Abstract
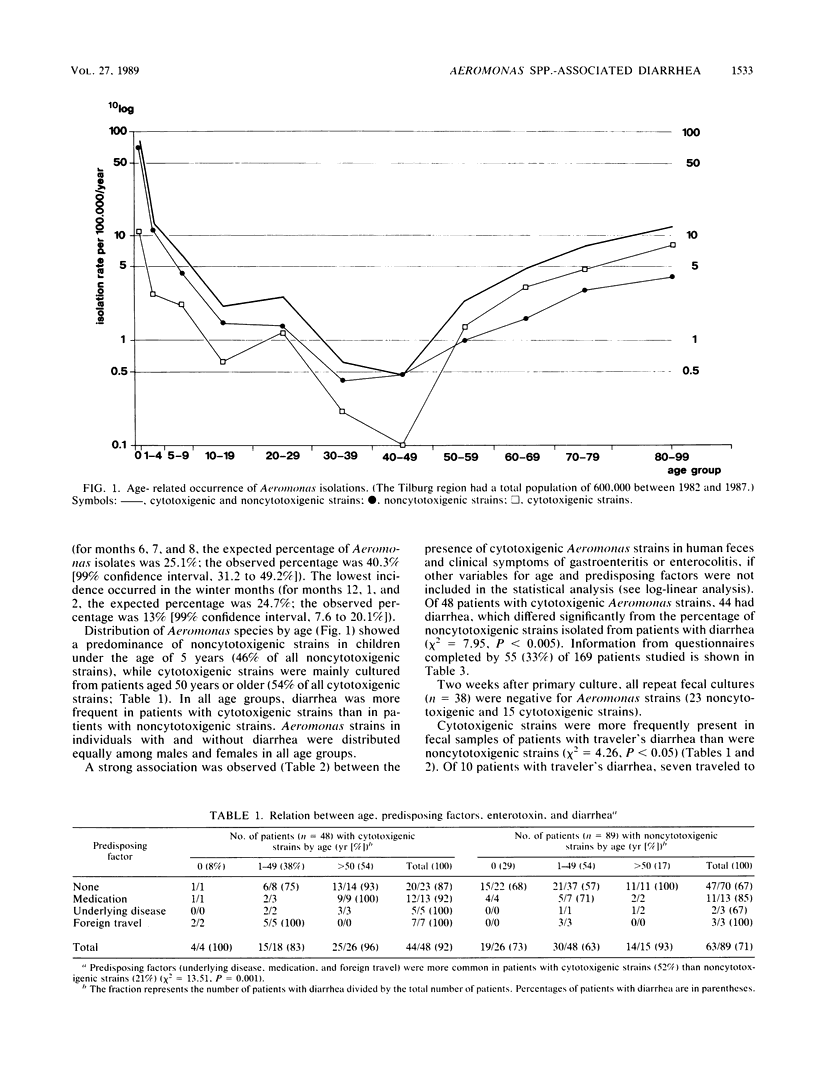
Between June 1982 and May 1987 Aeromonas species were isolated from 208 of 34,311 (0.61%) fecal samples submitted to a Regional Public Health Laboratory in The Netherlands. Aeromonas isolates were found most frequently in summer and rarely in winter. Of 169 Aermonas isolates that were available for further study, 19% were isolated from patients with a mixed infection, 5% from patients with underlying diseases, and 15% from patients who used medication that could predispose the intestinal tract to colonization with Aeromonas species. Aeromonas species that produced cytotoxins to Vero cells (cytotoxigenic) were found in hybridization groups 1 (11% of all isolates), 2 (1%), 3 (2%), and 8 (25%) and were identified phenotypically as A. hydrophila or A. sobria. Aeromonas species that did not produce cytotoxins to Vero cells (noncytotoxigenic) were found in hybridization groups 4 (57%) and 5A (4%) and were identified phenotypically as A. caviae. Distribution of Aeromonas species by age showed a predominance of noncytotoxigenic strains in children under the age of 5 years (46% of all noncytotoxigenic strains), while cytotoxigenic strains were mainly cultured from patients aged 50 years or older (54% of all cytotoxigenic strains). Significant correlations were found between cytotoxigenic strains and hospitalization, foreign travel, and contact with surface water. Cytotoxigenic strains were isolated significantly more often than noncytotoxigenic strains from patients with diarrhea, but in a multivariate analysis including age, previous medication, underlying disease, and foreign travel, this association was not significant.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altwegg M., Jöhl M. Isolation frequency of Aeromonas species in relation to patient age. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Feb;6(1):55–56. doi: 10.1007/BF02097193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. J., McWhorter A. C., Knutson J. K., Steigerwalt A. G. Escherichia vulneris: a new species of Enterobacteriaceae associated with human wounds. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):1133–1140. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.1133-1140.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catsaras M., Buttiaux R. Les Aeromonas dans les matières fécales humaines. Ann Inst Pasteur Lille. 1965;16:85–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty T., Montenegro M. A., Sanyal S. C., Helmuth R., Bulling E., Timmis K. N. Cloning of enterotoxin gene from Aeromonas hydrophila provides conclusive evidence of production of a cytotonic enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):435–441. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.435-441.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figura N., Marri L., Verdiani S., Ceccherini C., Barberi A. Prevalence, species differentiation, and toxigenicity of Aeromonas strains in cases of childhood gastroenteritis and in controls. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Mar;23(3):595–599. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.3.595-599.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George W. L., Nakata M. M., Thompson J., White M. L. Aeromonas-related diarrhea in adults. Arch Intern Med. 1985 Dec;145(12):2207–2211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gracey M., Burke V., Robinson J. Aeromonas-associated gastroenteritis. Lancet. 1982 Dec 11;2(8311):1304–1306. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91510-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gracey M., Burke V., Robinson J., Masters P. L., Stewart J., Pearman J. Aeromonas spp in travellers' diarrhoea. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 Sep 15;289(6446):658–658. doi: 10.1136/bmj.289.6446.658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman-Brenner F. W., Fanning G. R., Arduino M. J., Brenner D. J., Farmer J. J., 3rd Aeromonas schubertii, a new mannitol-negative species found in human clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Aug;26(8):1561–1564. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.8.1561-1564.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman-Brenner F. W., MacDonald K. L., Steigerwalt A. G., Fanning G. R., Brenner D. J., Farmer J. J., 3rd Aeromonas veronii, a new ornithine decarboxylase-positive species that may cause diarrhea. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 May;25(5):900–906. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.5.900-906.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg S. D., Schell W. L., Fanning G. R., Wachsmuth I. K., Hickman-Brenner F. W., Blake P. A., Brenner D. J., Farmer J. J., 3rd Aeromonas intestinal infections in the United States. Ann Intern Med. 1986 Nov;105(5):683–689. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-105-5-683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janda J. M., Brenden R. Importance of Aeromonas sobria in Aeromonas bacteremia. J Infect Dis. 1987 Mar;155(3):589–591. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.3.589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janda J. M., Reitano M., Bottone E. J. Biotyping of Aeromonas isolates as a correlate to delineating a species-associated disease spectrum. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jan;19(1):44–47. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.1.44-47.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay B. A., Guerrero C. E., Sack R. B. Media for the isolation of Aeromonas hydrophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Nov;22(5):888–890. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.5.888-890.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ketover B. P., Young L. S., Armstrong D. Septicemia due to Aeromonas hydrophila: clinical and immunologic aspects. J Infect Dis. 1973 Mar;127(3):284–290. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.3.284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuijper E. J., Peeters M. F. De betekenis van verschillende Aeromonas-soorten in de faeces van patiënten met en zonder diarree. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 1986 Feb 15;130(7):302–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuijper E. J., Steigerwalt A. G., Schoenmakers B. S., Peeters M. F., Zanen H. C., Brenner D. J. Phenotypic characterization and DNA relatedness in human fecal isolates of Aeromonas spp. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jan;27(1):132–138. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.1.132-138.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuijper E. J., Zanen H. C., Peeters M. F. Aeromonas-associated diarrhea in the Netherlands. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Apr;106(4):640–641. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-106-4-640_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson M. A., Burke V., Chang B. J. Invasion of HEp-2 cells by fecal isolates of Aeromonas hydrophila. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):680–683. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.680-683.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungh A., Wadström T. Aeromonas toxins. Pharmacol Ther. 1981;15(3):339–354. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(81)90049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millership S. E., Curnow S. R., Chattopadhyay B. Faecal carriage rate of Aeromonas hydrophila. J Clin Pathol. 1983 Aug;36(8):920–923. doi: 10.1136/jcp.36.8.920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishra S., Nair G. B., Bhadra R. K., Sikder S. N., Pal S. C. Comparison of selective media for primary isolation of Aeromonas species from human and animal feces. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Nov;25(11):2040–2043. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.11.2040-2043.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. R., Johnson P. C., DuPont H. L., Satterwhite T. K., Wood L. V. Lack of correlation between known virulence properties of Aeromonas hydrophila and enteropathogenicity for humans. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):62–65. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.62-65.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyer N. P. Clinical significance of Aeromonas species isolated from patients with diarrhea. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Nov;25(11):2044–2048. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.11.2044-2048.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namdari H., Bottone E. J. Correlation of the suicide phenomenon in Aeromonas species with virulence and enteropathogenicity. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Dec;26(12):2615–2619. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.12.2615-2619.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitarangsi C., Echeverria P., Whitmire R., Tirapat C., Formal S., Dammin G. J., Tingtalapong M. Enteropathogenicity of Aeromonas hydrophila and Plesiomonas shigelloides: prevalence among individuals with and without diarrhea in Thailand. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):666–673. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.666-673.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz A. J., McCardell B. A. DNA homology and immunological cross-reactivity between Aeromonas hydrophila cytotonic toxin and cholera toxin. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jan;26(1):57–61. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.1.57-61.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirinavin S., Likitnukul S., Lolekha S. Aeromonas septicemia in infants and children. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1984 Mar-Apr;3(2):122–125. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198403000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull P. C., Lee J. V., Miliotis M. D., Van de Walle S., Koornhof H. J., Jeffery L., Bryant T. N. Enterotoxin production in relation to taxonomic grouping and source of isolation of Aeromonas species. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):175–180. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.175-180.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff R. L., Wiseman S. L., Kitchens C. S. Aeromonas hydrophila bacteremia in ambulatory immunocompromised hosts. Am J Med. 1980 Feb;68(2):238–242. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90360-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


