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jul 24;303(4):178–182. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198007243030402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood R. E., Boat T. F., Doershuk C. F. Cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Jun;113(6):833–878. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.113.6.833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]