Abstract
Extracellular calmodulin (ExtCaM) regulates stomatal movement by eliciting a cascade of intracellular signaling events including heterotrimeric G protein, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and Ca2+. However, the ExtCaM-mediated guard cell signaling pathway remains poorly understood. In this report, we show that Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) NITRIC OXIDE ASSOCIATED1 (AtNOA1)-dependent nitric oxide (NO) accumulation plays a crucial role in ExtCaM-induced stomatal closure. ExtCaM triggered a significant increase in NO levels associated with stomatal closure in the wild type, but both effects were abolished in the Atnoa1 mutant. Furthermore, we found that ExtCaM-mediated NO generation is regulated by GPA1, the Gα-subunit of heterotrimeric G protein. The ExtCaM-dependent NO accumulation was nullified in gpa1 knockout mutants but enhanced by overexpression of a constitutively active form of GPA1 (cGα). In addition, cGα Atnoa1 and gpa1-2 Atnoa1 double mutants exhibited a similar response as did Atnoa1. The defect in gpa1 was rescued by overexpression of AtNOA1. Finally, we demonstrated that G protein activation of NO production depends on H2O2. Reduced H2O2 levels in guard cells blocked the stomatal response of cGα lines, whereas exogenously applied H2O2 rescued the defect in ExtCaM-mediated stomatal closure in gpa1 mutants. Moreover, the atrbohD/F mutant, which lacks the NADPH oxidase activity in guard cells, had impaired NO generation in response to ExtCaM, and H2O2-induced stomatal closure and NO accumulation were greatly impaired in Atnoa1. These findings have established a signaling pathway leading to ExtCaM-induced stomatal closure, which involves GPA1-dependent activation of H2O2 production and subsequent AtNOA1-dependent NO accumulation.
Plant guard cells control opening and closure of the stomata in response to phytohormones (e.g. abscisic acid [ABA]) and various environmental signals such as light and temperature, thereby regulating gas exchange for photosynthesis and water status via transpiration (Schroeder et al., 2001). Cytosolic calcium ([Ca2+]i) has been shown to be a key second messenger that changes in response to multiple stimuli in guard cells (McAinsh et al., 1995; Grabov and Blatt, 1998; Wood et al., 2000). A large proportion of Ca2+ is localized in extracellular space. It has been shown that external Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]o) promotes stomatal closure and induces oscillation in [Ca2+]i in guard cells (MacRobbie, 1992; McAinsh et al., 1995; Allen et al., 2001). However, how the guard cells perceive [Ca2+]o concentration and convert [Ca2+]o changes into [Ca2+]i changes was not understood until a calcium-sensing receptor (CAS) in the plasma membrane of guard cells in Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) was identified (Han et al., 2003). The external Ca2+ (Ca2+o)-induced [Ca2+]i increase is abolished in CAS antisense lines (Han et al., 2003). Both [Ca2+]o and [Ca2+]i show diurnal oscillation that is determined by stomatal conductance, whereas the amplitude of [Ca2+]i oscillation is reduced in CAS antisense lines (Tang et al., 2007). The reduced amplitude of [Ca2+]i diurnal oscillation in response to Ca2+o treatment suggests the potential existence of other [Ca2+]o sensor(s) that may transmit [Ca2+]o information into the [Ca2+]i response in coordination with CAS. Extracellular calmodulin (ExtCaM) could be such an additional [Ca2+]o sensor.
Calmodulin is a well-known Ca2+ sensor that is activated upon binding of Ca2+. It has been shown that calmodulin exists not only intracellularly but also extracellularly in many plant species (Biro et al., 1984; Sun et al., 1994, 1995; Cui et al., 2005). ExtCaM has been implicated in several important biological functions, such as the promotion of cell proliferation, pollen germination, and tube growth (Sun et al., 1994, 1995; Ma and Sun, 1997; Ma et al., 1999; Cui et al., 2005; Shang et al., 2005). ExtCaM is found in the cell wall of guard cells in Vicia faba and in the epidermis of Arabidopsis by immunogold labeling/electron microscopy and western-blot analyses, respectively, and the endogenous CaM in the extracellular space has been shown to regulate stomatal movements (Chen et al., 2003; Xiao et al., 2004). Under natural conditions, once the activity of ExtCaM has been inhibited by its membrane-impermeable antagonist W7-agrose or CaM antibody, stomatal opening under light is enhanced and stomatal closure in darkness is inhibited in V. faba and Arabidopsis (Chen et al., 2003; Xiao et al., 2004). [Ca2+]i and cytosolic hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) changes, two events involved in ExtCaM-regulated stomatal movement (Chen et al., 2004), are likely regulated by light/darkness (Chen and Gallie, 2004; Tang et al., 2007), suggesting that ExtCaM plays an important physiological role in the regulation of stomatal diurnal rhythm. Calmodulin-binding proteins have been found in the protoplast of suspension-cultured Arabidopsis cells, supporting the idea that ExtCaM functions as a peptide-signaling molecule (Cui et al., 2005). Furthermore, ExtCaM triggers [Ca2+]i elevation in guard cells of V. faba and Arabidopsis and in lily (Lilium daviddi) pollen (Chen et al., 2004; Xiao et al., 2004; Shang et al., 2005). These observations support the notion that ExtCaM could be a potential [Ca2+]o sensor for external calcium, and this external calcium sensing could subsequently regulate the [Ca2+]i level through a signaling cascade.
It is interesting that ExtCaM and ABA induce some parallel changes in second messengers in guard cell signaling. Our previous studies show that ExtCaM induces [Ca2+]i increase and H2O2 generation through the Gα-subunit (GPA1) of a heterotrimeric G protein, and increased H2O2 further elevates [Ca2+]i (Chen et al., 2004). G protein, Ca2+, and H2O2 are well-known second messengers in ABA-induced guard cell signaling (McAinsh et al., 1995; Grabov and Blatt, 1998; Pei et al., 2000; Wang et al., 2001; Zhang et al., 2001; Liu et al., 2007). However, the signaling cascade triggered by ExtCaM in guard cells is poorly understood. New ABA signaling components in guard cells could provide a clue in the study of the molecular mechanism of ExtCaM guard cell signaling.
Recently, nitric oxide (NO) has been shown to serve as an important signal molecule involved in many aspects of developmental processes, including floral transition, root growth, root gravitropism, adventitious root formation, xylogenesis, seed germination, and orientation of pollen tube growth (Beligni and Lamattina, 2000; Pagnussat et al., 2002; He et al., 2004; Prado et al., 2004; Gabaldón et al., 2005; Stohr and Stremlau, 2006). Increasing evidence points to a role for NO as an essential component in ABA signaling in guard cells (Garcia-Mata and Lamattina, 2001, 2002; Neill et al., 2002). It has been shown that nitrate reductase (NR) reduces nitrite to NO, and the nia1, nia2 NR-deficient mutant in Arabidopsis showed reduced ABA induction of stomatal closure (Desikan et al., 2002; Bright et al., 2006). Although animal nitric oxide synthase (NOS) activity has been detected in plants and inhibitors of mammalian NOS impair NO production in plants (Barroso et al., 1999; Corpas et al., 2001), the gene(s) encoding NOS in plants is still not clear. AtNOS1 in Arabidopsis was initially reported to encode a protein containing NOS activity (Guo et al., 2003). However, recent studies have raised critical questions regarding the nature of AtNOS1 and suggested that AtNOS1 appears not to encode a NOS (Crawford et al., 2006; Zemojtel et al., 2006). However, the originally described Atnos1 mutant is deficient in NO accumulation (Crawford et al., 2006). Consequently, AtNOS1 was renamed AtNOA1 (for NITRIC OXIDE ASSOCIATED1; Crawford et al., 2006). Therefore, the Atnoa1 mutant provides a useful tool for dissecting the function of NO in plants. At present, the molecules that regulate NO generation in ABA-mediated guard cell signaling are not clear. Evidence suggests that H2O2, a second messenger important for the regulation of many developmental processes and stomatal movement (Pei et al., 2000; Zhang et al., 2001; Coelho et al., 2002; Demidchik et al., 2003; Kwak et al., 2003), regulates NO generation in guard cells (Lum et al., 2002; He et al., 2005; Bright et al., 2006).
