Abstract
Nuclear receptors are ligand-regulated transcription factors that regulate key aspects of metazoan development, differentiation, and homeostasis. Nuclear receptors recognize target genes by binding to specific DNA recognition sequences, denoted hormone response elements (HREs). Many nuclear receptors can recognize HREs as either homodimers or heterodimers. Retinoid X receptors (RXRs), in particular, serve as important heterodimer partners for many other nuclear receptors, including thyroid hormone receptors (TRs), and RXR/TR heterodimers have been proposed to be the primary mediators of target gene regulation by T3 hormone. Here, we report that the retinoic acid receptors (RARs), a distinct class of nuclear receptors, are also efficient heterodimer partners for TRs. These RAR/TR heterodimers form with similar affinities as RXR/TR heterodimers on an assortment of consensus and natural HREs, and preferentially assemble with the RAR partner 5′ of the TR moiety. The corepressor and coactivator recruitment properties of these RAR/TR heterodimers and their transcriptional activities in vivo are distinct from those observed with the corresponding RXR heterodimers. Our studies indicate that RXRs are not unique in their ability to partner with TRs, and that RARs can also serve as robust heterodimer partners and combinatorial regulators of T3-modulated gene expression.
The Nuclear Receptors are a large family of interrelated, ligand-regulated transcription factors, and they regulate many crucial events in metazoan development, differentiation, and homeostasis. Members of this family include receptors that respond to endocrine hormones, including the estrogen receptors, vitamin D3 receptors (VDRs), thyroid hormone receptors (TRs), retinoic acid receptors (RARs), and retinoid X receptors (RXRs) (1–5). Other nuclear receptors respond to intermediates of lipid metabolism, such as the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs), or to xenobiotics, such as the pregnane X receptor (6–8). Still additional orphan receptors have been identified that are assigned to the nuclear receptor family based on shared structural and functional properties, but they have no known ligand (9–11).
Nuclear receptors bind to specific DNA sites and modulate the expression of adjacent target genes (12–15). Once bound to a specific DNA site, nuclear receptors can either repress or activate expression of their gene targets by recruiting auxiliary proteins, denoted corepressors and coactivators (16–25). Corepressors and coactivators modify chromatin and/or interact with the general transcriptional machinery so as to modulate target gene transcription (16–25). TRs and RARs typically recruit corepressors and repress gene expression in the absence of hormone, but release from corepressors, interact with coactivators, and activate target gene expression on binding to a hormone agonist, such as T3 thyroid hormone or all trans retinoic acid (ATRA) (23, 26, 27).
Most members of the nuclear receptor family bind to DNA as protein dimers, although several nuclear receptors can also bind to DNA as protein monomers or oligomers (12, 28–35). Each receptor in the dimer interacts with a conserved six- to eight-nucleotide sequence on the DNA, denoted a half-site; two half-sites therefore create a functional hormone response element (HRE) (12, 28–35). Both the sequence and the spacing/orientation of the two half-sites determine which nuclear receptors can bind to a given HRE (12, 28–35). PPARs have been proposed to preferentially recognize AGGTCA half-sites oriented as a direct repeat with a 1 base spacer (a DR-1), TRs to recognize AGGTCA half-sites in a DR-4, and RARs to recognize AGGTCA half-sites in a DR-5 (30, 33–35). In practice, however, nuclear receptors often recognize a broader set of HREs than those predicted by this idealized model. TRs, for example, can also bind to and regulate target gene expression through half-sites displayed as an inverted repeat with no spacer (INV-0) or as a divergent repeat with a 6 base spacer (DIV-6), whereas RARs can bind to and regulate INV-0 and DR-2 elements in addition to DR-5 elements (e.g. Refs. 28, 31, 36 and 37). In addition, half-sites found naturally in vivo often differ in sequence from the optimized AGGTCA half-sites determined by experimental dissections of artificial response elements.
Although steroid receptors, such as the estrogen receptors, generally bind to their cognate HREs as receptor homodimers, the majority of nonsteroid nuclear receptors have the capacity to form heterodimers with other members of the receptor family (reviewed in Refs. 12 and 38). This heterodimerization phenomenon has been extensively studied for the TRs, RARs, VDRs, and PPARs, all of which share the common ability to form heterodimers with RXRs (29, 31, 34–36, 39–45). In general, these RXR heterodimers form in preference to the corresponding homodimers in vitro and display enhanced transcriptional responses on target genes in cells. The DNA recognition properties of the heterodimer generally parallel those of the non-RXR partner: i.e. RXR/TRs preferentially recognize DR-4 elements, whereas RXR/RARs preferentially recognize DR-5 elements (29, 31, 34–36, 39–41, 44). The RXR moiety binds upstream of its partner on DR-3, -4, or -5 elements, but downstream of its partner on DR-1 or DR-2 elements (30, 33, 34). These receptor polarities help influence the transcriptional response of the heterodimer to hormone; on DR-3, -4, or -5 elements, the RXR moiety is restricted in its ability to activate target gene expression in response to RXR ligands, and the target gene is activated predominantly by ligands that bind to the VDR, TR, or RAR partner (40, 41, 46). Conversely, on DR-1 elements, ligands for either the RXR or PPAR partner can induce target gene expression (40, 41).
Although the status of RXR as a communal heterodimer partner is widely accepted, there have been suggestions that other pairs of nuclear receptors may also form functional heterodimers. Notably, RAR/TR heterodimers have been reported to form on an INV-0 element (47); however, the significance of this observation was undermined by the subsequent identification of DR-4 and DR-5 elements as high-affinity binding sites for TRs and RARs, and by indications that RAR/TR heterodimers are less stable than RXR/TR heterodimers under certain circumstances (48). We reexamined this question and report here that RAR/TR heterodimers form at high efficiency on a specific subset of DR-4, DR-5, and DIV-6 elements and can assemble with avidities approximating those observed with RXR/TR heterodimers. Notably, RAR/TR heterodimers can tether both corepressors and coactivators in vitro, whereas RXR/TR heterodimers are limited to recruiting coactivators. Hormone ligands for either receptor moiety (T3 or ATRA) induce only partial release of corepressor from the RAR/TR complex, with quantitative corepressor release only achieved when both ATRA and T3 are present. Conversely, either T3 or ATRA can induce efficient recruitment of the activator of TRs and RARs (ACTR) coactivator, whereas steroid receptor coactivator-1 (SRC-1) is preferentially recruited in response to T3 only. In keeping with these in vitro properties, cointroduction of TRs and RARs into cells results in unique transcriptional properties distinct from those of RXR/TR and RXR/RAR heterodimers. We conclude that RARs and TRs can form functional heterodimer complexes on appropriate response elements, recruit relevant cofactors, and produce a combinatorial regulation of target gene expression different from that observed for the corresponding homodimers or RXR heterodimers.
RESULTS
RAR/TR Heterodimers Assemble in Preference to Homodimers on DR-4 DNA Elements
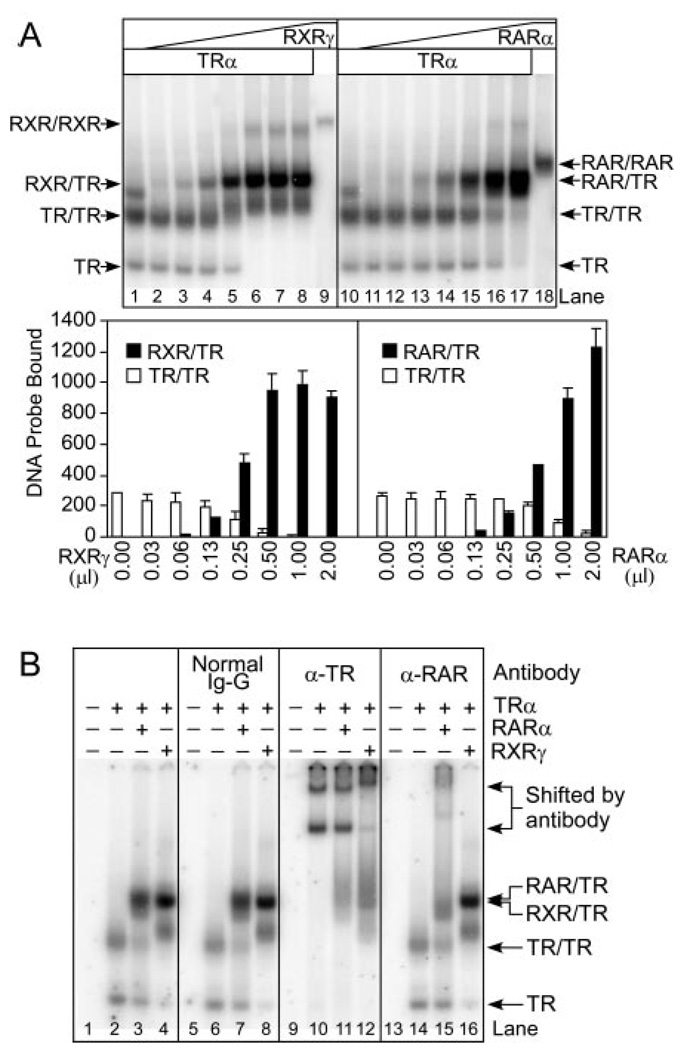
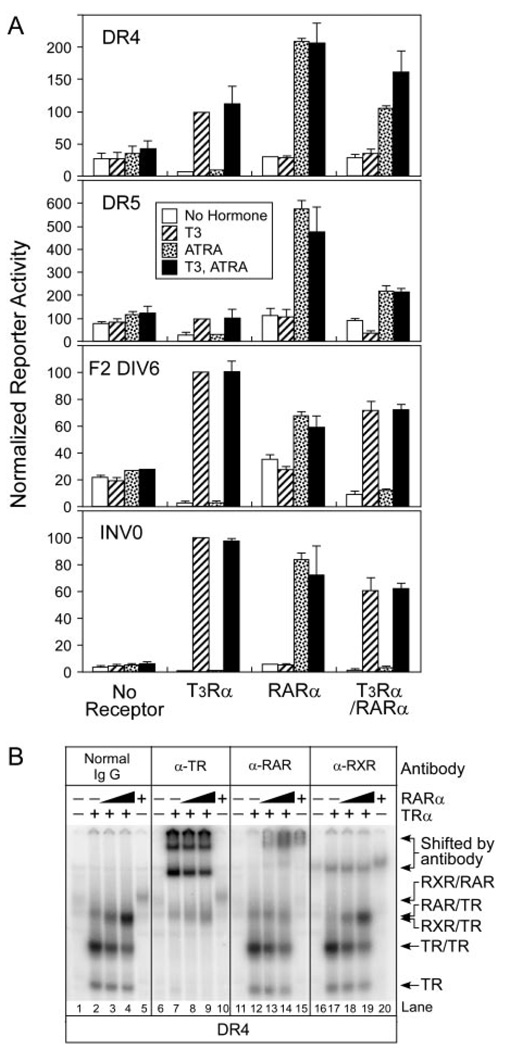
We first examined the ability of TRα, RXRγ, and RARα to bind to a prototype DR-4 element. We employed an EMSA using a radiolabeled DR-4 DNA probe and recombinant TRα, RXRγ, or RARα proteins isolated from a baculovirus/Sf-9 expression system (Fig. 1A; electrophoretograms are reproduced on top and quantified below). As anticipated from previous studies (31, 36), TRα formed both receptor monomers and receptor homodimers on the DR-4 element when tested alone (Fig. 1A, lane 1), but preferentially formed RXR/TR heterodimers in the presence of increasing amounts of RXRγ (Fig. 1A, lanes 2 to 8). RXRγ alone formed RXR homodimers inefficiently on this element (Fig. 1A, lane 9). No analogous protein/DNA complexes were detected using control extracts from Sf9 cells infected by nonrecombinant baculovirus (data not shown). The identities of these various receptor/ DNA complexes were confirmed by antibody supershift experiments; as anticipated, the electrophoretic mobilities of the TR monomers, homodimers, and RXR/TR heterodimers were all altered (supershifted) by anti-TR antibodies (Fig. 1B; compare lanes 2, 4, 10, and 12). None of these receptor complexes were reactive with either nonimmune IgGs or with anti-RAR antisera (lanes 6, 8, 14, and 16).
