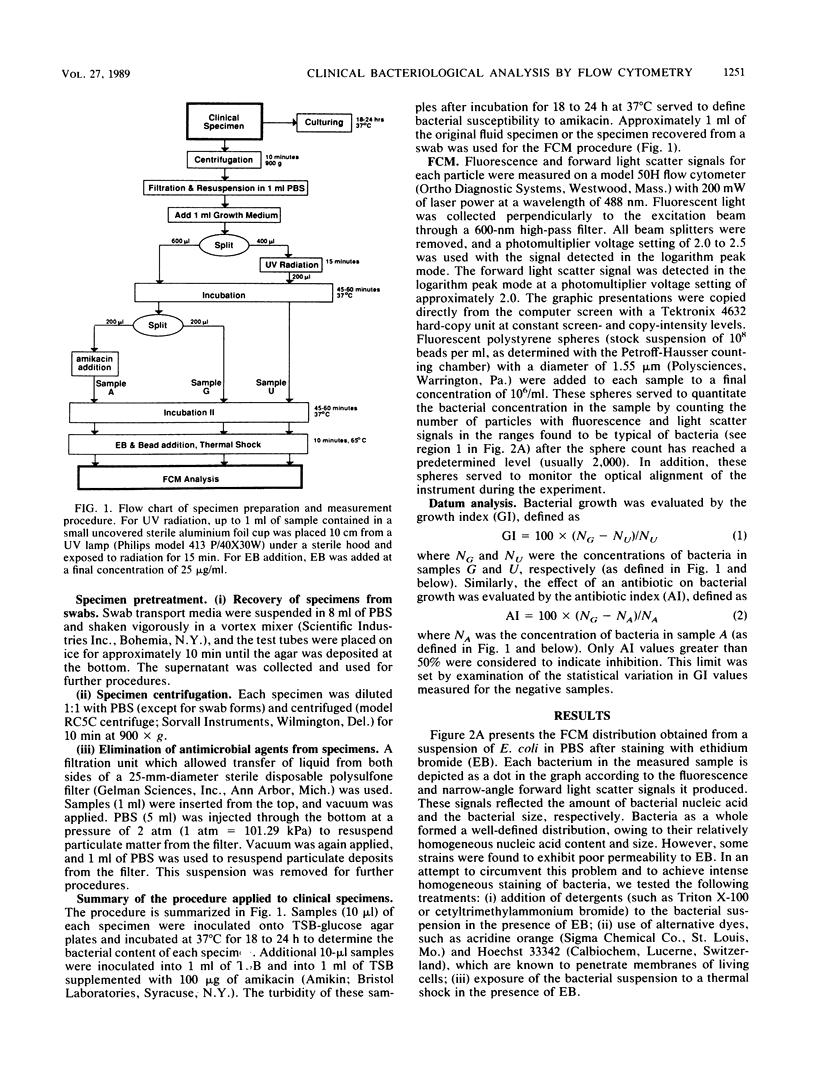
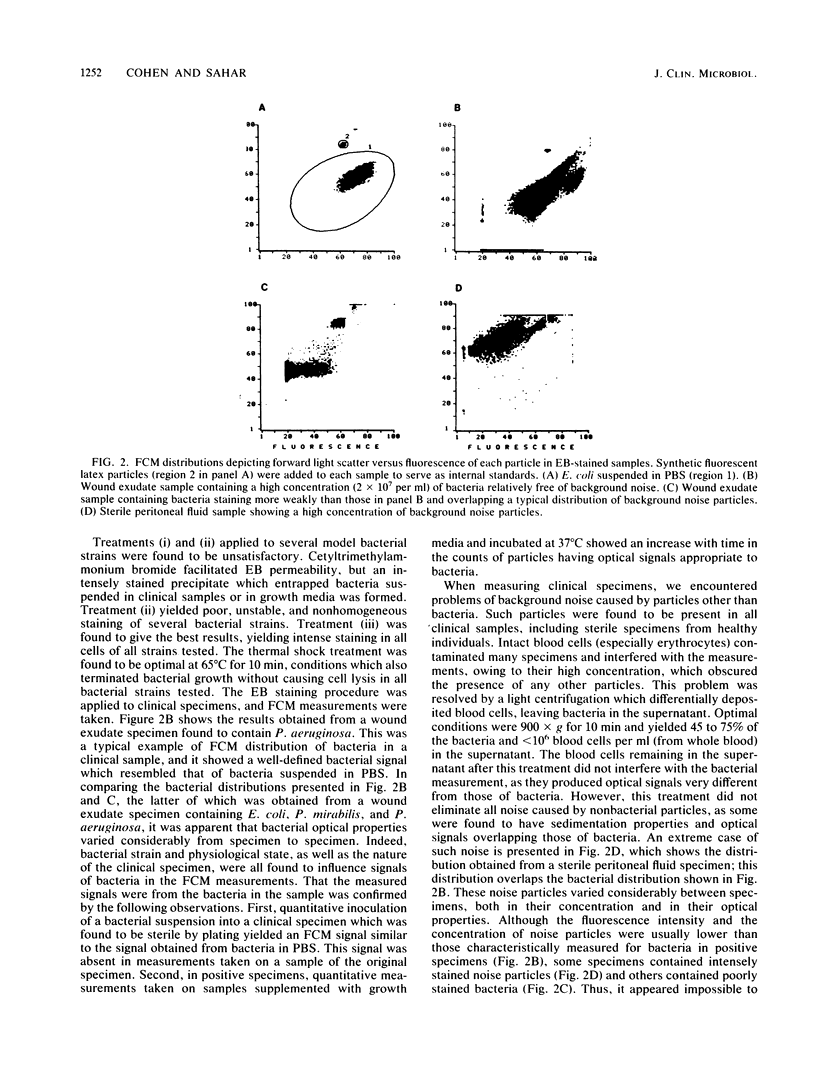
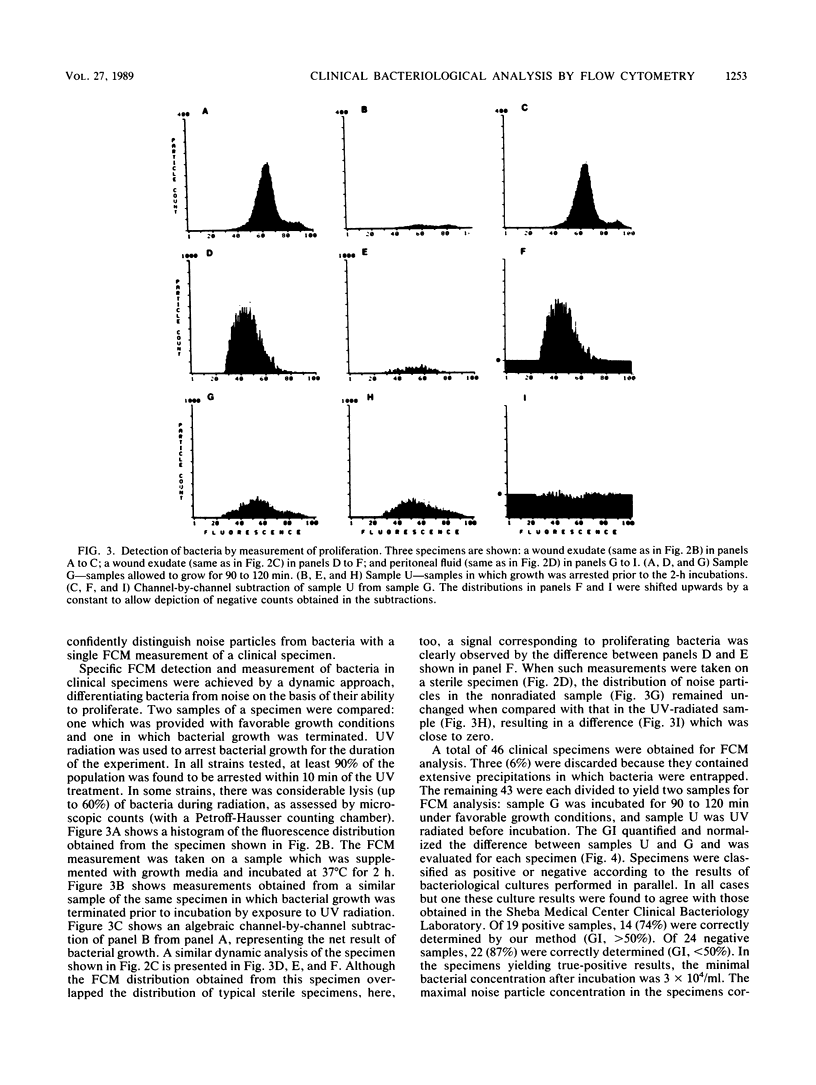
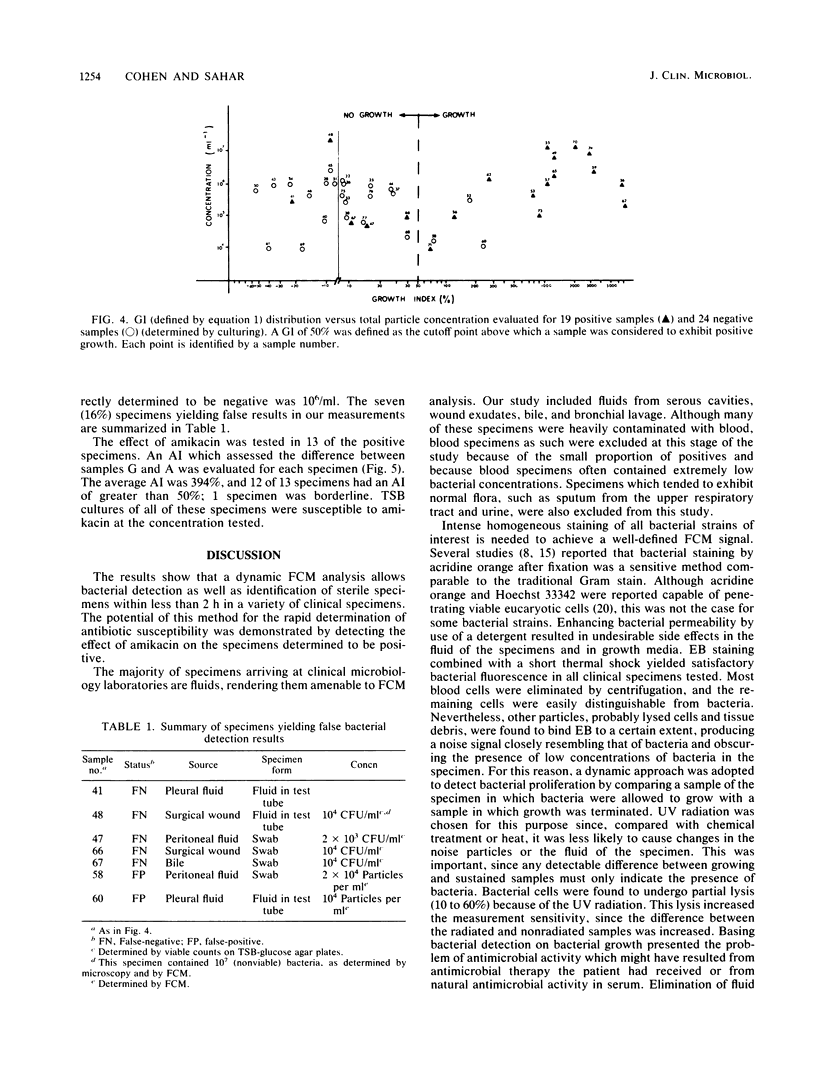
Abstract
A flow cytometry-based method for rapid and quantitative detection of bacteria in various clinical specimens and for rapid determination of antibiotic effect is described. Achieving such a measurement with high sensitivity required discrimination between bacteria and other particles which were often present in clinical samples in high concentrations. This discrimination was facilitated by detecting the bacterial characteristic light scatter and fluorescence signals following staining, e.g., with the fluorescent nucleic acid-binding dye ethidium bromide, as well as by measuring bacterial proliferation during short time intervals. Antibiotic susceptibility was measured by observing the inhibition of such proliferation. The method was applied to 43 clinical specimens from various sources, such as wound exudates, bile, serous cavity fluids, and bronchial lavage. Bacterial detection, achieved in less than 2 h, agreed with results of conventional methods with a sensitivity of 74% and a specificity of 88%. Susceptibility to amikacin was detected in 1 h in 92% of 13 positive specimens.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barry A. L., Joyce L. J., Adams A. P., Benner E. J. Rapid determination of antimicrobial susceptibility for urgent clinical situations. Am J Clin Pathol. 1973 May;59(5):693–699. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/59.5.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherubin C. E., Erg R., Appleman M. A critique of semiautomated susceptibility systems. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 May-Jun;9(3):655–659. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.3.655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyle M. B., McGonagle L. A., Plorde J. J., Clausen C. R., Schoenknecht F. D. Rapid antimicrobial susceptibility testing of isolates from blood cultures by direct inoculation and early reading of disk diffusion tests. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Sep;20(3):473–477. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.3.473-477.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doern G. V., Scott D. R., Rashad A. L. Clinical impact of rapid antimicrobial susceptibility testing of blood culture isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jun;21(6):1023–1024. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.6.1023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doern G. V., Scott D. R., Rashad A. L., Kim K. S. Evaluation of a direct blood culture disk diffusion antimicrobial susceptibility test. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Nov;20(5):696–698. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.5.696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellner P. D., Johnson E. Unreliability of direct antibiotic susceptibility testing on wound exudates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Feb;9(2):355–356. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.2.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield M. D., Clausen C. R., Smith A. L. The use of acridine orange as a rapid method for the quantitation of bacteremia in laboratory animals. Infection. 1985 May-Jun;13(3):137–139. doi: 10.1007/BF01642874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood D. In defence of turbidimetry. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1977 May;3(3):286–287. doi: 10.1093/jac/3.3.286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiehn T. E., Capitolo C., Armstrong D. Comparison of direct and standard microtiter broth dilution susceptibility testing of blood culture isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jul;16(1):96–98. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.1.96-98.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kluge R. M. Accuracy of Kirby-Bauer susceptibility tests read at 4, 8, and 12 hours of incubation: comparison with readings at 18 to 20 hours. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Aug;8(2):139–145. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.2.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornman K. S., Patters M., Kiel R., Marucha P. Detection and quantitation of Bacteroides gingivalis in bacterial mixtures by means of flow cytometry. J Periodontal Res. 1984 Nov;19(6):570–573. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1984.tb01316.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampe M. F., Aitken C. L., Dennis P. G., Forsythe P. S., Patrick K. E., Schoenknecht F. D., Sherris J. C. Relationship of early readings of minimal inhibitory concentrations to the results of overnight tests. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Oct;8(4):429–433. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.4.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauer B. A., Reller L. B., Mirrett S. Comparison of acridine orange and Gram stains for detection of microorganisms in cerebrospinal fluid and other clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Aug;14(2):201–205. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.2.201-205.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liberman D. F., Robertson R. G. Evaluation of a rapid Bauer-Kirby antibiotic susceptibility determination. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Mar;7(3):250–255. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.3.250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour J. D., Robson J. A., Arndt C. W., Schulte T. H. Detection of Escherichia coli in blood using flow cytometry. Cytometry. 1985 May;6(3):186–190. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990060303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirrett S., Reller L. B. Comparison of direct and standard antimicrobial disk susceptibility testing for bacteria isolated from blood. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Oct;10(4):482–487. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.4.482-487.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolte F. S., Contestable P. B., Lincalis D., Punsalang A., Jr Rapid, direct antibiotic susceptibility testing of blood culture isolates using the Abbott Avantage system. Am J Clin Pathol. 1986 Nov;86(5):665–669. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/86.5.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahar E., Lamed R., Ofek I. Rapid identification of Streptococcus pyogenes by flow cytometry. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jun;2(3):192–195. doi: 10.1007/BF02029514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dilla M. A., Langlois R. G., Pinkel D., Yajko D., Hadley W. K. Bacterial characterization by flow cytometry. Science. 1983 May 6;220(4597):620–622. doi: 10.1126/science.6188215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