Given the parallel signaling events induced by ABA and ExtCaM, we investigated whether NO is involved in the regulation of ExtCaM-induced stomatal closure in Arabidopsis and whether it is linked to G protein and H2O2, two key regulators of both ExtCaM and ABA regulation of stomatal movements. Using Arabidopsis mutants (e.g. GPA1 null mutants, the NO-producing mutant Atnoa1, and the guard cell H2O2 synthetic enzymatic mutant atrbohD/F) combined with pharmacological analysis, we present compelling evidence to establish a linear functional relationship between Gα, H2O2, and NO in ExtCaM guard cell signaling.
RESULTS
AtNOA1-Dependent NO Accumulation Is Required for ExtCaM-Induced Stomatal Closure
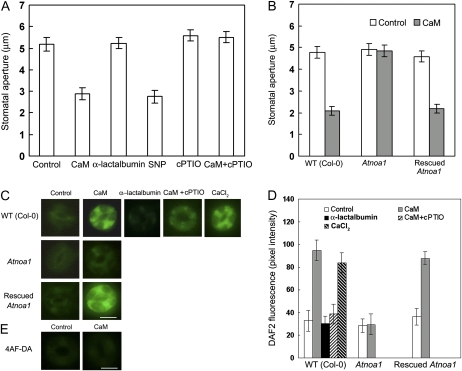
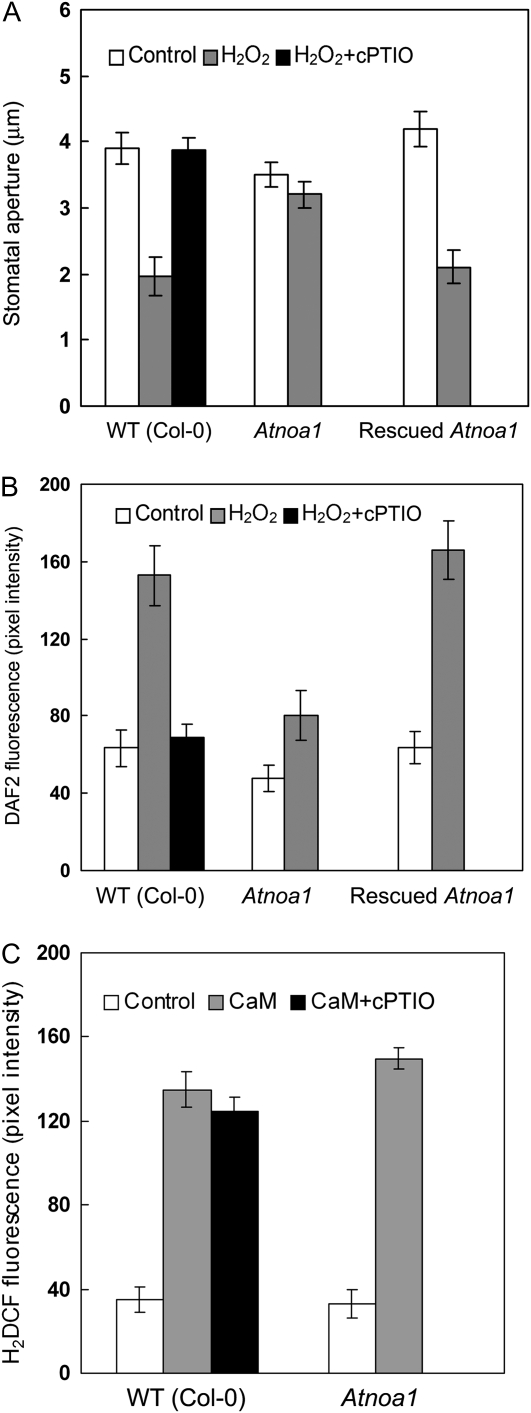
To investigate a potential role for NO in ExtCaM-induced stomatal closure, we examined the effect of the NO scavenger 2-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4,4,5,5-tetramethylimidazoline-1-oxyl 3-oxide potassium salt (cPTIO) on ExtCaM action. Both ExtCaM and the NO donor sodium nitroprusside (SNP) induced stomatal closure (Fig. 1A), as demonstrated previously (Garcia-Mata and Lamattina, 2001; Chen et al., 2004). cPTIO greatly reduced ExtCaM-induced stomatal closure compared with ExtCaM-treated stomata (P < 0.001; Fig. 1A). We then monitored changes in NO levels in response to applied ExtCaM using the NO-specific fluorescent dye diaminofluorescein diacetate (DAF2-DA; Garcia-Mata and Lamattina, 2002; Guo et al., 2003). ExtCaM treatment induced a dramatic increase in DAF2-DA staining in guard cells compared with the untreated control (P < 0.001), and cPTIO significantly reduced ExtCaM-induced NO generation in guard cells (P < 0.001; Fig. 1, C and D). The same concentration of α-lactalbumin, which contained an EF-hand like structure (Iyer and Qasba, 1999), had no effect on stomatal movement or NO levels in guard cells (Fig. 1, A, C, and D), indicating that induction of ExtCaM on stomatal closure and NO generation is CaM specific and is not induced by any other member of the EF-hand family of proteins. Application of calcium also caused NO synthesis, as did ExtCaM, supporting the possibility that ExtCaM transmits extracellular calcium changes into intracellular response (Fig. 1, C and D). Guard cells in wild-type (ecotype Columbia [Col-0]) epidermis were loaded with 4-aminofluorescein diacetate (4AF-DA), a negative control of DAF2-DA, and fluorescence intensity was examined when treated with ExtCaM. Fluorescence of 4AF in guard cells did not increase upon ExtCaM treatment (Fig. 1E). These results support an essential role for NO in regulating ExtCaM-induced stomatal closure.
Figure 1.
AtNOA1-dependent NO production regulates ExtCaM-induced stomatal closure. A, Open stomata in the wild type (WT) were incubated in MES buffer (control), 10−8 m CaM, 10−8 m α-lactalbumin, 60 μm SNP, 200 μm cPTIO, or 10−8 m CaM plus 200 μm cPTIO. B, Open stomata in the wild type, Atnoa1, and rescued Atnoa1 were incubated in MES buffer (control) or 10−8 m CaM. Stomatal apertures were measured 2 h after treatment. C and D, ExtCaM induces a NO increase in guard cells in the wild type and rescued Atnoa1 but fails in the Atnoa1 mutant. Open stomata in each genotype were incubated in 10 μm DAF2-DA buffer for 15 min and then incubated in MES buffer (control), 10−8 m α-lactalbumin, 1 mm CaCl2, 10−8 m CaM, or 10−8 m CaM plus 200 μm cPTIO for 30 min in darkness. Fluorescence images and intensities in guard cells were recorded and are shown in C and D, respectively. E, Open stomata in the wild type were incubated in 10 μm 4AF-DA, a negative control of DAF2-DA, for 15 min and then incubated in MES buffer or 10−8 m CaM for 30 min in darkness, and fluorescence images in guard cells were recorded. Bars = 10 μm.
We next determined whether the Atnoa1 mutant, which is defective in NO accumulation (Guo et al., 2003), exhibited different ExtCaM-induced guard cell responses. NO levels in guard cells and stomatal apertures in the Atnoa1 mutant and rescued Atnoa1 line were examined following ExtCaM treatment. ExtCaM-induced stomatal closure was impaired significantly in Atnoa1 compared with the ExtCaM-treated wild type (P < 0.001; Fig. 1B), consistent with the blocking effect of the NO scavenger cPTIO on ExtCaM-induced stomatal closure (P < 0.001). These results were supported by NO changes: ExtCaM-induced NO accumulation was almost completely abolished in the Atnoa1 mutant (P > 0.05; Fig. 1, C and D). Both stomatal closure and NO accumulation upon ExtCaM treatment in the rescued Atnoa1 line were similar to that of the wild type (P > 0.05; Fig. 1, B–D). These data indicate that AtNOA1-mediated NO accumulation plays an essential role in ExtCaM-induced stomatal closure.