Fig. 1. RARα/TRα Heterodimers Assemble on a DR-4 DNA Response Element.
EMSAs were used to determine the ability of TRα, RARα, and RXRγ receptors to bind to DNA as homodimers and heterodimers in the absence of hormone. A, TRα forms heterodimers with both RARα and RXRγ. TRα protein (~40 ng) was incubated with a radiolabeled DR-4 probe together with increasing amounts of RXRγ (~28 ng/µl; lanes 2–8) or RARα (~28 ng/µl; lanes 11–18). Controls included TRα alone (lanes 1 and 10), RXRγ alone (lane 9), and RARα alone (lane 18); equal amounts of nonrecombinant extracts were employed where necessary to keep all assays equivalent. Arrows indicate DNA complexes representing TR monomers (TR), TR homodimers (TR/TR), RAR/TR heterodimers (RAR/TR), and RXR/TR heterodimers (RXR/TR). The amount of radiolabeled DNA probe migrating as TRα homodimer (open bars), RXRγ/TRα heterodimer (filled bars, left panel), or RARα/TRα heterodimer (filled bars, right panel) was quantified below. The mean and se of two or more experiments are shown. B, The identity of the various receptor/DNA complexes was confirmed by antibody supershift experiments. EMSAs were performed as in panel A, except the resulting receptor/DNA complexes were incubated with the antisera indicated above each panel before electrophoresis. TRα, RARα, and RXRγ were used individually or in combination (as indicated above the panels) at approximately 30, 14, and 7 ng per assay, respectively. The positions of the various receptor/DNA complexes and the complexes supershifted by antisera are indicated on the right.
Although RARα, when tested alone, bound to the DR-4 element weakly as a homodimer (Fig. 1A, lane 18), mixing of TRα and RARα resulted in the formation of a novel DNA binding complex that formed at high efficiency and migrated at an mobility intermediate to that of TRα and RARα homodimers (Fig. 1A, lanes 11–17). This presumptive RAR/TR heterodimer complex was supershifted by antibodies to RAR and to TR, but was unaffected by nonimmune IgG or by anti-RXR antibodies (Fig. 1B, lanes 3, 7, 11, and 15, and data not shown); no comparable complex was detected using nonrecombinant baculovirus/Sf-9 extracts (Fig. 1B, lanes 1, 5, 9, and 13). Heterodimer formation was cooperative (i.e. heterodimers formed in preference to RAR, TR, or RXR homodimers, and bound substantially more DNA probe than did the equivalent receptor homodimers), and could be observed over a wide range of absolute RARα and TRα concentrations (Fig. 1A, and data not shown). All experiments were performed in DNA probe excess, and equivalent RARα and RXRγ concentrations were employed in both left and right panels of Fig. 1A. To rule out any possible contribution of Ultraspiracle, an insect RXR ortholog potentially present in Sf9 cell preparations, to these heterodimer complexes, we repeated our experiments using highly purified receptors isolated either from the baculovirus system or from Escherichia coli (i.e. a context lacking all nuclear receptors); equivalent results were obtained as in Fig. 1 (data not shown). We conclude that RARα can form heterodimers with TRα on a consensus DR-4 element with an efficiency approaching that of the prototypic RXR/TR heterodimers previously characterized.
RAR/TR Heterodimers Form on DR-4, DR-5, DIV-6, and INV-0 Elements with Distinct Efficiencies
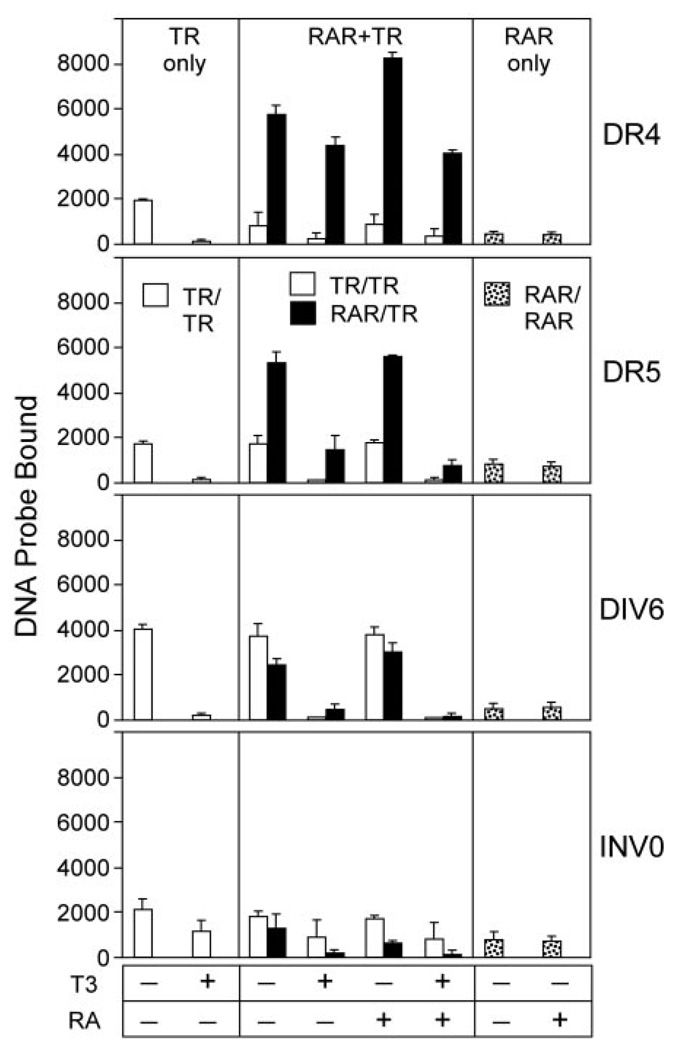
We next tested whether RAR/TR heterodimers also assembled on a variety of other TR and RAR response elements. In addition to the DR-4 element tested above, RARα/TRα heterodimers formed efficiently and in preference to RARα or TRα homodimers on a DR-5 (a prototypic RAR response element) (Fig. 2). RARα/TRα heterodimer formation could also be detected on the DIV-6 elements, at lower efficiency than TR homodimer formation (Fig. 2). An INV-0 element was employed in the initial identification of RAR/TR heterodimers (47); this element is, however, significantly less efficient at heterodimer formation than the other DNA elements tested here (Fig. 2). We also tested the effect of hormone ligand on the formation of these receptor complexes. As previously reported (e.g. Ref. 49), addition of T3 hormone destabilized TR homodimer formation on all response elements tested (Fig. 2, TR only). RAR/TR heterodimers were also disrupted by T3 hormone when bound to the DIV-6 and INV-0 elements, or (to a lesser extent) on the DR-5, but were refractory to T3 when assembled on the DR-4 (Fig. 2). Notably, all RARα/TRα heterodimer complexes tested were refractory to ATRA (Fig. 2). We conclude that the RARα/TRα heterodimer can be recruited to an assortment of known TR and RAR response element configurations, and that these complexes display distinct sensitivities to hormone ligands when bound to these distinct half-site configurations.
Fig. 2. RARα/TRα Heterodimers Form on a Series of Prototypic DNA Response Elements.
The ability of RARα and TRα to bind as homodimers and as heterodimers to a variety of DNA response elements was tested using an EMSA protocol as in Fig. 1. Radiolabeled DR-4, DR-5, DIV-6, and INV-0 DNA elements, all composed of AGGTCA half-site repeats, were tested. TRα and RARα proteins, used at 40 and 28 ng respectively, were assayed alone (left and right panels), or as an RARα/TRα mixture (center panels). Where indicated, T3 or ATRA was also included at 1 µM in the EMSA binding buffer. The amount of radiolabeled DNA probe migrating as a TRα homodimer (open bars), RARα homodimer (stippled bars), or RARα/TRα heterodimer (filled bars) under each condition was quantified; the mean and se of three experiments are shown.
Different TR and RAR Isotypes Share the Ability to Form Heterodimers, but at Different Efficiencies
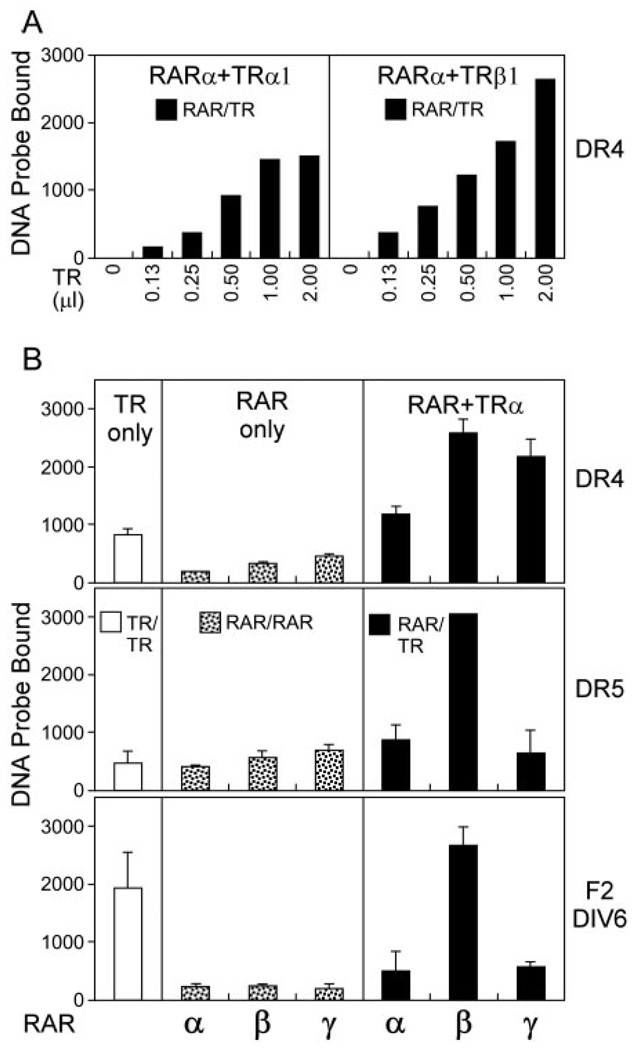
Many nuclear receptors are expressed from multiple genetic loci, and/or by alternative mRNA splicing to generate a series of interrelated, but nonidentical receptor isoforms (3, 11, 37). Different isoforms of a given receptor class often play distinct, if partially overlapping roles in the organism. We examined whether the different isoforms of TR and RAR displayed different abilities to form heterodimers. The two widely expressed TR isoforms, α1 and β1, formed heterodimers with RARα on a DR-4 element at approximately equal efficiencies, and in preference to TR monomers or homodimers (Fig. 3A). Reciprocally, we also examined the ability of the three major isotypes of RAR (α, β, and γ) to form heterodimers with TRα; DR-4, DR-5, and the F2-DIV6 elements were tested. Tested alone, all three RAR isoforms formed homodimers at approximately equal efficiency (Fig. 3B). When combined with TRα1, all three RAR isoforms were recruited into RAR/TR heterodimers, with somewhat different efficiencies depending on the nature of the response element (Fig. 3B, and data not shown). RARβ exhibited a substantially stronger heterodimerization with TRα than did either RARα or γ, and this was particularly evident on the DR-5 and DIV-6 sequences. We conclude that the major isoforms of TR and RAR share the ability to heterodimerize on the response elements tested here, with RARβ displaying the greatest aptitude in this regard.
Fig. 3. The Ability to Form RAR/TR Heterodimers Is Shared by Different Receptor Isotypes.
The ability of different RAR and TR isotypes to bind as heterodimers was tested using an EMSA protocol as in Fig. 1. A, Both TRα and TRβ1 can form heterodimers with RARα on a DR-4 element. A fixed amount of RARα (21 ng) was mixed with increasing amounts of either TRα or TRβ (40 ng/µl) as indicated below the panel. The amount of radiolabeled DNA probe migrating as a RAR/TR heterodimer was quantified and is presented (filled bars). B, Three isoforms of RAR form heterodimers with TRα with different efficiencies. TRα (40 ng) and RARα, β, or γ protein preparations (normalized to yield equal homodimer formation when tested alone; ~21 ng for RARα) were assayed alone (left and center panels), or as a RAR/TRα mixture (right panels). DR-4, DR-5, and the F2-DIV-6 element were employed as radiolabeled probes. The amount of radiolabeled DNA probe migrating as a TRα homodimer (open bars), RAR homodimer (stippled bars), or RAR/TRα heterodimer (filled bars) was quantified and is presented. The mean and range of two experiments are shown. No hormone was used in these assays.
RAR/TR Heterodimers Form with a Preferred Polarity and Half-Site Specificity
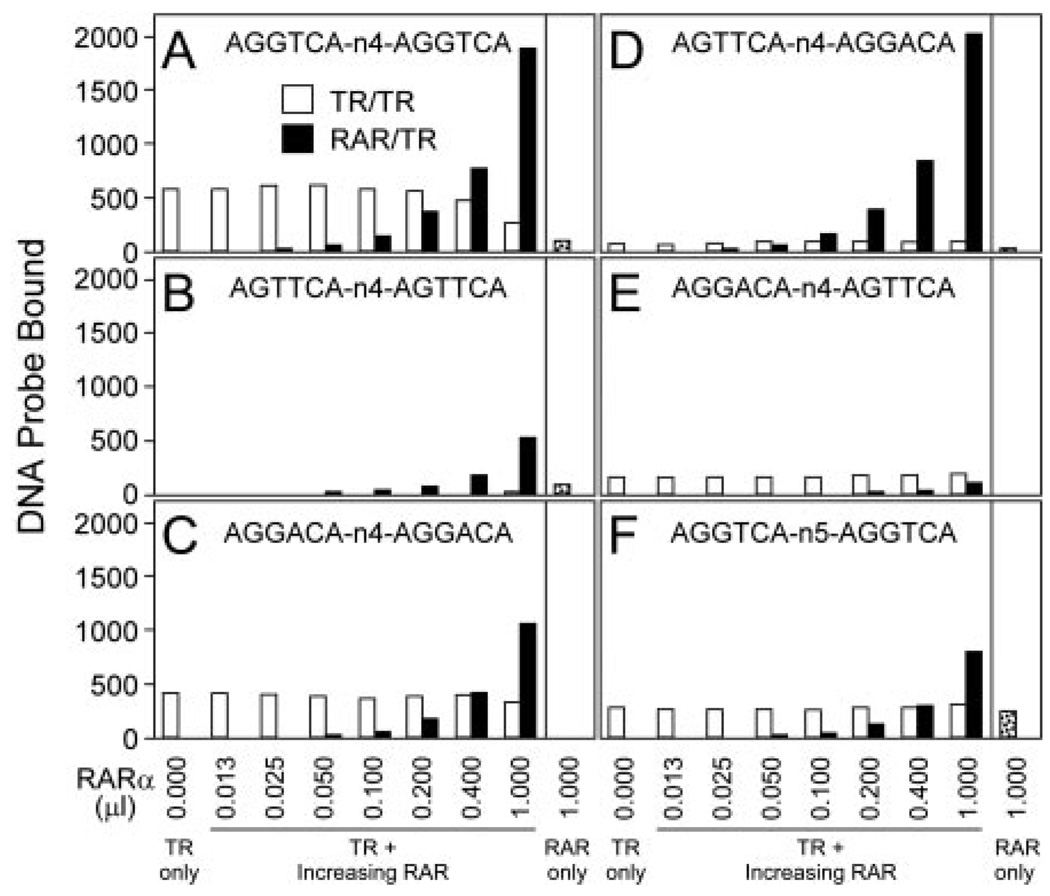
Although both RARs and TRs can recognize response elements composed of consensus AGGTCA repeats, they differ in the ability to also recognize variant halfsites that depart from this idealized sequence (e.g. Refs. 50 and 51). RARs can efficiently recognize AGTTCA half-sites, whereas TRs can recognize AGGACA half-sites (30, 33, 50–52). We therefore created a series of DR-4 elements bearing different combinations of consensus and nonconsensus half-sites and examined the ability of RARα/TRα heterodimers to bind to these HREs by EMSA. As noted above, a DR-4 composed of consensus AGGTCA half-sites was efficiently bound by RARα/TRα heterodimers and was also recognized by both TRα and RARα homodimers (Fig. 4A). Altering both half-sites to either an AGTTCA half-site or to an AGGACA half-site retained formation of the corresponding RARα or TRα homodimer, respectively, while destabilizing formation of the RARα/TRα heterodimer (Fig. 4, B and C, and data not shown). Significantly, placing the RARα-selective AGTTCA half-site upstream and the TRα-selective AGGACA half-site downstream selectively stabilized RARα/TRα heterodimer formation compared with the TRα homodimer (Fig. 4D), whereas the reciprocal half-site polarity virtually abolished the ability of the RARα/TRα heterodimer to bind to the HRE (Fig. 4E). This data indicates that the RAR moiety in the RAR/TR heterodimer preferentially binds to the upstream half-site and the TR moiety to the downstream half-site. Intriguingly, the same TR-3′ orientation has been assigned to RXR/TR heterodimers (12).
Fig. 4. RAR/TR Heterodimers Assemble with a Defined Polarity on DR-4 DNA Response Element.
The ability of TRα to bind as a homodimer or as an RARα/TRα heterodimer to DNA elements bearing different half-sites was tested using the EMSA protocol in Fig. 1. A set of radiolabeled DNA elements was created containing a combination of consensus (AGGTCA), RAR-selective (AGTTCA), or TR-selective (AGGACA) half-sites, oriented as a DR-4 or a DR-5, as indicated in each panel (A–F). TRα protein (~40 ng) was incubated with each DNA probe either alone or together with increasing amounts of RARα (~28 ng/µl) as indicated below the panels, and the resulting DNA complexes were resolved by EMSA. The amount of radiolabeled probe migrating as a TRα homodimer (open bars) or as an RARα/TRα heterodimer (filled bars) was quantified as in Fig. 1. RARα homodimers formed in the absence of TRα were also quantified (stippled bars). Comparable results were obtained in repeated studies; a representative experiment is presented. No hormone was used in these assays.
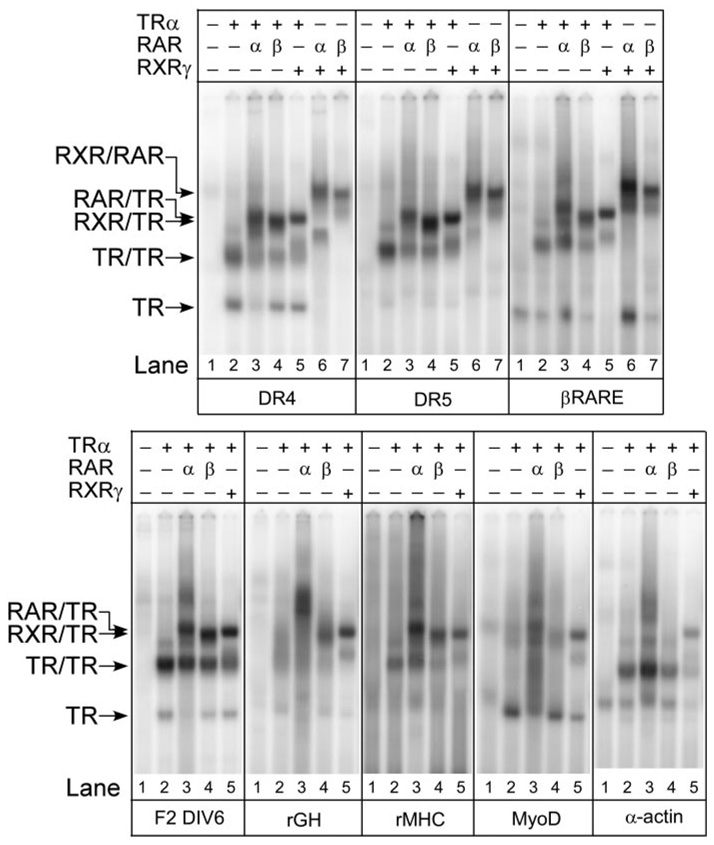
We extended these studies to test the ability of the RAR/TR heterodimers to bind to natural response elements found in hormone-responsive genes (Fig. 5). Many of these elements depart from the idealized sequences investigated above, and bind to TR and to RAR homodimers less efficiently than do optimized repeats. RAR/TR heterodimers formed at approximately the same efficiency as RXR/TR heterodimers on three elements: the RAR response element in the β-RAR promoter, the TR response elements in the chicken lysozyme (F2-DIV6), and the TR-response element in the rat myosin heavy chain (rMHC) promoters (Fig. 5). RXR/TR heterodimers were favored on the α-actin response element, whereas the binding pattern to the rat GH (rGH) and myosin D (MyoD) promoter elements (which contain three half-sites) yielded a weak and complex pattern. We conclude that many, but not all, naturally occurring TR response elements are capable of recruiting the RARα/TRα heterodimer.
Fig. 5. RAR/TR Heterodimers Bind to Natural DNA Response Elements.
TRα, RARα, RARβ, and RXRγ proteins were tested for the ability to bind to different natural and synthetic DNA elements using an EMSA protocol as in Fig. 1. TRα, RARα, and RXRγ were used at approximately 40 ng, 20 ng, and 11 ng per assay, respectively; RARβ was titrated to yield equal homodimer formation as RARα. Radiolabeled DNA probes included a consensus DR-4, a consensus DR-5, the retinoid response element in the RARβ promoter (β-RARE), or the T3-response elements found in the F2-lysozyme promoter (F2-DIV-6), rGH promoter, rMHC promoter, human MyoD promoter, and α-actin promoter. For each probe, receptor preparations were tested individually or in combination as indicated above each panel. The positions of receptor/DNA complexes representing TR monomers, TR homodimers, RAR/TR heterodimers, RXR/TR heterodimers, and RXR/RAR heterodimers are indicated to the left of the panels. Comparable results were obtained in repeated studies; a representative experiment is presented. No hormone was used in these assays.