G Protein α Subunit Modulates AtNOA1-Dependent NO Production in ExtCaM-Induced Stomatal Closure
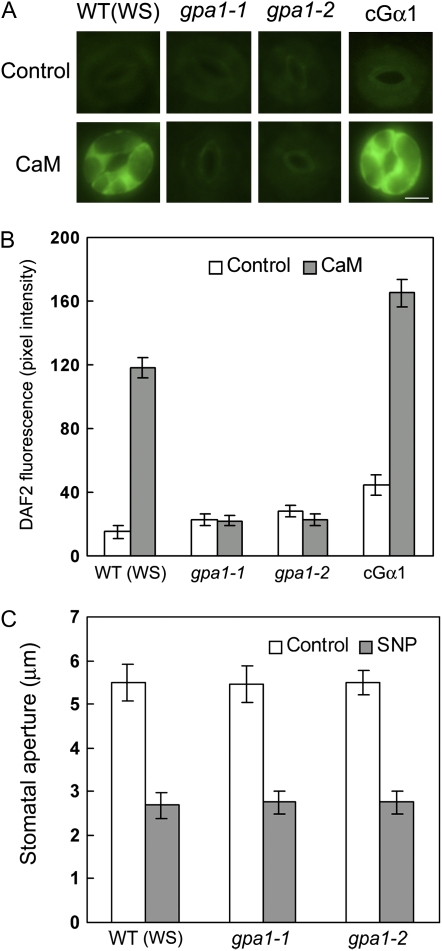
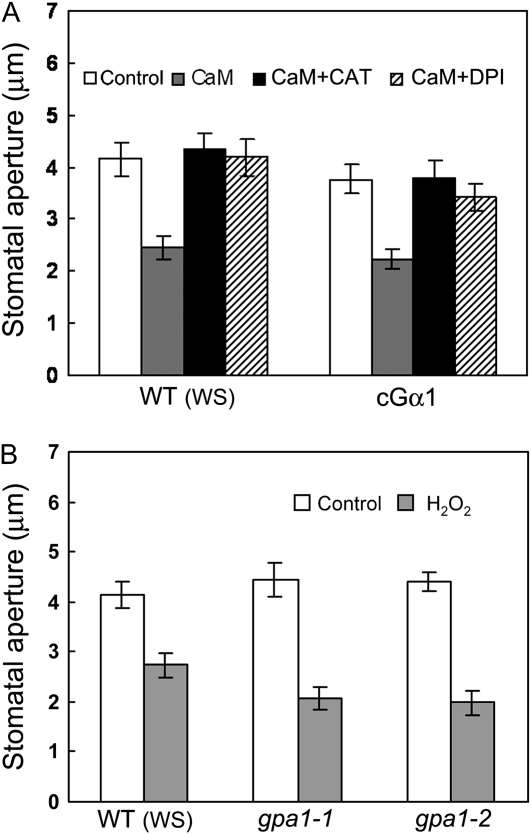
The GPA1 G protein α subunit (Gα) has been shown to modulate ABA regulation of stomatal opening (Wang et al., 2001) and closure (Liu et al., 2007) and ExtCaM induction of stomatal closure (Chen et al., 2004). To investigate whether Gα also regulates ExtCaM induction of NO generation, we examined NO levels in guard cells of the gpa1 null mutants and of transgenic lines expressing a constitutively active form of GPA1 (cGα; Okamoto et al., 2001; Wang et al., 2001). NO levels in the guard cells of two independent cGα lines were higher than that of the wild type (ecotype Wassilewskija [Ws]) in response to ExtCaM (P < 0.001), but ExtCaM failed to induce NO accumulation in gpa1-1 and gpa1-2 mutants (P > 0.05; Fig. 2, A and B; data from one line of cGα are shown). These results clearly indicate that Gα is required for ExtCaM induction of NO generation. These data are consistent with the faster response of cGα stomata to ExtCaM and the impaired stomatal closure of gpa1 with ExtCaM treatment, as reported previously (Chen et al., 2004). Furthermore, the NO donor SNP induced stomatal closure in gpa1-1 and gpa1-2 mutants (P < 0.001; Fig. 2C), further supporting that NO acts downstream of Gα during ExtCaM-induced stomatal closure.
Figure 2.
GPA1 modulates NO synthesis in ExtCaM guard cell signaling. A and B, Guard cells preloaded with 10 μm DAF2-DA in the wild type (WT/WS), gpa1 mutants, and the cGα line were incubated in MES buffer (control) or 10−8 m CaM for 30 min in darkness. Fluorescence images and intensities in guard cells were recorded and are shown in A and B, respectively. Bar = 10 μm. C, Open stomata in the wild type, gpa1-1, and gpa1-2 were incubated in MES buffer (control) or 60 μm SNP. Stomatal apertures were measured 2 h after treatment. WS, Ecotype Ws.
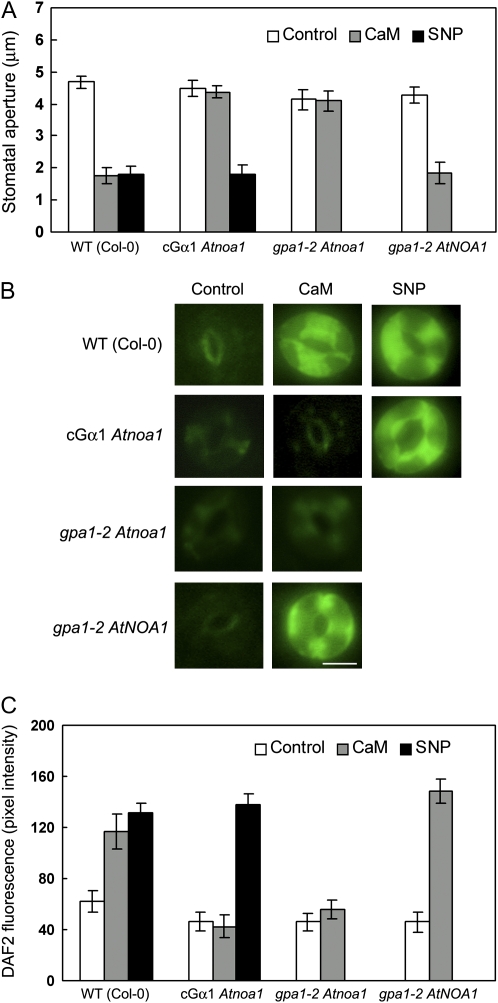
To further test the role of Gα in the regulation of NO generation in ExtCaM guard cell signaling, we performed crosses between the cGα1 line (Okamoto et al., 2001) and the Atnoa1 mutant and between gpa1-2 and Atnoa1 and examined stomatal responses and NO levels in guard cells in the double mutants. As shown in Figure 3, cGα1 Atnoa1 stomata did not close when treated with ExtCaM (P > 0.05; Fig. 3A) and ExtCaM failed to arouse NO production in guard cells of cGα1 Atnoa1 (P > 0.05; Fig. 3, B and C). The NO donor SNP rescued the defects of cGα1 Atnoa1 in stomatal closure and NO generation, suggesting that the defects of cGα1 Atnoa1 are due to a lack of NO production (Fig. 3).
Figure 3.
The effect of GPA1 depends on AtNOA1-mediated NO production. A, Open stomata in the wild type (WT), cGα1 Atnoa1 and gpa1-2 Atnoa1 double mutants, and gpa1-2 AtNOA1 lines were incubated in MES buffer (control), 10−8 m CaM, or 60 μm SNP. Stomatal apertures were measured 2 h after treatment. B and C, Guard cells preloaded with 10 μm DAF2-DA in the wild type, cGα1 Atnoa1 and gpa1-2 Atnoa1 double mutants, and gpa1-2 AtNOA1 lines were incubated in MES buffer (control), 10−8 m CaM, or 60 μm SNP for 30 min in darkness. Fluorescence images and intensities in guard cells were recorded and are shown in B and C, respectively. Bar = 10 μm.
At the same time, ExtCaM-induced stomatal response and NO level in the gpa1-2 Atnoa1 double mutant were similar to those in both gpa1-2 and Atnoa1 mutants (P > 0.05; Fig. 3), indicating that GPA1 and AtNOA1 act in the same pathway. Furthermore, we introduced the 35S: AtNOA1 gene into the gpa1-2 mutant. NO level and stomatal response following ExtCaM treatment were examined in three independent transgenic lines, and one set of representative data is shown. Stomatal closure and NO generation in guard cells in gpa1-2 AtNOA1 were similar to those of the wild type when treated with ExtCaM (P > 0.05; Fig. 3). Taken together, our results clearly demonstrate that the GPA1 G protein acts upstream of NO production to activate ExtCaM-induced stomatal closure.
Essential Role of H2O2 Generation in Gα-Induced NO Production in ExtCaM Guard Cell Signaling
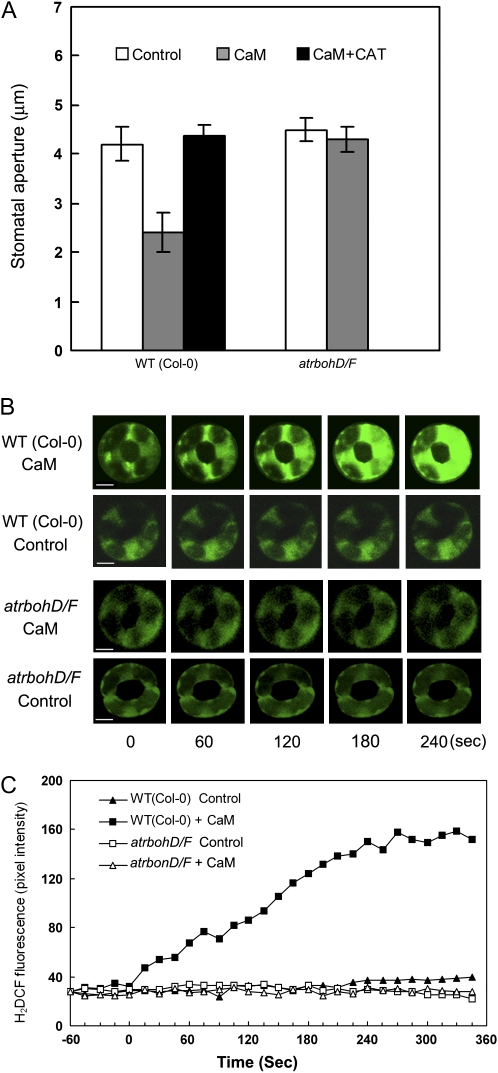
Pharmacological evidence supports a role for H2O2 in the mediation of ExtCaM-induced stomatal closure in V. faba (Chen et al., 2004). In this study, we vigorously tested the role of H2O2 in Arabidopsis using both pharmacological and genetic approaches. Stomata of atrbohD/F failed to close upon ExtCaM treatment, resembling the response of the wild type (Col-0) pretreated with catalase (CAT), a H2O2 scavenger (P > 0.05; Fig. 4A). Furthermore, we measured H2O2 changes using the fluorescent probe 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescein diacetate (H2DCFDA). As shown in Figure 4, ExtCaM induced a dramatic increase in H2O2 level in wild-type guard cells (P < 0.001) but not in atrbohD/F guard cells, while H2O2 level in the control guard cells did not change significantly during the recording period (Fig. 4, B and C). These results demonstrate that ExtCaM-induced stomatal closure depends on its activation of H2O2 production in guard cells.
Figure 4.
Impaired H2O2 synthesis blocks ExtCaM-induced stomatal closure. A, Open stomata in the wild type (WT) and atrbohD/F were incubated in MES buffer (control), 10−8 m CaM, or 10−8 m CaM plus 100 units mL−1 CAT. Stomatal apertures were measured 2 h after treatment. B and C, Fluorescence images (B) and a quantitative curve of fluorescence intensity (C) show that ExtCaM induces an H2O2 increase in the wild type but fails in atrbohD/F. H2O2 changes in guard cells preloaded with 50 μm H2DCFDA were measured with a confocal laser scanning microscope, and 10−8 m CaM or MES buffer (control) was added at 0 s, as indicated in C. Both fluorescence intensities and images of the guard cells were recorded every 15 s. The experiments were repeated at least three times with seven to 10 cells each time, and one time set of data is presented. Bars = 10 μm.
We next sought to determine whether Gα and H2O2 act in the same signaling pathway triggered by ExtCaM. We examined whether gpa1 and cGα affect H2O2 generation in response to an ExtCaM stimulus. As shown in Figure 5, both diphenylene iodonium (DPI), an inhibitor of NADPH oxidases, and CAT blocked the stomatal response to ExtCaM in cGα lines as well as in the wild type (Ws; P > 0.05; Fig. 5A; data from one cGα line are shown). cGα lines have been reported to show faster stomatal closure in response to ExtCaM, although they exhibit the same final stomatal apertures as ExtCaM-treated wild-type controls (Chen et al., 2004). Therefore, the large final stomatal aperture in cGα lines under the treatment of ExtCaM together with DPI or CAT demonstrates that the effect of higher Gα activity depends on the generation of H2O2. Furthermore, exogenously applied H2O2 induced stomatal closure in gpa1 mutants (P < 0.001; Fig. 5B), indicating that action of H2O2 does not depend on the activity of Gα. These results suggest that H2O2 acts downstream of Gα.
Figure 5.
H2O2 is required for action of cGα in ExtCaM guard cell signaling. A, Open stomata in the wild type (WT/WS) and cGα lines were incubated in MES buffer (control), 10−8 m CaM, 10−8 m CaM plus 10 μm DPI, or 10−8 m CaM plus 100 units mL−1 CAT. B, Open stomata in the wild type, gpa1-1, and gpa1-2 were incubated in MES buffer (control) or 5 × 10−5 m H2O2. Stomatal apertures were measured 2 h after treatment. WS, Ecotype Ws.
We next investigated whether H2O2 is essential for NO generation by examining the NO level in the atrohD/F double mutant upon treatment with ExtCaM. ExtCaM failed to induce NO generation in guard cells of atrbohD/F or the wild type (Col-0) incubated with CAT (P > 0.05; Fig. 6, A and B). The NO donor SNP induced stomatal closure of atrbohD/F (P < 0.001; Fig. 6C), supporting that NO acts downstream of H2O2. These results indicate that H2O2 is essential for NO generation induced by ExtCaM. Based on these results and our previous finding that Gα is required for ExtCaM-induced H2O2 generation in guard cells (Chen et al., 2004), we speculate that Gα-mediated NO production depends on H2O2 generation induced by ExtCaM.
Figure 6.
H2O2 generation is required for NO production in ExtCaM guard cell signaling. A and B, ExtCaM induces NO synthesis in the wild type (WT) but fails in atrbohD/F and the wild type incubated with CAT. Guard cells preloaded with 10 μm DAF2-DA in the wild type and atrbohD/F were incubated in MES buffer (control), 10−8 m CaM, or 10−8 m CaM plus 100 units mL−1 CAT for 30 min in darkness. Fluorescence images and intensities in the guard cells were recorded and are shown in A and B, respectively. Bar = 10 μm. C, Open stomata in the wild type and atrbohD/F were incubated in MES buffer (control) or 60 μm SNP. Stomatal apertures were measured 2 h after treatment.
AtNOA1-Dependent NO Accumulation Is Crucial for H2O2-Induced Stomatal Closure
Since interruption of H2O2 generation blocked ExtCaM-induced NO generation, we further investigated the relationship between H2O2 and NO. H2O2 induced stomatal closure in the wild type (Col-0) control and the rescued Atnoa1 line but not in the wild type incubated with cPTIO (P > 0.05); meanwhile, H2O2 failed to induce stomatal closure in the Atnoa1 mutant (P > 0.05; Fig. 7A). H2O2 induced NO generation in guard cells of the wild type and the rescued Atnoa1 line, and cPTIO reduced NO generation that was induced by H2O2 (P < 0.001); H2O2 also stimulated NO production in Atnoa1, whereas the level was greatly lower than that in the H2O2-treated wild type (P < 0.001; Fig. 7B). However, ExtCaM induced H2O2 generation both in Atnoa1 and in the wild type incubated with cPTIO (P > 0.05; Fig. 7C). These results suggest that H2O2-induced stomatal closure mainly depends on AtNOA1-mediated NO generation.