RAR/TR Heterodimers Recruit Corepressors, Whereas RXR/TR Heterodimers Do Not
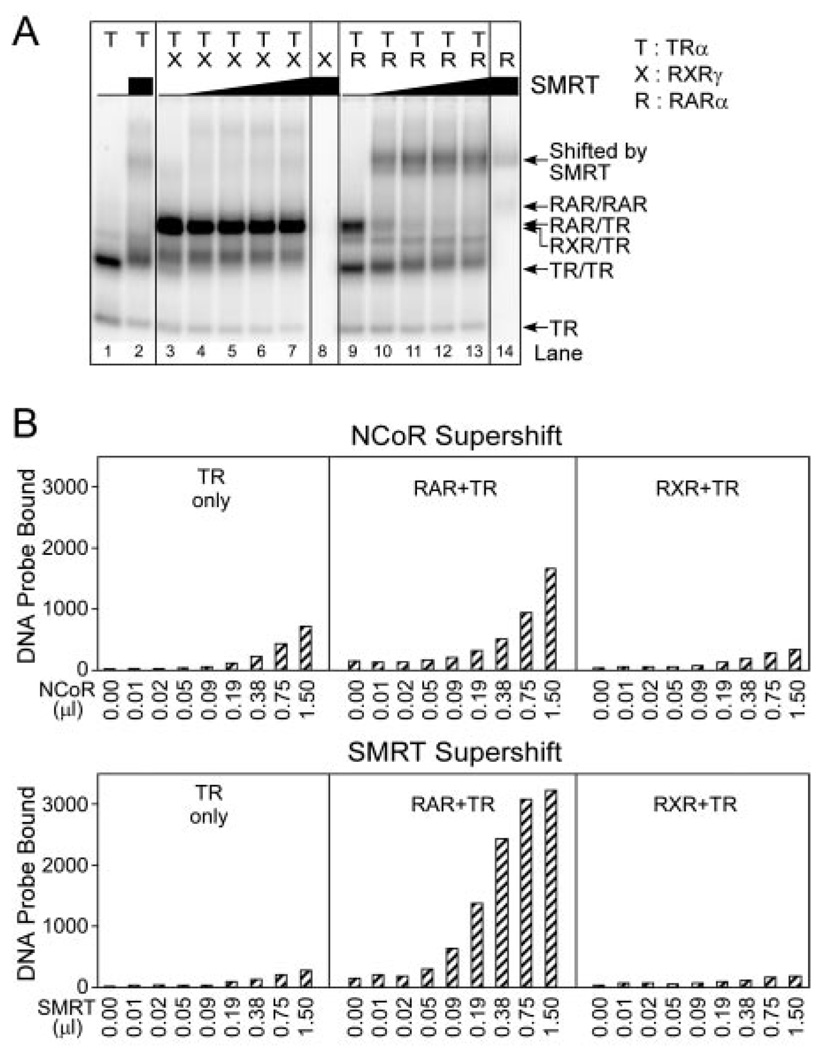
RARα and TRα can either repress or activate target gene transcription, depending on the hormone ligand, the nature of the DNA binding site, and the impact of other signal transduction pathways operative in the target cell (27). These bimodal transcriptional properties reflect the ability of these receptors to recruit auxiliary proteins, denoted corepressors and coactivators (16–25). The silencing mediator of RARs and TRs (SMRT)/nuclear hormone receptor corepressor (N-CoR) family of corepressors are typically recruited in the absence of hormone, whereas the binding of hormone agonist induces the release of corepressor and the binding of coactivators, such as SRC-1 and ACTR (26). Notably, although TRα homodimers bind N-CoR and SMRT with high avidity, RXRγ/TRα heterodimers exhibit little or no ability to recruit N-CoR or SMRT in vitro, and are inefficient at mediating transcriptional repression in vivo (53–55). We therefore compared the ability of TR homodimers, RXRγ/TRα heterodimers, and RARα/TRα heterodimers to recruit SMRT and N-CoR corepressors. RARα/TRα heterodimers were strongly supershifted by incubation with a SMRT construct in the absence of hormone, indicative of a strong receptor-corepressor interaction (Fig. 6A, lanes 9–13); this was also observed on DR-5 and DIV-6 DNA elements (data not shown). This high avidity of the RARα/TRα heterodimer for corepressor contrasted sharply with the weak corepressor binding seen for RXRγ/TRα heterodimers, and was, in fact, greater than the strong SMRT binding already noted for TR homodimers (Fig. 6A, lanes 1 and 2, lanes 3–7, and data not shown).
Fig. 6. RAR/TR Heterodimers Recruit SMRT and N-CoR Corepressors.
The ability of RARα/TRα and RXRγ/TRα heterodimers to bind to SMRT or N-CoR corepressor was determined using a radiolabeled DR-4 DNA probe and an EMSA supershift protocol. A, PhosphorImager depiction of EMSA. TRα homodimers (lanes 1 and 2), RXRγ homodimers (lane 8), RARα homodimers (lane 14), RXRγ/TRα heterodimers (lanes 3–7), or RARα/TRα heterodimers (lanes 9–13) were allowed to bind to the radiolabeled DR-4 DNA probe as in Fig. 1, but in the presence of differing concentrations of a GST-SMRT construct, as indicated above the panels. The positions of the various receptor/DNA complexes are indicated on the right; an interaction with SMRT results in a supershifted receptor/DNA complex of slower mobility (indicated). TRα, RARα, and RXRγ were used at 40, 11, and 11 ng per assay, respectively; GST-SMRT was used at 200 ng/µl. B, SMRT binds to RARα/TRα heterodimers more efficiently than does N-CoR. TRα only (left panels), RXRγ/TRα heterodimers (right panels), and RARα/TRα heterodimers (center panels) were allowed to bind to a radiolabeled DR-4 DNA probe in the presence of increasing concentrations of either GST-N-CoR (top) or GST-SMRT (bottom); both corepressor preparations were 200 ng protein/µl. The amount of supershifted complex was quantified by PhosphorImager analysis and is presented. Comparable results were obtained in repeated studies; a representative experiment is presented. No hormone was used in these assays.
SMRT has been proposed to preferentially interact with RARs, whereas its paralog, N-CoR, has been proposed to bind preferentially to TRs (e.g. Refs. 54 and 56–60). This preference of N-CoR for TRα homodimers was observed in our EMSA (Fig. 6B), whereas neither N-CoR nor SMRT interacted significantly with RXRγ/TRα heterodimers. Notably, although both SMRT and N-CoR interacted strongly with the RARα/TRα heterodimer, SMRT was recruited more efficiently than N-CoR over a range of corepressor concentrations (Fig. 6B). No protein complex was observed when either N-CoR or SMRT corepressor was incubated with DNA probe in the absence of a nuclear receptor (data not shown). We conclude that the RAR/TR heterodimer is particularly efficient in corepressor recruitment, and it displays a preference for SMRT over N-CoR.
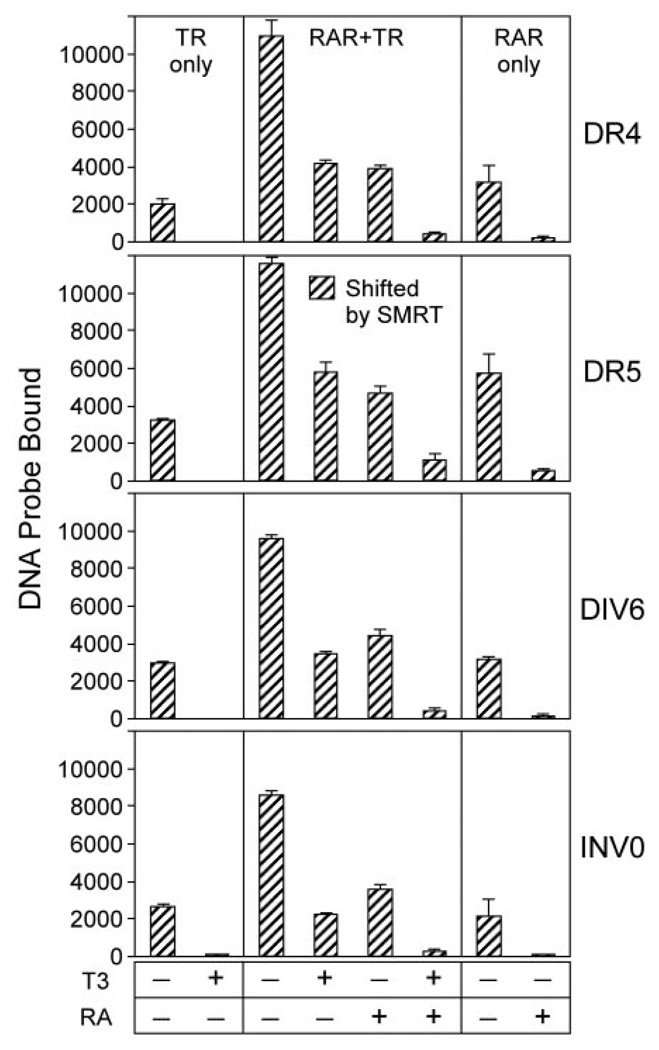
We also examined the effects of hormone ligand on the interaction of corepressor with the RAR/TR heterodimer. Addition of saturating amounts (1 µM) of T3 hormone induced a complete release of SMRT from TRα homodimers but caused only partial release of SMRT from the RARα/TRα heterodimer (Fig. 7). Similarly, although 1 µM ATRA fully released SMRT from RARα homodimers, ATRA, tested alone, induced only a partial release of SMRT from the RARα/TRα heterodimer (Fig. 7). Joint addition of both T3 and ATRA induced the quantitative release of SMRT from the RARα/TRα heterodimer (Fig. 7). This requirement for both hormone ligands for full corepressor release from the RARα/TRα heterodimer extended to all response element configurations tested here (Fig. 7). It should be noted that, as previously observed for TR homodimers (55), SMRT actually stabilizes the formation of RARα/TRα heterodimers on many of these elements (i.e. addition of SMRT enhanced the formation of RAR/TR heterodimers in the absence of hormone and counteracted the destabilizing influence of T3 hormone on heterodimer binding to the DR-5, DIV-6, and INV-0 elements; compare Fig. 2 and Fig. 7). We conclude that the RARα/TRα heterodimer requires the presence of hormone agonists for both receptor partners to obtain full release of corepressor.
Fig. 7. Both T3 and ATRA Are Required for Efficient SMRT Release from RARα/TRα Heterodimers.
TRα homodimers (left panels), RARα homodimers (right panels), and RARα/TRα heterodimers (center panels) were assembled on the indicated DNA probes in the presence of the GST-SMRT construct as in Fig. 6. T3 alone, ATRA alone, or T3 and ATRA together were added at 1 µM concentrations, and the resulting protein/DNA complexes were resolved by EMSA. The amount of receptor/DNA complex bound by SMRT (i.e. supershifted by GST-SMRT) was quantified for each condition and is presented (cross-hatched bars). TRα, RARα, and GST-SMRT were used at 40, 28, and 200 ng per assay, respectively. The mean and se of three experiments are shown.
RARα/TRα Heterodimers Recruit Either ACTR or SRC-1 Coactivator, Depending on the Hormone Agonist Provided
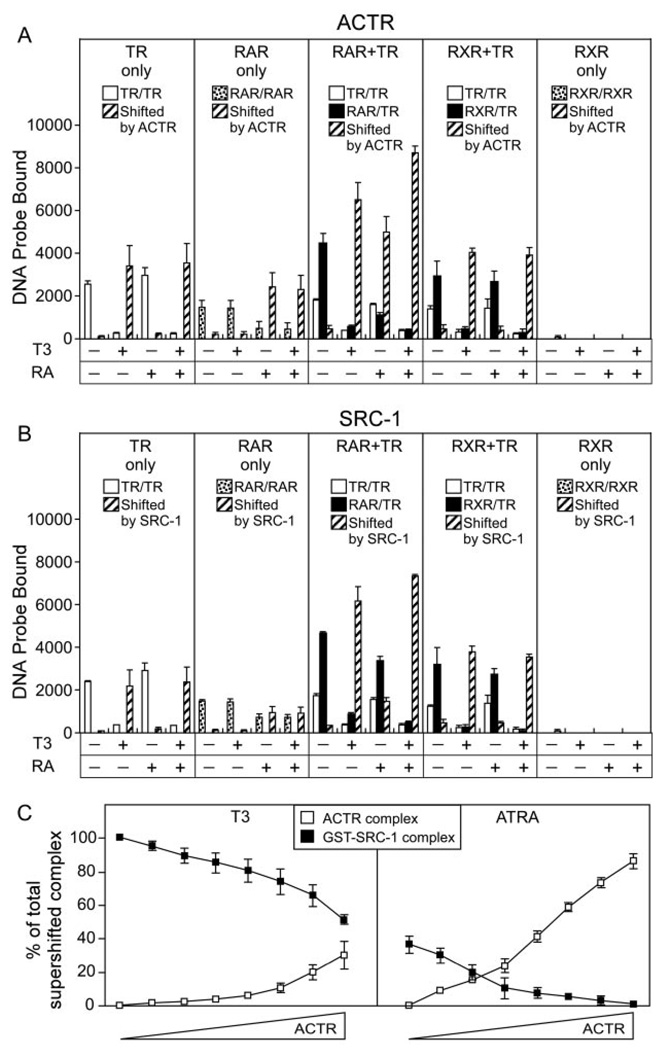
We next used the EMSA supershift protocol to determine the ability of RAR/TR heterodimers to recruit p160 coactivators, such as ACTR and SRC-1. Little or no interaction with ACTR was observed in the absence of hormone whether testing TRα homodimers, RARα homodimers, RARα/TRα heterodimers, or RXRγ/TRα heterodimers (Fig. 8A). As anticipated, addition of T3 hormone to the TR homodimers or addition of ATRA to the RAR homodimers induced strong ACTR interaction, whereas addition of T3, but not 9-cis retinoic acid, induced ACTR binding to the RXRγ/TRα heterodimers (consistent with reports that RXR is a silent partner on DR-4 elements) (Fig. 8A). Intriguingly, T3 alone, ATRA alone, or the two hormones together were sufficient to induce strong ACTR binding by the RARα/TRα heterodimers, suggesting that both receptors are active partners in this latter complex. A somewhat different phenomenon was observed with SRC-1. As expected, SRC-1 was recruited to TRα homodimers by T3, to RXRγ/TRα heterodimers by T3, and to RARα homodimers by ATRA (Fig. 8B). Unlike ACTR, however, the RARα/TRα heterodimer recruited SRC-1 primarily in response to T3, and only inefficiently in response to ATRA (Fig. 8B).