Figure 7.
H2O2-induced stomatal closure depends on AtNOA1-mediated NO production. A, Open stomata in the wild type (WT), rescued Atnoa1, and Atnoa1 were incubated in MES buffer (control), 5 × 10−5 m H2O2, or 5 × 10−5 m H2O2 plus 200 μm cPTIO. Stomatal apertures were measured 2 h after treatment. B, Guard cells preloaded with 10 μm DAF2-DA in the wild type, rescued Atnoa1, and Atnoa1 were incubated in MES buffer (control), 5 × 10−5 m H2O2, or 5 × 10−5 m H2O2 plus 200 μm cPTIO for 30 min in darkness, and fluorescence intensities in guard cells were recorded. ExtCaM-induced H2O2 generation does not depend on AtNOA1-mediated NO production. C, Guard cells preloaded with 50 μm H2DAFDA in the wild type and Atnoa1 were incubated in MES buffer (control), 10−8 m CaM, or 10−8 m CaM plus 200 μm cPTIO for 30 min in darkness, and fluorescence intensities in guard cells were recorded.
DISCUSSION
In this report, we have provided convincing evidence for a new signaling pathway controlling stomatal movement. Our combined genetic, pharmacological, and biochemical analyses show that ExtCaM stimulates AtNOA1-dependent production of NO, which acts as a second messenger to activate stomatal closure. Furthermore, we found that ExtCaM-triggered NO production is mediated by the activation of Gα of the heterotrimeric G protein in Arabidopsis. We also showed that the modulation of NO production by Gα requires NADPH oxidase-dependent H2O2 generation. Therefore, together with previous findings (Chen et al., 2004; Joo et al., 2005; Bright et al., 2006), our results support an ExtCaM-activated guard cell signaling pathway that includes a cascade of ExtCaM, heterotrimeric G protein, NADPH oxidase, and AtNOA1-dependent NO generation.
NO Plays an Important Role in ExtCaM Guard Cell Signaling
The role of NO in the regulation of stomatal closure has been well documented. The NO donor SNP was reported to induce stomatal closure in V. faba, Salpichroa organifolia, and Tradescantia species and to reduce transpiration in wheat (Triticum aestivum; Garcia-Mata and Lamattina, 2001). A requirement of NO in ABA-mediated stomatal closure has also been found in pea (Pisum sativum) and Arabidopsis (Desikan et al., 2002; Neill et al., 2002; Bright et al., 2006). Our results in this report provide convincing evidence that NO plays an important role in the regulation of ExtCaM-induced stomatal closure. The NO scavenger cPTIO reversed ExtCaM-induced stomatal closure (Fig. 1A), indicating that NO is required for ExtCaM-induced stomatal closure. The apertures of open stomata measured in this study are consistent with those in reports by Guo et al. (2003) and Liu et al. (2007) but somewhat larger than those reported by Desikan et al. (2002) and Bright et al. (2006). This discrepancy may be due to the different concentrations of KCl in the buffers used in these studies. The concentration of KCl in the MES/KCl buffer is 5 mm in the methods described by Desikan et al. (2002) and Bright et al. (2006) and 50 mm in the methods described by Liu et al. (2007). DAF2-DA is a NO-specific fluorescent dye. Using DAF2-DA dye, our results indicated that ExtCaM induced NO production in Arabidopsis (Fig. 1, C and D), further supporting the essential role of NO in ExtCaM signaling.
In animal systems, it has been reported that extracellular calcium induces NO production (Miles et al., 1998). In this study, we have checked NO levels after treatment with extracellular calcium, and the results indicated that NO levels in the guard cells of the wild type increased when treated with extracellular calcium (Fig. 1, C and D), suggesting that ExtCaM may act as an extracellular calcium sensor. We propose that G protein, H2O2, and NO play essential roles in transducing the extracellular calcium signal.
NR has been demonstrated to be an enzyme that mediates NO synthesis in plants. NR-mediated NO generation has also been suggested to regulate stomatal closure induced by ABA (Desikan et al., 2002; Bright et al., 2006). Although it has been shown that the NOS inhibitor nitro-l-Arg methyl ester suppresses stomatal closure and NO generation in guard cells of pea in response to ABA (Neill et al., 2002), the gene(s) encoding NOS in plants is not clear. AtNOA1 was initially isolated as a NOS in Arabidopsis (Guo et al., 2003), whereas the AtNOA1 protein showed no NOS activity in recent studies (Crawford et al., 2006; Zemojtel et al., 2006). Interestingly, AtNOA1 contains a GTP-binding domain and has been shown to be a member of the circularly permuted GTPase family for RNA/ribosome binding and to be involved in ribosome assembly (Moreau et al., 2008). Although it is not clear how AtNOA1 affects NO accumulation indirectly, the Atnoa1 mutant shows impaired stomatal closure and less NO accumulation in response to ABA and salt stress (Guo et al., 2003; Zhao et al., 2007). In this study, we showed that ExtCaM-induced NO accumulation requires AtNOA1: ExtCaM failed to induce stomatal closure and NO generation in the guard cells in Atnoa1, consistent with the blocking effect of cPTIO on ExtCaM-induced stomatal closure and NO production (Fig. 1). Thus, our pharmacological and genetic results suggest that NO is an essential molecule in ExtCaM-induced stomatal closure and that NO accumulation induced by ExtCaM depends on AtNOA1.
AtNOA1 was found to be targeted to mitochondria in Arabidopsis root (Guo and Crawford, 2005). However, recent evidence shows that AtNOA1 localizes in chloroplast (Flores-Pérez et al., 2008; Gas et al., 2009). Organelle localization of AtNOA1 suggests that activation of this protein requires signal transduction from extracellular stimuli to intracellular organelle. In this study, we show that AtNOA1-dependent NO accumulation in response to ExtCaM requires the activation of G protein and the accumulation of H2O2.
Modulation of NO Generation by G Protein in ExtCaM-Induced Stomatal Closure
Involvement of heterotrimeric G proteins in guard cell signaling has been supported by genetic evidence from null mutants for GPA1 and the G protein-coupled receptors GCR1 and GCR2 (Wang et al., 2001; Pandey and Assmann, 2004; Liu et al., 2007). Guard cells in gpa1 mutants were insensitive to ABA inhibition of inward K+ currents and pH independent of ABA activation of anion channels (Wang et al., 2001) and induction of stomatal closure (Liu et al., 2007). It is speculated that G protein regulates ion channels directly in guard cells, whereas modulation of radical oxygen species (ROS) by G protein has been found both in ExtCaM-induced stomatal closure and in ozone stress responses (Chen et al., 2004; Joo et al., 2005). In addition, sphingosine-1-phosphate has been found to be a signaling molecule involved in ABA regulation of guard cell turgor (Ng et al., 2001), and the Gα subunit acts downstream of sphingosine-1-phosphate during this process (Coursol et al., 2003). Those reports indicate that Gα may play a central mediating role in guard cell signaling. ExtCaM and ABA likely act independently to regulate the G protein pathway, although this has not been experimentally demonstrated However, Gα regulation of NO generation in guard cells has not been reported. In mammalian cells, heterotrimeric G protein regulates endothelial NOS activity by increasing cellular levels of endothelial NOS (Andreeva et al., 2006). If such G protein-dependent regulation of NO generation exists in Arabidopsis, NO production will be decreased in gpa1 mutants and increased in cGα lines. Our results were consistent with this speculation. gpa1 guard cells generated less NO and cGα lines generated higher NO levels when treated with ExtCaM (Fig. 2, A and B). Furthermore, the similarity of cGα Atnoa1 and gpa1-2 Atnoa1 double mutants to the Atnoa1 mutant in response to ExtCaM, the rescue of gpa1 mutants by AtNOA1 in stomatal closure and NO generation in response to ExtCaM (Fig. 3), and the enhancement of stomatal closure by SNP in gpa1 mutants (Fig. 2C) suggest that Gα action depends on AtNOA1-mediated NO generation. These results suggest that Gα acts upstream of NO generation in ExtCaM-mediated guard cell signaling.