Fig. 8. Coactivators Are Recruited by RARα/TRα Heterodimers in Response to Cognate Hormones.
The ability of various TR, RAR, and RXR complexes to bind ACTR coactivator in response to different hormones was determined. A, TRα homodimers (TR only), RARα homodimers (RAR only), RXRγ homodimers (RXR only), RARα/TRα heterodimers (RAR + TR), and RXRγ/TRα heterodimers (RXR + TR) were assembled on a radiolabeled DR-4 DNA probe in the presence of a GST-ACTR coactivator construct. T3 alone, ATRA alone, 9-cis retinoic acid, or T3 + ATRA was included in the binding assay at 1 µM concentrations as indicated below the panels. The resulting protein/DNA complexes were resolved by EMSA. The amount of radiolabeled probe migrating as a TRα (open bars), RARα, or RXRγ homodimer (stippled bars); as an RAR/TR or RXR/TR heterodimer (filled bars); or as an ACTR supershifted receptor/DNA complex (crosshatched bars) was quantified under each condition and is presented. TRα, RARα, RXRγ, and GST-ACTR were used at 40 ng, 21 ng, 7 ng, and 1 µg per assay respectively. B, The same experiment as in panel A was performed employing a GST-SRC-1 coactivator construct (1 µg per assay). C, The EMSA supershift experiments in A and B were repeated using a competition strategy. RARβ/TRα heterodimers, assembled on a DR-4 DNA probe, were mixed with 2 µg of the SRC-1 construct either alone or with increasing amounts (0.0156 to 1 µg in 2-fold increments) of the ACTR construct; the experiment was performed in the presence of 1 µM T3 or ATRA, as indicated. The amount of RARβ/TRα/DNA complex supershifted into a SRC-1 or into an ACTR complex was determined for each ACTR concentration as for panels A and B. The mean and se of three experiments are shown.
To demonstrate this phenomenon more rigorously, we used a competition experiment, introducing both an ACTR and a SRC-1 construct together in the EMSA (in these experiments the glutathione S-transferase (GST)-portion of the GST-ACTR construct was cleaved off by thrombin to allow us to distinguish the two different coactivator complexes by their distinct mobilities). In the presence of T3, the RARα/TRα heterodimer formed a strong, supershifted complex with SRC-1 that required approximately equimolar levels of ACTR to compete into an ACTR-supershifted complex (Fig. 8C, left panel). In the presence of ATRA, however, the RARα/TRα heterodimer formed a much weaker complex with SRC-1 that was readily competed into an ACTR-supershifted complex at low ACTR concentrations (Fig. 8C, right panel). SRC-1 and ACTR interactions with the RARα/TRα heterodimer appeared to be mutually exclusive, with no evidence of simultaneous interaction of both coactivators observed (data not shown). These results indicate that the RAR/TR heterodimer can recruit either SRC-1 or ACTR coactivators in response to T3, but recruits ACTR in strong preference to SRC-1 in response to ATRA. RAR, like RXR, binds upstream of TR in the heterodimer, and perhaps RAR assumes a silent partner-like status in regard to SRC-1 (40, 41). Our results indicate that RARα/TRα heterodimers display unique combinatorial responses to hormone agonists distinct from those observed for homodimers or RXR heterodimers.
Heterodimer Formation with TR in Mammalian Cells Attenuates the Ability of RAR to Activate Target Genes in Response to Retinoid Hormone
We tested the ability of different receptor combinations to regulate transcription in transfected CV-1 cells. CV-1 cells do not express endogenous TRs, and express only low levels of RARs. As expected, ectopic expression of TRα in these CV-1 cells resulted in repression of the DR-4 AGGTCA luciferase reporter in the absence of T3 hormone, and activation in the presence of T3 (Fig. 9A). Although nominally a TR- response element, consensus DR-4 elements are known to also bind to and mediate transcriptional activation by RARs, although more weakly than DR-5 elements (35, 36); consistent with these results, we also observed that expression of RARα in the CV-1 cells conferred detectable DR-4 reporter gene activation in response to ATRA (note that RARα-mediated repression in the absence of hormone is more difficult to detect than that of TRα, in part due to endogenous expression of RARβ and γ) (61). Cointroduction of TRα and RARα, permitting heterodimer formation, resulted in a significant reduction in transcriptional activation of the DR-4 element in response to T3 or ATRA compared with either receptor tested alone, but maintained the ability to activate when both ligands were added together (Fig. 9A, top panel). Similarly, a DR-5 reporter was responsive to RARα plus ATRA, and (more weakly) to TRα and T3 when these receptors were introduced individually, yet was substantially attenuated when both receptors were introduced simultaneously; this attenuated response of the DR-5 element, unlike that of the DR-4, was not further reversed hen T3 and ATRA were added together compared with ATRA tested individually. A reduction of reporter expression by the cointroduction of TRα and RARα, relative to each receptor introduced individually, was also observed on a DIV-6 or a INV-0 element; suppression of the ATRA response of these latter two elements was particularly evident, although significant T3-mediated activation was retained (Fig. 9A). Reporters nonpermissive for heterodimer formation (e.g. an AGGACAnnnnAGTTCA element; Fig. 4) displayed little or no activation in response to any receptor or hormone combination (data not shown).
Fig. 9. TRα and RARα Form Heterodimers and Mediate Combinatorial Transcriptional Regulation When Coexpressed in Mammalian Cells.
Transient transfections were performed to assay reporter gene regulation and heterodimer formation by RARs and TRs. A, A reporter plasmid (100 ng) bearing the response elements indicated was introduced into CV-1 cells together with 2 ng of an empty pSG5 expression vector (no receptor), 2 ng of pSG5-TRα, 2 ng of pSG5-RARα, or 2 ng each of the combined TRα and RARα expression vectors, as indicated below the panels. A pCH110 β-galactosidase reporter (25 ng) was included in all transfections as an internal control. After transfection, the cells were transferred into fresh media supplemented with ethanol carrier alone (open bars), 500 nM T3 (cross-hatched bars), 500 nM ATRA (stippled bars), or T3 and ATRA together (filled bars). The cells were subsequently lysed and analyzed for luciferase and β-galactosidase activity. Relative luciferase activity (absolute luciferase divided by β-galactosidase activity) is presented for three transfection experiments; the average and SD values are shown. B, COS-1 cells were transfected with empty pSG5 expression vector or the pSG5 vector expressing TRα or RARα. Nuclear extracts were isolated and mixed with radiolabeled DR-4 probe, and the resulting receptor/DNA complexes were resolved by EMSA. Two concentrations of RARα were employed in the mixing experiments with TRα (lanes 3, 4, 8, 9, 13, 14, 18, and 19). Antibody (either normal IgG, anti-TR, anti-RAR, or anti-RXR, as in Fig. 1B) was included in the EMSA binding reactions, indicated above each panel, to confirm the identity of the various receptor/DNA complexes by supershift.
To confirm the ability of RARs and TRs to form heterodimers in transfected cells, we isolated nuclear extracts from our cell transfection experiments and employed these extracts in EMSA experiments. Transfecting cells with a TRα expression vector led to the formation of protein/DR-4 DNA complexes corresponding in mobility to TR monomers, homodimers, and (to a lesser extent) TR/RXR heterodimers (the last arising presumably from endogenous RXRs present in virtually all vertebrate cells) (Fig. 9B, lane 2). All three of these complexes could be supershifted by addition of antibodies to TRs and/or RXRs, but not to RARs (Fig. 9B, lanes 7, 12, and 17). Expression of RARα led to formation of complexes corresponding to RAR homodimers and to RAR/TR heterodimers (Fig. 9B, lanes 3, 4, and 5), confirmed by supershift experiments using corresponding antisera (Fig. 9B, lanes 13, 14, and 15). Analogous results were obtained with a DR-5 probe (data not shown). We conclude that RAR/TR heterodimers assemble in our mammalian cell transfection experiments, and generally display transcriptional properties distinct from those of the parental receptors introduced alone.
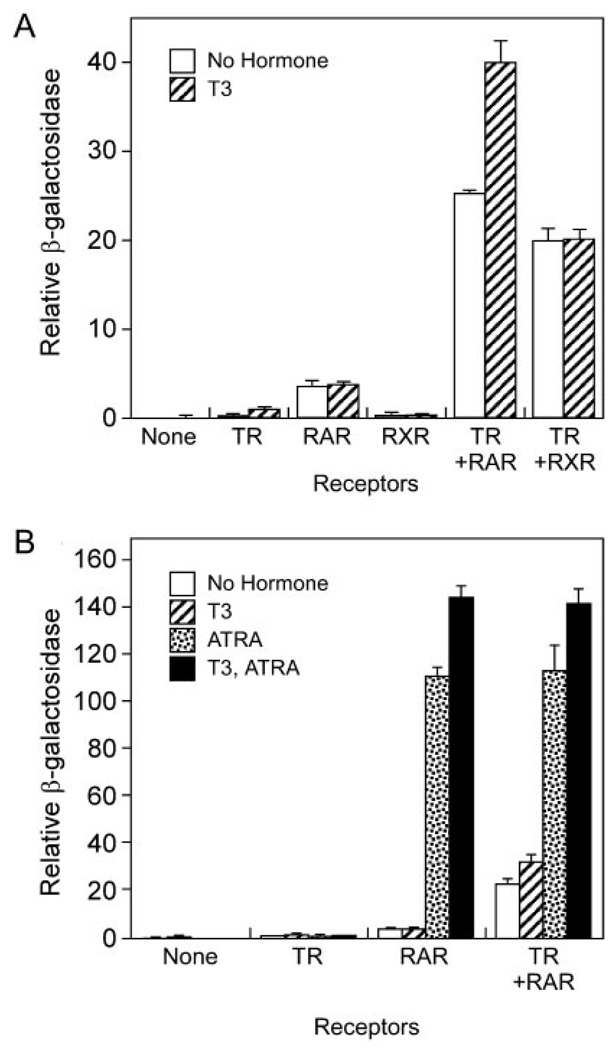
A background of RXRs, RARs, and/or other endogenous nuclear receptors exists in virtually all vertebrate cell lines, potentially complicating our CV-1 cell transfection results. We therefore also examined the transcriptional properties of RAR/TR heterodimers in Saccharomyces cerevisae, which lack endogenous nuclear receptors (62). Many mammalian nuclear receptors, when expressed in yeast, can activate appropriate reporter constructs in response to cognate hormone; yeast lack SMRT and N-CoR, however, and many nuclear receptors do not repress in yeast, but instead display constitutive activation properties in the absence of hormone (62, 63). Consistent with previous studies (62), introducing TRβ1 into S. cerevisae together with a DR-4-lac Z reporter resulted in a modest activation of β-galactosidase expression that was further elevated by addition of T3 (Fig. 10A). Introduction of RARβ alone with the same reporter resulted in a somewhat stronger, constitutive β-galactosidase expression that was unaffected by T3, whereas RXRγ alone had only a weak effect on this reporter (Fig. 10A). Notably, cointroduction of RARβ and TRβ1 together, or RXRγ and TRβ1 together, conferred much stronger reporter gene activation than did introduction of these receptors individually (Fig. 10A), consistent with the preferential heterodimer formation and DNA binding observed for these receptor combinations in vitro. Cointroduction of RARβ and TRβ1 enhanced the TRβ1 response to T3, but not the RARβ response to ATRA, relative to the same receptors assayed individually (Fig. 10B). Differences in the response of RAR/TR heterodimes to different hormones in yeast vs. mammalian cells probably reflect the different coactivator and corepressor environments in these two contexts, as well as the lack of endogenous RXRs in the former. Although yeast represent only an incomplete approximation of nuclear receptor function, our results provide additional evidence that RARs and TRs can interact functionally to produce unique combinatorial regulation in a cellular context lacking any other nuclear receptors.
Fig. 10. RAR and TR Function Combinatorially in S. cerevisae.
Expression vectors (pG1 or pHG2) for RARβ, TRβ, or RXRγ were introduced, singularly or in the combinations indicated, together with a DR-4 β-galactosidase reporter (Δss-DR4) into the W303 strain of S. cerevisae as previously described (62). The yeast were propagated 12 h in the presence of 5 µM T3, 5 µM ATRA, or equivalent amounts of ethanol carrier, as indicated, harvested, and assayed for β-galactosidase activity and for culture density. Relative β-galactosidase activity (β-galactosidase normalized to culture density) was determined for two independent transformants for each receptor combination; the mean and range are provided. A, Cointroduction of either RARβ or RXRγ enhances reporter gene activation by TRβ1 relative to TRβ1 alone. B, Cointroduction of RARβ and TRβ1 enhances the TRβ1 response to T3, but not the RARβ response to ATRA, relative to the same receptors assayed individually.
DISCUSSION
RAR/TR Heterodimers Form in Preference to Homodimers and at Efficiencies Approaching Those of RXR/TR and RXR/RAR Heterodimers
A key advance in understanding nuclear receptor function was the realization that many nuclear receptors can form heterodimers (reviewed in Refs. 12 and 38). Heterodimer formation modifies the affinity of nuclear receptors for DNA, alters their transcriptional properties, and permits combinatorial regulation of target gene in response to their individual ligands. RXRs are important heterodimer partners for a wide assortment of other nuclear receptors, including TRs, RARs, VDRs, and PPARs (12, 38). Nonetheless, there is nothing obvious to the structure, transcriptional properties, or phylogeny of RXR that excludes the possibility of other functional heterodimer partnerships. Early studies noted the ability of RAR/TRs to form heterodimers on a INV-0 (TREpal) DNA sequence and reported that these heterodimers can inhibit transcriptional repression relative to TR homodimers (47, 48). The physiological significance of these RAR/TR heterodimers was called into question, however, by subsequent studies implicating DR elements, not INV-0 elements, in target gene regulation by TRs and RARs, and by observations that RXRs form very strong heterodimers with these and many other nuclear receptors (29, 31, 34–36, 39–43, 45, 48, 49).
We reexamined this question for several reasons. TRs are strong transcriptional repressors when introduced into cells in the absence of hormone, yet RXR/TR heterodimers do not efficiently recruit corepressors (53–55). Although TR-mediated repression may, in part, be mediated by TR homodimers, these studies left open the possibility that TRs might also repress by heterodimerizing with other nuclear receptors that do support the recruitment of corepressors. Also notable is that many DR-4 and DR-5 elements are not absolutely selective for either TRs or RARs, but instead display detectable cross-recognition by these two different receptors (e.g. Refs. 33, 35, and 36; and our unpublished observations). The ability of these dual elements to recruit both TR and RAR homodimers suggested that they might also be permissive for recruitment of RAR/TR heterodimers.
We report here that RARs and TRs do form heterodimers at high efficiency on suitable response elements in vitro. These heterodimers can be detected using either purified preparations of TR and RAR, or unfractionated cell extracts, and both TR and all three RAR isotypes tested are competent for heterodimer formation, although at different efficiencies. On model DR-4 and DR-5 elements, RAR/TR heterodimers assemble with similar efficiency as do the corresponding RXR heterodimers, and in clear preference to homodimers. A weaker formation of RAR/TR heterodimers occurs on a DIV-6 element, whereas the INV-0 type of element is least permissive for heterodimer formation. Previous studies of RAR/TR heterodimerization using INV-0 elements may therefore have understated the heterodimerization potential of these receptors (47). It was reported that the RAR/TR heterodimer can be disrupted by addition of T3, questioning the role of these heterodimers in hormonemediated gene regulation (48). Although we observe that binding of RAR/TR heterodimers to the DIV-6 and INV-0 elements is disrupted by T3, the RAR/TR heterodimer on a DR-4 element is fully stable to T3, and the RAR/TR heterodimer on a DR-5 element is only partially destabilized by T3. Addition of SMRT further stabilizes formation of RAR/TR dimers on all elements examined and minimizes the disruptive effects of T3. ATRA had no effect on the heterodimer on any element tested. Our results indicate that hormone is not necessarily disruptive of RAR/TR heterodimer formation.
RAR/TR Heterodimer Assembly Is DNA Sequence Dependent and Anisotropic
Although both RARs and TRs can bind to AGGTCA half-sites, the ability of these receptors to recognize variants of these consensus half-sites differs (33, 35, 36, 50–52). By creating response elements containing suitable combinations of RAR-selective or TR-selective half-sites, DNA elements could be recruited that preferentially bound RAR/TR heterodimers. Analysis of these elements indicates that RAR/TR heterodimers form in a polar fashion, with the RAR moiety binding preferentially to the upstream half-site. This observation provides an intriguing parallel to RXR/TR heterodimers, which also assemble with a TR downstream orientation (30, 34). Structural studies have identified specific proteinprotein contacts on RXR and TR that define the optimal DR-4 spacing for these heterodimers and that help contribute to their polarity on these DR elements (e.g. Ref. 44). Analogous protein-protein contacts may define the spacing and polarity of the RAR/TR heterodimers characterized here. Notably, RARs bind upstream of RXRs on DR-2 elements, providing a precedent for an RA R-upstream orientation (30, 40, 41). It should also be noted that a variety of dimerization interfaces have been identified for different nuclear receptors on different repeat elements; as a result, the RAR/TR dimerization interface may resemble, but need not be identical to, the RXR/TR interface (13, 64).
RAR/TR Heterodimers Exhibit Distinct Corepressor and Coactivator Interactions Relative to Homodimers and to RXR Heterodimers
Nuclear receptors mediate gene regulation by recruiting auxiliary corepressors and coactivators. TRα recruits corepressor as a receptor homodimer, but not as a RXR/TR heterodimer, and selectively interacts with N-CoR relative to SMRT (53–55, 60). In contrast, RARα homodimers (and RXR/RAR heterodimers) both recruit corepressor and display a preference for SMRT over N-CoR (55, 60). We report here that RAR/TR heterodimers recruit corepressor with high efficiency and display a preference for SMRT over N-CoR. RAR/TR heterodimers also display a novel combinatorial response to hormone; addition of ligand for either receptor, T3 or ATRA, results in a partial release of SMRT, whereas both ligands must be added to obtain quantitative corepressor release. Therefore, TRs can form at least three distinct complexes, each with distinct regulatory properties: RXR/TR heterodimers that do not bind corepressor, TR homodimers that bind corepressor yet release it in response to T3, and RAR/TR heterodimers that bind corepressor yet require both T3 and ATRA for complete corepressor dissociation.
Reciprocally, the p160 family of proteins, such as SRC-1, glucocorticoid receptor-interacting protein, and ACTR, serve as important coactivators for a wide range of nuclear receptors and are recruited in response to agonist (16, 18, 20, 25–27, 65). Intriguingly, T3 was both necessary and sufficient to recruit the SRC-1 coactivator to the RAR/TR heterodimer, whereas ATRA neither induced SRC-1 recruitment when tested alone nor further enhanced coactivator binding over T3 alone. In this context, RAR appeared to serve as a silent partner in a superficially similar fashion to that seen for RXR in RXR/TR heterodimers. The silent partner status of RXR has been linked to its upstream location on DR-4 repeats, consistent with the polarity of the RAR/TR heterodimer in our experiments (40, 41, 66). However, the silent partner status of RXR depends on cell and promoter context, and we observed that a second p160 coactivator, ACTR, is recruited to the RAR/TR heterodimer by either T3 or ATRA.
Consistent with the inefficient release of corepressor in vitro in response to ATRA or T3 alone, coexpression of RAR and TR in CV-1 cells results in only modest reporter gene expression in response to a single hormone ligand. In contrast, addition of both ATRA and T3 together fully releases corepressor in vitro and more strongly induces reporter gene expression in cells when driven by a DR-4 element. The combined effect of T3 and ATRA was less obvious on reporters containing a DR-5 or DIV-6. Presumably, the specific mixture and concentration of different coactivators and corepressors in a given cell and the ability of T3 and ATRA to induce exchange of these corepressors and coactivators on different response elements all contribute to the transcriptional response of the RAR/TR heterodimer. Additional studies will be necessary to better define the combinatorial functions of the RAR/TR heterodimer in these different contexts and to compare these to RXR/TR and RXR/RAR heterodimers.
Possible Extension of the Heterodimer Paradigm to Other Members of the Nuclear Receptor Family
Do other members of the nuclear receptor family also assemble into physiologically relevant heterodimers on appropriate DNA sequences? Heterodimers have been reported between PPARs and TRs, between VDRs and TRs, and between PPARs and liver X receptors (67–69), although not all of these studies have been confirmed and the overall significance of some of these findings remains to be more fully established (e.g. Refs. 70 and 71). An ability of nuclear receptors to form a multiplicity of heterodimers is very attractive conceptually. Heterodimer formation provides a means of coupling different hormone pathways to one another. Heterodimer formation is also a well-established means by which the DNA binding and transcriptional properties of a fixed cast of transcription factors can be geometrically expanded through combinatorial interactions among the individual proteins. It is tempting to speculate that additional heterodimer pairs, in addition to the classical RXR partnerships, will be identified and characterized in the future.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Molecular Clones
The mammalian expression vectors containing avian RXRγ, avian TRα, human TRβ1, and human RARα, β, or γ were described previously (50, 55, 72). For expression of GST fusion proteins, PCR-generated fragments encoding the S1 and S2 domains of SMRTα (representing codons 2077–2517), the N2 and N3 domains of N-CoR (representing codons 1681–2218), or SRC-1 (representing codons 568–891) were cloned into pGEX-KG. The pGEX-KG-ACTR clone represented ACTR codons 621–821. The M-pTK-Luc-F2 DIV-6 reporter was constructed by excising the DR-4 element in the M-pTK-Luc vector (61) with XhoI and SalI and replacing it with the F2 DIV-6 lysozyme element (composed of two annealed oligonucleotides, 5′-TCGAA TTATT GACCC CAGCT GACCT CAAGT TACG-3′ and 5′-TCGAC GTAAC TTGAC CTCAG CTGGG GTCAA TAAT-3′). Reporter clones containing two F2-DIV-6 elements were selected. The pTK-Luc-DR4 (2×), pTK-Luc-DR5 (2×), and pTKLuc- INV0 (2×) reporters were described previously (55, 73, 74).
Oligonucleotides and DNA Probes
Oligonucleotides were obtained as complementary, singlestranded DNAs (MWG Biotech, High Point, NC) and were annealed to create double-stranded DNAs with four-base overhangs. For use as probes in EMSA, the overhangs were filled in with 32P-radiolabeled nucleotides and the Klenow fragment of DNA polymerase I. The oligonucleotides used in the EMSAs were as follows: DR-4, 5′-TCGAAT AAGGT CAAAT AAGGT CAGAG-3′; DR-5, 5′-TCGAC AGAGG TCAAC GAGAG GTCAG AG-3′; DIV-6, 5′-TCGAT ACGAT CGTGA CCTAT TAGGA GGTCA ACAGA CGGG-3′; INV-0, 5′-TCGAG ATCTC AGGTC ATGAC CTGA-3′; AGTTCA-(n4)AGTTCA, 5′-TCGAC AGAGT TCAAG AGACT TCAGA G-3′; AGGACA(n4)AGGACA, 5′-TCGAC TAAGGA CAAAT AAGGA CAGAG-3′; AGTTCA(n4)AGGACA, 5′-TCGAC AGAGT TCAAA TAAGG ACAGA G-3′; AGGACA(n4)AGTTCA, 5′-TCGAC TAAGG ACAAG AGACT TCAGA G-3′; rMHC, 5′-AGCTC TCTGG AGGTG ACAGG AGGAC AGCAG CCCTG A-3′ (75); MyoD, 5′-AGCTC TGAGG TCAGT ACAGG CTGGA GGAGT AGA-3′ (76); α-actin, 5′-AGCTG GGCAA CTGGG TCGGG TCAGGA GGG-3′ (77); rGH, 5′-TCGAG GAAAG GTAAG ATCAG GGACG TGACC GCAGG AG A-3′; F2 DIV-6, 5′-TCGAA TTATT GACCC CAGCT GACCT CAAGT TACG-3′ (78); and β-RARE, 5′-AGCTG GGTAG GGTTC ACCGA AAGTT CACTC G-3′ (79).