Gα Regulation of NO Production in ExtCaM-Induced Stomatal Closure Depends on H2O2 Generation
ROS has been shown to be an important second messenger in ABA-induced stomatal movement in both Arabidopsis and V. faba (Pei et al., 2000; Zhang et al., 2001). Pharmacological results show that H2O2 is also involved in ExtCaM-induced stomatal closure and acts downstream of Gα in V. faba (Chen et al., 2004). In this report, we confirmed the essential role of ROS in the ExtCaM-mediated guard cell response using the atrbohD/F double mutant in Arabidopsis. The atrbohD/F mutant showed impaired ROS increases and stomatal closure when treated with ExtCaM (Fig. 4), providing genetic evidence for the involvement of ROS in ExtCaM guard cell signaling. Furthermore, ExtCaM-triggered stomatal closure in cGα lines was blocked by CAT or DPI, and the defect in stomatal closure in gpa1 was rescued by H2O2 (Fig. 5). These results indicate that H2O2 acts downstream of Gα in ExtCaM guard cell signaling.
Reports from several groups imply that H2O2 induces NO generation in guard cells of Phaseolus aureus, V. faba, and Arabidopsis (Lum et al., 2002; He et al., 2005; Bright et al., 2006). It has been shown that antioxidant ascorbate and CAT partially reverse SNP-induced H2DCF fluorescence and stomatal closure in V. faba (He et al., 2005). However, Bright et al. (2006) reported that SNP-induced stomatal closure is not affected by CAT in Arabidopsis, implying that guard cell responses differ between Arabidopsis and V. faba. In this study, we showed that ExtCaM-induced H2O2 synthesis is essential for NO production, since ExtCaM-induced NO production was greatly impaired in the guard cells of atrbohD/F and CAT blocked the ExtCaM-induced NO production in the guard cells of the wild type (Fig. 6, A and B). Nitro-l-Arg methyl ester inhibits H2O2-mediated NO generation in guard cells of P. aureus and V. faba, implying that NOS activity is related to H2O2-mediated NO generation (Lum et al., 2002; He et al., 2005). However, using Arabidopsis Atnoa1 and nia1, nia2 mutants, Bright et al. (2006) reported that it is NR, not AtNOA1, that is responsible for the stomatal closure and NO generation in guard cells in response to H2O2, although Desikan et al. (2002) showed that stomatal closure in the nia1, nia2 double mutant was induced by H2O2 as in the wild type. Our data indicate that H2O2-induced stomatal closure was greatly impaired by pretreatment with cPTIO. Meanwhile, H2O2-induced stomatal closure and NO generation were significantly reduced in Atnoa1 (Fig. 7, A and B). These results indicate that H2O2-induced stomatal closure and NO production depend mainly on AtNOA1, which contradicts the findings of Bright et al. (2006) but is somewhat supported by Desikan et al. (2002). The discrepancy in the AtNOA1 or NR source of H2O2 induction of NO generation may be due to the nitrogen nutrition conditions in the soil, because NR is a nitrate-dependent enzyme (Raven, 2003).
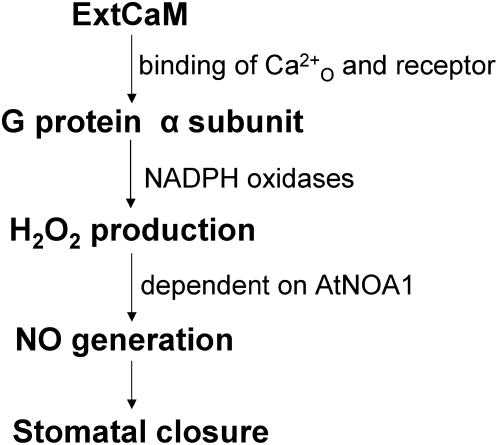
In this study, we present pharmacological, biochemical, and genetic evidence to support the essential role played by AtNOA1-dependent NO generation in ExtCaM-induced stomatal closure. We also show that a signaling cascade of heterotrimeric G protein, NADPH oxidase-dependent H2O2 generation, and AtNOA1-dependent NO production regulates ExtCaM-mediated guard cell responses. Both ExtCaM and H2O2 raise the [Ca2+]i level by promoting Ca2+o influx through Ca2+ channels in the plasma membrane (Pei et al., 2000; Xiao et al., 2004; Shang et al., 2005). In addition, ExtCaM receptor-like binding protein has been found in the plasma membrane (Cui et al., 2005). Based on these observations, we propose a working model for ExtCaM action: ExtCaM is activated by Ca2+o binding; active ExtCaM converts Ca2+o status to intracellular events through its receptor-like binding protein in the plasma membrane. ExtCaM could elevate the [Ca2+]i level by at least two means: (1) by promoting Ca2+o influx directly, or (2) by stimulating Ca2+ channels in the plasma membrane via increased H2O2. [Ca2+]i increases induced by ExtCaM might trigger Ca2+-dependent NO accumulation, and subsequently NO further releases Ca2+ from intracellular Ca2+ stores (Sokolovski et al., 2005). ExtCaM could act as another Ca2+o sensor together with CAS to regulate [Ca2+]i oscillation under natural conditions. A similar pathway appears to be responsible for ABA regulation of stomatal closure: ABA activates G protein (Liu et al., 2007) to arouse H2O2 generation by NADPH oxidases (Kwak et al., 2003), which subsequently induces NO levels by raising the [Ca2+]i level, and increased NO may cause [Ca2+]i elevation (Desikan et al., 2004). Therefore, a signaling cascade involving G protein, H2O2, NO, and calcium may integrate both ABA and ExtCaM to regulate stomatal movement (Fig. 8).
Figure 8.
Model showing the possible signaling pathway for ExtCaM-induced stomatal closure. ExtCaM activates G protein to induce H2O2 generation by NADPH oxidases, which increases NO production depending on AtNOA1; NO subsequently arouses stomatal closure.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
Seeds of the wild type and various mutants of Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) were sown in potting mix and grown in a greenhouse under a 16-h-light/8-h-dark cycle, a photon flux density of 0.30 mmol m−2 s−1, and a day/night temperature cycle of 18°C/22°C for 3 to 4 weeks. Seeds of cGα lines (background Ws) overexpressing a constitutively active form of GPA1 and gpa1-1 and gpa1-2 mutants (background Ws) were obtained from Dr. L.G. Ma (National Institute of Biological Sciences). cGα plants were grown in the presence of 70 nm dexamethasone (Sigma) according to the method described by Okamoto et al. (2001). atrbohD/F double mutant seeds (background Col-0) were obtained from Dr. M.A. Torres (University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill). Seeds of Atnoa1 mutant and the rescued Atnoa1 line (background Col-0) and the construct 35S:AtNOA1 were obtained from Dr. N.M. Crawford (University of California at San Diego). The cGα1 Atnoa1 and gpa1-2 Atnoa1 double mutants and the gpa1-2 mutant for transformation were back-crossed three times with Col-0 to remove the Ws background of cGα1 or gpa1-2. Genotypes of all mutants were confirmed by PCR analysis. Recombinant AtCaM2 protein was obtained from Dr. S.J. Cui (Hebei Normal University; Cui et al., 2005).
Transformation of Arabidopsis and PCR Analysis of Mutants
AtNOA1 cDNA was cut from pBIN-JIT (Guo et al., 2003) and ligated into binary vector pCAMBIA-1300 with hygromycin selection. Transformation of pCAMBIA-1300 harboring 35S:AtNOA1 into the gpa1-2 mutant was performed according to the flower-dip method (Clough and Bent, 1998). Hygromycin-resistant seedlings were transferred to soil for examination of the NO level and stomatal response to ExtCaM. Data from three independent transgenic lines were obtained, and representative results are shown. Primers for PCR analysis of the mutants are shown in the Supplemental Materials and Methods S1.
Stomatal Bioassay
Stomatal assays were performed essentially as described by Chen et al. (2004). Abaxial epidermal strips were peeled gently and incubated in MES buffer (10 mm MES-Tris, 50 mm KCl, and 0.1 mm CaCl2, pH 6.1) for 90 min under light to open the stomata. To study the effects of CaM, α-lactalbumin, SNP, and H2O2 on stomatal closure, the epidermal strips with open stomata were transferred to and incubated in MES buffer containing 10−8 m CaM, 10−8 m α-lactalbumin, 60 μm SNP, or 5 × 10−5 m H2O2 for 2 h. To investigate the effect of cPTIO, CAT, or DPI on CaM-induced stomatal closure, the strips with open stomata were transferred to and incubated in MES buffer containing10−8 m CaM plus 200 μm cPTIO, 100 units mL−1 CAT, or 10 μm DPI for 2 h. To investigate the effect of cPTIO on the effect of H2O2-induced stomatal closure, the strips with open stomata were transferred to and incubated in MES buffer containing 5 × 10−5 m H2O2 plus 200 μm cPTIO for 2 h. Stomatal apertures were measured with a microscope. Fifty stomata were randomly selected for three independent repeats. The data are presented as means ± se (n = 150).
Fluorescence Microscopy
NO was visualized using the specific fluorescent NO dye DAF2-DA (Sigma). Abaxial epidermal strips with open stomata were loaded with 10 μm DAF2-DA for 15 min, followed by a wash step. The strips were subsequently incubated in MES buffer alone, 10−8 m CaM, 10−8 m α-lactalbumin, 1 mm CaCl2, or 5 × 10−5 m H2O2 in MES buffer (or coincubated with other reagents as indicated in the figure legends) for 30 min. All images were acquired with a fluorescence microscope (Nikon; ELLIPE TE2000-U) with the following settings: excitation = 488 nm, emission = 515 nm; the fluorescence intensities were analyzed using MetaMorph. Data are presented as mean pixel intensities. Fifty guard cells were recorded for each treatment for three independent repeats.
Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
H2O2 measurement in guard cells was carried out using the method described previously (Chen et al., 2004). Abaxial epidermal strips with open stomata were incubated in 50 μm H2DCFDA (Molecular Probes; D399) for 15 min at room temperature and then washed three times. The strips were then incubated in MES buffer alone or 10−8 m CaM in MES buffer (or coincubated with 200 μm cPTIO) for 30 min. The H2O2 fluorescence in guard cells was measured using a confocal laser scanning microscope (Bio-Rad; CLSM 1024) with the following settings: excitation = 488 nm, emission = 535 nm. For real-time recording of H2DCF fluorescence intensity, images were recorded every 15 s. When the fluorescence stabilized around 60 s after scanning, CaM solution was added directly to the buffer in which the strips were placed, and we treated this agent addition point as zero time. Fluorescence changes were recorded, and relative fluorescence intensity was calculated by subtracting the basal signal at different time points as indicated in the figure legends. The experiments were repeated at least three times with seven to 10 cells each time, and one set of data is presented to illustrate the changes in fluorescence intensity.
Sequence data from this article can be found in the GenBank/EMBL data libraries under accession numbers At2g26300 (AtGPA1), At3g47450 (AtNOA1), At5g47910 (AtrbohD), and At1g64060 (AtrbohF).
Supplemental Data
The following materials are available in the online version of this article.
Supplemental Materials and Methods S1. Primers for PCR analysis of mutants.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. L.G. Ma, Dr. M.A. Torres, and Dr. N.M. Crawford for providing the seeds and constructs. We also thank Dr. S.J. Cui for providing purified AtCaM2 protein.
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (grant no. 30670173 to Y.-L.C.), the Doctor Foundation of Hebei Province (grant no. B2003107 to Y.-L.C.), Hebei Normal University (grant no. B2002213 to Y.-L.C.), and the Science Foundation of Hebei Normal University (grant no. L2006Y06 to J.-H.L.).
The author responsible for distribution of materials integral to the findings presented in this article in accordance with the policy described in the Instructions for Authors (www.plantphysiol.org) is: Yu-Ling Chen (yulingchen@mail.hebtu.edu.cn).
The online version of this article contains Web-only data.
References
- Allen GJ, Chu SP, Harrington CL, Schumacher K, Hoffmann T, Tang YY, Grill E, Schroeder JI (2001) A defined range of guard cell calcium oscillation parameters encodes stomatal movements. Nature 411 1053–1057 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreeva AV, Vaiskunaite R, Kutuzov MA, Profirovic J, Skidgel RA, Voyno-Yasenetskaya T (2006) Novel mechanisms of G protein-dependent regulation of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase. Mol Pharmacol 69 975–982 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barroso JB, Corpas FJ, Carreras A, Sandalio LM, Valderrama R, Palma JM, Lupiáñez JA, del Río LA (1999) Localization of nitric-oxide synthase in plant peroxisomes. J Biol Chem 274 36729–36733 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beligni MV, Lamattina L (2000) Nitric oxide stimulates seed germination and de-etiolation, and inhibits hypocotyl elongation, three light inducible responses in plants. Planta 210 215–221 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biro RL, Sun DY, Serlin BS, Terry ME, Datta N, Sopory SK, Roux SJ (1984) Characterization of oat calmodulin and radioimmunoassay of its subcellular distribution. Plant Physiol 75 382–386 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bright J, Desikan R, Hancock JT, Weir IS, Neill SJ (2006) ABA-induced NO generation and stomatal closure in Arabidopsis are dependent on H2O2 synthesis. Plant J 45 113–122 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen YL, Huang R, Xiao YM, Lü P, Chen J, Wang XC (2004) Extracellular calmodulin-induced stomatal closure is mediated by heterotrimeric G protein and H2O2. Plant Physiol 136 4096–4103 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen YL, Zhang XQ, Chen J, Wang XC (2003) Existence of extracellular calmodulin in the lower epidermis of the leaves of Vicia faba and its role in regulating stomatal movements. Acta Bot Sin 45 40–46 [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z, Gallie DR (2004) The ascorbic acid redox state controls guard cell signaling and stomatal movement. Plant Cell 16 1143–1162 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: A simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16 735–743 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coelho SM, Taylor AR, Ryan KP, Sousa-Pinto I, Brown MT, Brownlee C (2002) Spatiotemporal patterning of reactive oxygen production and Ca2+ wave propagation in Fucus rhizoid cells. Plant Cell 14 2369–2381 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corpas FJ, Barroso JB, del Río LA (2001) Peroxisomes as a source of reactive oxygen species and nitric oxide signal molecules in plant cells. Trends Plant Sci 6 145–150 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coursol S, Fan LM, Le Stunff H, Spiegel S, Gilroy S, Assmann SM (2003) Sphingolipid signalling in Arabidopsis guard cells involves heterotrimeric G proteins. Nature 423 651–654 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford NM, Galli M, Tischner R, Heimer YM, Okamoto M, Mack A (2006) Response to Zemojtel et al.: Plant nitric oxide synthase: back to square one. Trends Plant Sci 11 526–527 [Google Scholar]
- Cui S, Guo X, Chang F, Cui Y, Ma L, Sun Y, Sun D (2005) Apoplastic calmodulin receptor-like binding proteins in suspension-cultured cells of Arabidopsis thaliana. J Biol Chem 280 31420–31427 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demidchik V, Shabala SN, Coutts KB, Tester MA, Davies JM (2003) Free oxygen radicals regulate plasma membrane Ca2+- and K+- permeable channels in plant root cells. J Cell Sci 116 81–88 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desikan R, Cheung M, Bright J, Hancock JT, Neill SJ (2004) ABA, hydrogen peroxide and nitric oxide signalling in stomatal guard cells. J Exp Bot 55 205–212 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desikan R, Griffiths R, Hancock JT, Neill S (2002) A new role for an old enzyme: nitrate reductase-mediated nitric oxide generation is required for abscisic acid-induced stomatal closure in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99 16314–16318 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores-Pérez U, Sauret-Güeto S, Gas E, Jarvis P, Rodríguez-Concepción M (2008) A mutant impaired in the production of plastome-encoded proteins uncovers a mechanism for the homeostasis of isoprenoid biosynthetic enzymes in Arabidopsis plastids. Plant Cell 20 1303–1315 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabaldón C, Ros-Gómez LV, Pedreňo MA, Ros-Barceló A (2005) Nitric oxide production by the differentiating xylem of Zinnia elegans. New Phytol 165 121–130 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Mata