EMSAs
Nuclear receptor proteins were expressed in a recombinant baculovirus/Sf-9 cell system and were isolated as nuclear extracts (72). GST-corepressor and GST-coactivator proteins for the supershift assays were produced in E. coli strain BL21 transfected with the corresponding pGEX-KG vectors (pGEXKG-SMRT, pGEX-KG-N-CoR, pGEX-KG-ACTR, or pGEXKG-SRC-1) and were purified by binding to and elution from glutathione-agarose matrix (Sigma-Aldrich, Inc., St. Louis, MO) (80, 81). EMSAs were performed by mixing 4 µl of appropriately diluted nuclear receptor preparation, 32P-radiolabeled oligonucleotide probe (20–30 ng of DNA, ~ 300,000 cpm) and 10 µl of binding buffer [15 mM Tris (pH 7.6), 4.5% glycerol, 20 µg/µl BSA, 200 mM KCl, 3 mM MgCl2, 200 µg/ml polydeoxyinosinic deoxycytidylic acid, 2 mM dithiothreitol] in a 20-µl total volume. The reaction mixture was incubated at 25 C for 25 min, and the resulting protein/DNA complexes were resolved by nondenaturing gel electrophoresis through 6% polyacrylamide gel (37.5:1 acrylamide/bisacrylamide) in 0.5 × Tris-borate EDTA. Radiolabeled DNA and DNA/protein complexes were visualized by PhosphorImager analysis (STORM system; Molecular Dynamics, Inc., Sunnyvale, CA) and quantified using ImageQuant software (Molecular Dynamics). For supershift experiments using corepressors and coactivators, the nuclear receptor preparations were incubated with the appropriate GST fusion protein for 5 min on ice. Hormones, if indicated, were added to 1 µM after incubation with corepressor or coactivator. For antibody supershifts, the protein/DNA complexes were allowed to form at 25 C for 20 min, and 1 µl of a suitable antiserum was then added. The incubation was continued for an additional 15 min at 25 C before gel electrophoresis. RXR-directed antiserum (a gift from Pierre Chambon, Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale, Strasborg, France), normal rabbit IgG, RARα-directed antiserum (C-20; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., Santa Cruz, CA), and rabbit polyclonal TRα-directed antiserum (55) were used.
EMSAs were also performed using nuclear extracts from COS-1 cells transiently transfected with the appropriate nuclear receptor expression vectors. COS-1 cells were maintained in DMEM (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (HyClone, Logan, UT) in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2 at 37 C. For transfections, cells were plated in 100-mm culture dishes and were processed using the Effectene protocol as recommended by the manufacturer (QIAGEN, Valencia, CA) using a total of 5 µg of pSG5-receptor expression vector plus pUC18. Cells were harvested 48 h after transfection by mechanical scrapping and were washed in cold PBS. The cells were swelled in hypotonic buffer [10 mM HEPES (pH 7.9), 10 mM KCl, 1 mM EDTA, 0.05% Nonidet P-40, 0.5 mM dithiothreitol, protease inhibitor cocktail] and were lysed using a Dounce homogenizer (15–20 stroke with a tight pestle). The nuclei were collected by centrifugation, resuspended in high-salt buffer [20 mM HEPES (pH 7.9), 420 mM KCl, 1 mM EDTA, 25% glycerol, 0.5 mM dithiothreitol, protease inhibitor cock-tail], and incubated on ice for 30 min. The nuclear extracts were clarified by centrifugation and were employed in EMSAs after suitable dilution in dilution buffer [20 mM HEPES (pH 7.9), 300 mM KCl, 1 mM EDTA, 0.5 mM dithiothreitol, 25% glycerol].
Reporter Gene Assays
CV-1 cells were maintained as described for COS cells. For transfections, 3.0 × 104 CV-1 cells were plated per well in 24-well plates and were incubated for 24 h at 37 C. The cells were then washed with PBS and placed in DMEM supplemented with 10% hormone-depleted fetal bovine serum. Transfections were initiated employing the Effectene protocol described above, but using 2 ng of the appropriate empty pSG-5, pSG5-TRα, and/or pSG5-hRARα vector; 100 ng of each reporter plasmid; 25 ng of pCH110 as a β-galactosidase internal transfection control; and a sufficient amount of pUC18 to adjust the total DNA concentration to 250 ng (55, 82). After a 24-h incubation, the transfection medium was replaced with fresh, hormone-stripped medium; ethanol carrier alone, ATRA, and/or T3 were added to 500 nM, and the cells were incubated for an additional 24 h. The cells were then washed with PBS, harvested, and lysed in 100 µl of Triton lysis buffer (0.2% Triton X-100, 91 mM K2HPO4, and 9.2 mM KH2PO4). Luciferase and β-galactosidase activity was measured as previously reported (55, 82).
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Liming Liu for superb technical assistance.
This work was supported by Public Health Service/National Institutes of Health Award R37 CA53394.
Abbreviations
- ACTR
Activation of TRs and RARs
- ATRA
and all-trans retinoic acid
- DIV
divergent repeat
- DR
direct repeat
- GST
glutathione S-transferase
- HRE
hormone response element
- INV
inverted repeat
- MyoD
myosin D
- N-CoR
nuclear hormone receptor corepressor
- PPAR
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
- RAR
retinoic acid receptor
- rGH
rat GH
- rMHC
rat myosin heavy chain
- RXR
retinoid X receptor
- SMRT
silencing mediator of RARs and TRs
- SRC-1
steroid receptor coactivator-1
- TR
thyroid hormone receptor
- VDR
vitamin D3 receptor
Footnotes
Molecular Endocrinology is published monthly by The Endocrine Society (http://www.endo-society.org), the foremost professional society serving the endocrine community.
References
- 1.Apriletti JW, Ribeiro RC, Wagner RL, Feng W, Webb P, Kushner PJ, West BL, Nilsson S, Scanlan TS, Fletterick RJ, Baxter JD. Molecular and structural biology of thyroid hormone receptors. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol Suppl. 1998;25:S2–S11. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1998.tb02293.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Beato M, Klug J. Steroid hormone receptors: an update. Human Reprod Update. 2000;6:225–236. doi: 10.1093/humupd/6.3.225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Chambon P. A decade of molecular biology of retinoic acid receptors. FASEB J. 1996;10:940–954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Mangelsdorf DJ, Thummel C, Beato M, Herrlich P, Schutz G, Umesono K, Blumberg B, Kastner P, Mark M, Chambon P, Evans RM. The nuclear receptor superfamily: the second decade. Cell. 1995;83:835–839. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90199-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Zhang J, Lazar MA. The mechanism of action of thyroid hormones. Annu Rev Physiol. 2000;62:439–466. doi: 10.1146/annurev.physiol.62.1.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hihi AK, Michalik L, Wahli W. PPARs: transcriptional effectors of fatty acids and their derivatives. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2002;59:790–798. doi: 10.1007/s00018-002-8467-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kliewer SA, Lehmann JM, Milburn MV, Willson TM. The PPARs and PXRs: nuclear xenobiotic receptors that define novel hormone signaling pathways. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1999;54:345–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Waxman DJ. P450 gene induction by structurally diverse xenochemicals: central role of nuclear receptors CAR, PXR, and PPAR. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1999;369:11–23. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1999.1351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Laudet V. Evolution of the nuclear receptor superfamily: early diversification from an ancestral orphan receptor. J Mol Endocrinol. 1997;19:207–226. doi: 10.1677/jme.0.0190207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Pereira FA, Tsai MJ, Tsai SY. COUP-TF orphan nuclear receptors in development and differentiation. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2000;57:1388–1398. doi: 10.1007/PL00000624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Whitfield GK, Jurutka PW, Haussler CA, Haussler MR. Steroid hormone receptors: evolution, ligands, and molecular basis of biologic function. J Cell Biochem Suppl. 1999;32 – 33:110–122. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-4644(1999)75:32+<110::aid-jcb14>3.0.co;2-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Glass CK. Some new twists in the regulation of gene expression by thyroid hormone and retinoic acid receptors. J Endocrinol. 1996;150:349–357. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1500349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Khorasanizadeh S, Rastinejad F. Nuclear-receptor interactions on DNA-response elements. Trends Biochem Sci. 2001;26:384–390. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(01)01800-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kumar R, Thompson EB. The structure of the nuclear hormone receptors. Steroids. 1999;64:310–319. doi: 10.1016/s0039-128x(99)00014-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ribeiro RC, Apriletti JW, Wagner RL, West BL, Feng W, Huber R, Kushner PJ, Nilsson S, Scalan T, Fletterick RJ, Schaufele F, Baxter JD. Mechanisms of thyroid hormone action: insights from x-ray crystallographic and functional studies. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1998;53:351–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Chen JD, Li H. Coactivation and corepression in transcriptional regulation by steroid/nuclear hormone receptors. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 1998;8:169–190. doi: 10.1615/critreveukargeneexpr.v8.i2.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ito M, Roeder RG. The TRAP/SMCC/mediator complex and thyroid hormone receptor function. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2001;12:127–134. doi: 10.1016/s1043-2760(00)00355-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Jenster G. Coactivators and corepressors as mediators of nuclear receptor function: an update. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1998;143:1–7. doi: 10.1016/s0303-7207(98)00145-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Koenig RJ. Thyroid hormone receptor coactivators and corepressors. Thyroid. 1998;8:703–713. doi: 10.1089/thy.1998.8.703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lee JW, Lee YC, Na SY, Jung DJ, Lee SK. Transcriptional coregulators of the nuclear receptor superfamily: coactivators and corepressors. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2001;58:289–297. doi: 10.1007/PL00000856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.McKenna NJ, O’Malley BW. Minireview: nuclear receptor coactivators–an update. Endocrinology. 2002;143:2461–2465. doi: 10.1210/endo.143.7.8892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ordentlich P, Downes M, Evans RM. Corepressors and nuclear hormone receptor function. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2001;254:101–116. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-10595-5_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Privalsky ML. The role of corepressors in transcriptional regulation by nuclear hormone receptors. Ann Review Physiol. 2004;66:315–360. doi: 10.1146/annurev.physiol.66.032802.155556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Rachez C, Freedman LP. Mediator complexes and transcription. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001;13:274–280. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(00)00209-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Xu L, Glass CK, Rosenfeld MG. Coactivator and corepressor complexes in nuclear receptor function. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1999;9:140–147. doi: 10.1016/S0959-437X(99)80021-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Glass CK, Rosenfeld MG. The coregulator exchange in transcriptional functions of nuclear receptors. Genes Dev. 2000;14:121–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Privalsky ML. Regulation of SMRT and N-CoR corepressor function. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2001;254:117–136. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-10595-5_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Forman BM, Evans RM. Nuclear hormone receptors activate direct, inverted, and everted repeats. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1995;761:29–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1995.tb31366.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kliewer SA, Umesono K, Mangelsdorf DJ, Evans RM. Retinoid X receptor interacts with nuclear receptors in retinoic acid, thyroid hormone and vitamin D3 signalling. Nature. 1992;355:446–449. doi: 10.1038/355446a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kurokawa R, Yu VC, Näär A, Kyakumato S, Han Z, Silverman S, Rosenfeld MG, Glass CK. Differential orientations of the DNA-binding domain and carboxyterminal dimerization interface regulate binding site selection by nuclear receptor heterodimers. Genes Dev. 1993;7:1423–1435. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7b.1423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lazar MA, Berrodin TJ, Harding HP. Differential DNA binding by monomeric, homodimeric, and potentially heteromeric forms of the thyroid hormone receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1991;11:5005–5015. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Moore DD, Brent GA. Thyroid hormone—half-sites and insights. New Biologist. 1991;3:835–844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Näär AM, Boutin JM, Lipkin SM, Yu VC, Holloway JM, Glass CK, Rosenfeld MG. The orientation and spacing of core DNA-binding motifs dictate selective transcriptional responses to three nuclear receptors. Cell. 1991;65:1267–1279. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90021-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Perlmann T, Rangarajan PN, Umesono K, Evans RM. Determinants for selective RAR and TR recognition of direct repeat HREs. Genes Dev. 1993;7:1411–1422. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7b.1411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Umesono K, Murakami KK, Thompson CC, Evans RM. Direct repeats as selective response elements for the thyroid hormone, retinoic acid, and vitamin D3 receptors. Cell. 1991;65:1255–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90020-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Forman BM, Casanova J, Raaka BM, Ghysdael J, Samuels HH. Half-site spacing and orientation determines whether thyroid hormone and retinoic acid receptors and related factors bind to DNA response elements as monomers, homodimers, or heterodimers. Mol Endocrinol. 1992;6:429–442. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.3.1316541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Lazar MA. Thyroid hormone receptors: multiple forms, multiple possibilities. Endocr Rev. 1993;14:184–193. doi: 10.1210/edrv-14-2-184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Mangelsdorf DJ, Evans RM. The RXR heterodimers and orphan receptors. Cell. 1995;83:841–850. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90200-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Bourguet W, Vivat V, Wurtz JM, Chambon P, Gronemeyer H, Moras D. Crystal structure of a heterodimeric complex of RAR and RXR ligand-binding domains. Mol Cell. 2000;5:289–298. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80424-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Kurokawa R, DiRenzo J, Boehm M, Sugarman J, Gloss B, Rosenfeld MG, Heyman RA, Glass CK. Regulation of retinoid signalling by receptor polarity and allosteric control of ligand binding. Nature. 1994;371:528–531. doi: 10.1038/371528a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Kurokawa R, Söderström M, Hörlein A, Halachmi S, Brown M, Rossenfeld MG, Glass CK. Polarity-specific activities of retinoic acid receptors determined by a co-repressor. Nature. 1995;377:451–454. doi: 10.1038/377451a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Hallenbeck PL, Marks MS, Lippoldt RE, Ozato K, Nikodem VM. Heterodimerization of thyroid hormone (TH) receptor with H-2RIIBP (RXR β) enhances DNA binding and TH-dependent transcriptional activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1992;89:5572–5576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Leid M, Kastner P, Lyons R, Nakshatri H, Saunders M, Zacharewski T, Chen JY, Staub A, Garnier JM, Mader S, Chambon P. Purification, cloning, and RXR identity of the HeLa cell factor with which RAR or TR heterodimerizes to bind target sequences efficiently. Cell. 1992;68:377–395. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90478-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Rastinejad F. Retinoid X receptor and its partners in the nuclear receptor family. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2001;11:33–38. doi: 10.1016/s0959-440x(00)00165-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Zhang XK, Hoffmann B, Tran PB, Graupner G, Pfahl M. Retinoid X receptor is an auxiliary protein for thyroid hormone and retinoic acid receptors. Nature. 1992;355:441–446. doi: 10.1038/355441a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Schulman IG, Li C, Schwabe JW, Evans RM. The phantom ligand effect: allosteric control of transcription by the retinoid X receptor. Genes Dev. 1997;11:299–308. doi: 10.1101/gad.11.3.299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Glass CK, Lipkin SM, Devary OV, Rosenfeld MG. Positive and negative regulation of gene transcription by a retinoic acid-thyroid hormone receptor heterodimer. Cell. 1989;59:697–708. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Yen PM, Sugawara A, Chin WW. Triiodothyronine (T3) differentially affects T3-receptor/retinoic acid receptor and T3-receptor/retinoid X receptor heterodimer binding to DNA. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:23248–23252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Yen PM, Darling DS, Carter RL, Forgione M, Umeda PK, Chin WW. Triiodothyronine (T3) decreases binding to DNA by T3-receptor homodimers but not receptorauxiliary protein heterodimers. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:3565–3568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Hauksdottir H, Privalsky ML. DNA recognition by the aberrant retinoic acid receptors implicated in human acute promyelocytic leukemia. Cell Growth Differ. 2001;12:85–98. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Judelson C, Privalsky ML. DNA recognition by normal and oncogenic thyroid hormone receptors—unexpected diversity in half-site specificity controlled by nonzinc-finger determinants. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:10800–10805. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.18.10800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Katz RW, Koenig RJ. Nonbiased identification of DNA sequences that bind thyroid hormone receptor α1 with high affinity. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:19392–19397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Cohen RN, Wondisford FE, Hollenberg AN. Two separate NCoR (nuclear receptor corepressor) interaction domains mediate corepressor action on thyroid hormone response elements. Mol Endocrinol. 1998;12:1567–1581. doi: 10.1210/mend.12.10.0188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Cohen RN, Putney A, Wondisford FE, Hollenberg AN. The nuclear corepressors recognize distinct nuclear receptor complexes. Mol Endocrinol. 2000;14:900–914. doi: 10.1210/mend.14.6.0474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Yoh SM, Privalsky ML. Transcriptional repression by thyroid hormone receptors. A role for receptor homodimers in the recruitment of SMRT corepressor. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:16857–16867. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M010022200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Chen JD, Evans RM. A transcriptional co-repressor that interacts with nuclear hormone receptors. Nature. 1995;377:454–457. doi: 10.1038/377454a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Hörlein AJ, Näär AM, Heinzel T, Torchia J, Gloss B, Kurokawa R, Ryan A, Kamei Y, Soderstrom M, Glass CK, Rosenfeld MG. Ligand-independent repression by the thyroid hormone receptor mediated by a nuclear receptor co-repressor. Nature. 1995;377:397–404. doi: 10.1038/377397a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Sande S, Privalsky ML. Identification of TRACs (T3 receptor-associating cofactors), a family of cofactors that associate with, and modulate the activity of, nuclear hormone receptors. Mol Endocrinol. 1996;10:813–825. doi: 10.1210/mend.10.7.8813722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Webb P, Anderson CM, Valentine C, Nguyen P, Marimuthu A, West BL, Baxter JD, Kushner PJ. The nuclear receptor corepressor (N-CoR) contains three isoleucine motifs (I/LXXII) that serve as receptor interaction domains (IDs) Mol Endocrinol. 2000;14:1976–1985. doi: 10.1210/mend.14.12.0566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Zamir I, Zhang J, Lazar MA. Stoichiometric and steric principles governing repression by nuclear hormone receptors. Genes Dev. 1997;11:835–846. doi: 10.1101/gad.11.7.835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Hauksdottir H, Farboud B, Privalsky ML. Retinoic acid receptors β and γ do not repress, but instead activate target gene transcription in both the absence and presence of hormone ligand. Mol Endocrinol. 2003;17:373–385. doi: 10.1210/me.2002-0340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Hall BL, Smit-McBride Z, Privalsky ML. Reconstitution of retinoid-X receptor function and combinatorial regulation of other nuclear hormone receptors in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1993;90:6929–6933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.6929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Privalsky ML, Sharif M, Yamamoto KR. The viral ErbA oncogene protein, a constitutive repressor in animal cells, is a hormone-regulated activator in yeast. Cell. 1990;63:1277–1286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90423-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Khorasanizadeh S, Rastinejad F. Transcription factors: the right combination for the DNA lock. Curr Biol. 1999;9:R456–R458. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(99)80281-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.McKenna NJ, Xu J, Nawaz Z, Tsai SY, Tsai MJ, O’Malley BW. Nuclear receptor coactivators: multiple enzymes, multiple complexes, multiple functions. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1999;69:3–12. doi: 10.1016/s0960-0760(98)00144-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Germain P, Iyer J, Zechel C, Gronemeyer H. Coregulator recruitment and the mechanism of retinoic acid receptor synergy. Nature. 2002;415:187–192. doi: 10.1038/415187a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Bogazzi F, Hudson LD, Nikodem VM. A novel heterodimerization partner for thyroid hormone receptor. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:11683–11686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Gbaguidi GF, Agellon LB. The atypical interaction of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α with liver X receptor α antagonizes the stimulatory effect of their respective ligands on the murine cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase gene promoter. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002;1583:229–236. doi: 10.1016/s1388-1981(02)00217-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Schrader M, Muller KM, Nayeri S, Kahlen JP, Carlberg C. Vitamin D-3 thyroid hormone receptor heterodimer polarity directs ligand sensitivity of transactivation. Nature. 1994;370:382–386. doi: 10.1038/370382a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Raval-Pandya M, Freedman LP, Li H, Christakos S. Thyroid hormone receptor does not heterodimerize with the vitamin D receptor but represses vitamin D receptor-mediated transactivation. Mol Endocrinol. 1998;12:1367–1379. doi: 10.1210/mend.12.9.0165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Thompson PD, Hsieh JC, Whitfield GK, Haussler CA, Jurutka PW, Galligan MA, Tillman JB, Spindler SR, Haussler MR. Vitamin D receptor displays DNA binding and transactivation as a heterodimer with the retinoid X receptor, but not with the thyroid hormone receptor. J Cell Biochem. 1999;75:462–480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Chen HW, Privalsky ML. The erbA oncogene represses the actions of both retinoid X and retinoid A receptors but does so by distinct mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol. 1993;13:5970–5980. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.10.5970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Hong SH, Privalsky ML. The SMRT corepressor is regulated by a MEK-1 kinase pathway: inhibition of corepressor function is associated with SMRT phosphorylation and nuclear export. Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20:6612–6625. doi: 10.1128/mcb.20.17.6612-6625.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Yoh SM, Privalsky ML. Resistance to thyroid hormone (RTH) syndrome reveals novel determinants regulating interaction of T3 receptor with corepressor. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2000;159:109–124. doi: 10.1016/s0303-7207(99)00201-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Brent GA, Williams GR, Harney JW, Forman BM, Samuels HH, Moore DD, Larsen PR. Capacity for cooperative binding of thyroid hormone (T3) receptor dimmers defines wild type-T3 response elements. Mol Endocrinol. 1992;6:502–514. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.4.1584220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Muscat GE, Mynett-Johnson L, Dowhan D, Downes M, Griggs R. Activation of myoD gene transcription by 3,5,3′-triiodo-l-thyronine: a direct role for the thyroid hormone and retinoid X receptors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994;22:583–591. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.4.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Muscat GE, Griggs R, Downes M, Emery J. Characterization of the thyroid hormone response element in the skeletal α-actin gene: negative regulation of T3 receptor binding by the retinoid X receptor. Cell Growth Differ. 1993;4:269–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Baniahmad A, Kohne AC, Renkawitz R. A transferable silencing domain is present in the thyroid hormone receptor, in the v-erbA oncogene product and in the retinoic acid receptor. EMBO J. 1992;11:1015–1023. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05140.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.de Thé H, Vivanco-Ruiz MM, Tiollais P, Stunnenberg H, Dejean A. Identification of a retinoic acid responsive element in the retinoic acid receptor β gene. Nature. 1990;343:177–180. doi: 10.1038/343177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Guan KL, Dixon JE. Eukaryotic proteins expressed in Escherichia coli: an improved thrombin cleavage and purification procedure of fusion proteins with glutathione S-transferase. Anal Biochem. 1991;192:262–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(91)90534-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Hong SH, Wong CW, Privalsky ML. Signaling by tyrosine kinases negatively regulates the interaction between transcription factors and SMRT (silencing mediator of retinoic acid and thyroid hormone receptor) corepressor. Mol Endocrinol. 1998;12:1161–1171. doi: 10.1210/mend.12.8.0160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Yoh SM, Chatterjee VK, Privalsky ML. Thyroid hormone resistance syndrome manifests as an aberrant interaction between mutant T3 receptors and transcriptional corepressors. Mol Endocrinol. 1997;11:470–480. doi: 10.1210/mend.11.4.9914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]