C, Lamattina L (2001) Nitric oxide induces stomatal closure and enhances the plant adaptive plant responses against drought stress. Plant Physiol 126 1196–1204 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Mata C, Lamattina L (2002) Nitric oxide and abscisic acid cross talk in guard cells. Plant Physiol 128 790–792 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gas E, Flores-Pérez U, Sauret-Güeto S, Rodrίguez-Concepción M (2009) Hunting for plant nitric oxide synthase provides new evidence of a central role for plastids in nitric oxide metabolism. Plant Cell 21 18–23 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabov A, Blatt MR (1998) Membrane voltage initiates Ca2+ waves and potentiates Ca2+ increases with abscisic acid in stomatal guard cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95 4778–4783 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo FQ, Crawford NM (2005) Arabidopsis nitric oxide synthase1 is targeted to mitochondria and protects against oxidative damage and dark-induced senescence. Plant Cell 17 3436–3450 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo FQ, Okamoto M, Crawford NM (2003) Identification of a plant nitric oxide synthase gene involved in hormonal signaling. Science 302 100–103 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han S, Tang R, Anderson LK, Woerner TE, Pei ZM (2003) A cell surface receptor mediates extracellular Ca2+ sensing in guard cells. Nature 425 196–200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He JM, Xu H, She XP, Song XG, Zhao WM (2005) The role and interrelationship of hydrogen peroxide and nitric oxide in the UV-B-induced stomatal closure in broad bean. Funct Plant Biol 32 237–247 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He Y, Tang RH, Hao Y, Stevens RD, Cook CW, Ahn SM, Jing L, Yang Z, Chen L, Guo F, et al (2004) Nitric oxide represses the Arabidopsis floral transition. Science 305 1968–1971 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iyer LK, Qasba PK (1999) Molecular dynamics simulation of α-lactalbumin and calcium binding c-type lysozyme. Protein Eng 12 129–139 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joo JH, Wang S, Chen JG, Jones AM, Fedoroff NV (2005) Different signaling and cell death roles of heterotrimeric G protein α and β subunits in the Arabidopsis oxidative stress response to ozone. Plant Cell 17 957–970 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwak JM, Mori IC, Pei ZM, Leonhardt N, Torres MA, Dangl JL, Bloom RE, Bodde S, Jones JDG, Schroeder JI (2003) NADPH oxidase AtrbohD and AtrbohF genes function in ROS-dependent ABA signaling in Arabidopsis. EMBO J 22 2623–2633 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu X, Yue Y, Li B, Nie Y, Li W, Wu WH, Ma L (2007) A G protein-coupled receptor is a plasma membrane receptor for the plant hormone abscisic acid. Science 315 1712–1716 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lum HK, Butt YK, Lo SC (2002) Hydrogen peroxide induces a rapid production of nitric oxide in mung bean (Phaseolus aureus). Nitric Oxide 6 205–213 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma LG, Sun DY (1997) The effects of extracellular calmodulin on initiation of Hippeastrum rutilum pollen germination and tube growth. Planta 202 336–340 [Google Scholar]
- Ma LG, Xu XD, Cui SJ, Sun DY (1999) The presence of a heterotrimeric G protein and its role in signal transduction of extracellular calmodulin in pollen germination and tube growth. Plant Cell 11 1351–1364 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacRobbie E (1992) Calcium and ABA-induced stomatal closure. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 338 5–18 [Google Scholar]
- McAinsh MR, Webb AAR, Taylor JE, Hetherington AM (1995) Stimulus-induced oscillations in guard cell cytosolic free calcium. Plant Cell 7 1207–1219 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles PR, Bowman L, Rengasamy A, Huffman L (1998) Constitutive nitric oxide production by rat alveolar macrophages. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 274 L360–L368 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau M, Lee GI, Wang Y, Crane BR, Klessig DF (2008) AtNOS/A1 is a functional Arabidopsis thaliana cGTPase and not a nitric oxide synthase. J Biol Chem 283 32957–32967 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neill SJ, Desikan R, Clarke A, Hancock JT (2002) Nitric oxide is a novel component of abscisic acid signalling in stomatal guard cells. Plant Physiol 128 13–16 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng CK, Carr K, McAinsh MR, Powell B, Hetherington AM (2001) Drought-induced guard cell signal transduction involves sphingosine-1-phosphate. Nature 410 596–599 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H, Matsui M, Deng XW (2001) Overexpression of the heterotrimeric G-protein α-subunit enhances phytochrome mediated inhibition of hypocotyl elongation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 13 1639–1652 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagnussat GC, Simontacchi M, Puntarulo S, Lamattina L (2002) Nitric oxide is required for root organogenesis. Plant Physiol 129 954–956 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandey S, Assmann SM (2004) The Arabidopsis putative G protein coupled receptor GCR1 interacts with the G protein α subunit GPA1 and regulates abscisic acid signaling. Plant Cell 16 1616–1632 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pei ZM, Murata Y, Benning G, Thomine S, Klüsener B, Allen GJ, Grill E, Schroeder JI (2000) Calcium channels activated by hydrogen peroxide mediate abscisic acid signaling in guard cells. Nature 406 731–734 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prado AM, Porterfield DM, Feijó JA (2004) Nitric oxide is involved in growth regulation and re-orientation of pollen tubes. Development 131 2707–2714 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raven JA (2003) Can plants rely on nitrate? Trends Plant Sci 8 314–315; author reply 315–316 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder JI, Allen GJ, Hugouvieux V, Kwak JM, Waner D (2001) Guard cell signal transduction. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 52 627–658 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shang ZL, Ma LG, Zhang HL, He RR, Wang XC, Cui SJ, Sun DY (2005) Ca2+ influx into lily pollen grains through a hyperpolarization-activated Ca2+-permeable channel which can be regulated by extracellular CaM. Plant Cell Physiol 46 598–608 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokolovski S, Hills A, Gay R, Garcia-Mata C, Lamattina L, Blatt MR (2005) Protein phosphorylation is a prerequisite for intracellular Ca2+ release and ion channel control by nitric oxide and abscisic acid in guard cells. Plant J 43 520–529 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stohr C, Stremlau S (2006) Formation and possible roles of nitric oxide in plant roots. J Exp Bot 57 463–470 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun DY, Bian YQ, Zhao BH, Zhao LY, Yu XM, Duan SJ (1995) The effect of extracellular calmodulin on cell wall regeneration of protoplasts and cell division. Plant Cell Physiol 36 133–138 [Google Scholar]
- Sun DY, Li HB, Cheng G (1994) Extracellular calmodulin accelerates the proliferation of suspension-cultured cells of Angelica dahurica. Plant Sci 99 1–8 [Google Scholar]
- Tang RH, Han S, Zheng H, Cook CW, Choi CS, Woerner TE, Jackson EB, Pei ZM (2007) Coupling diurnal cytosolic Ca2+ oscillations to the CAS-IP3 pathway in Arabidopsis. Science 315 1423–1426 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang XQ, Ullah H, Jones AM, Assmann SM (2001) G protein regulation of ion channels and abscisic acid signaling in Arabidopsis guard cells. Science 292 2070–2072 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood NT, Allan AC, Haley A, Viry-Moussaïd M, Trewavas AJ (2000) The characterization of differential calcium signaling in tobacco guard cells. Plant J 24 335–344 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao Y, Chen YL, Huang R, Chen J, Wang XC (2004) Depolymerization of actin cytoskeleton is involved in stomatal closure induced by extracellular calmodulin in Arabidopsis. Sci China C Life Sci 47 454–460 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zemojtel T, Fröhlich A, Palmieri MC, Kolanczyk M, Mikula I, Wyrwicz LS, Wanker EE, Mundlos S, Vingron M, Martasek P, et al (2006) Plant oxide synthase: a never-ending story? Trends Plant Sci 11 524–525 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X, Zhang L, Dong F, Gao J, Galbraith DW, Song CP (2001) Hydrogen peroxide is involved in abscisic acid-induced stomatal closure in Vicia faba. Plant Physiol 126 1438–1448 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao MG, Tian QY, Zhang WH (2007) Nitric oxide synthase-dependent nitric oxide production is associated with salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 144 206–217 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.