Abstract
The pathogenetic role of soluble products of Trichomonas vaginalis growth in culture is controversial. To evaluate this role, T. vaginalis was grown in broth and cell culture and the cell-free filtrate was applied to fresh cell culture monolayers. When adjusted to pH 6.5, filtrates obtained from 22-h culture growth totally disrupted McCoy, HEp-2, human foreskin fibroblast, and Chinese hamster ovary cell monolayers within 6 h. These detached cells remained greater than 90% viable. This cell-detaching factor (CDF) was heat and acid labile, with a pH optimum of 6.5. CDF has trypsinlike activity which disrupts monolayer cells, but cells do not die if the pH is controlled. CDF was purified by ethanol precipitation, ammonium sulfate fractionation, and ion-exchange and gel filtration column chromatography. A 200,000-molecular-weight glycoprotein which was also immunogenic by immunoblot with human sera reactive to T. vaginalis was isolated in this manner. This confirms the presence of a specific soluble CDF derived from T. vaginalis whose application may be important as a diagnostic tool and in further studies of pathogenesis.
Full text
PDF


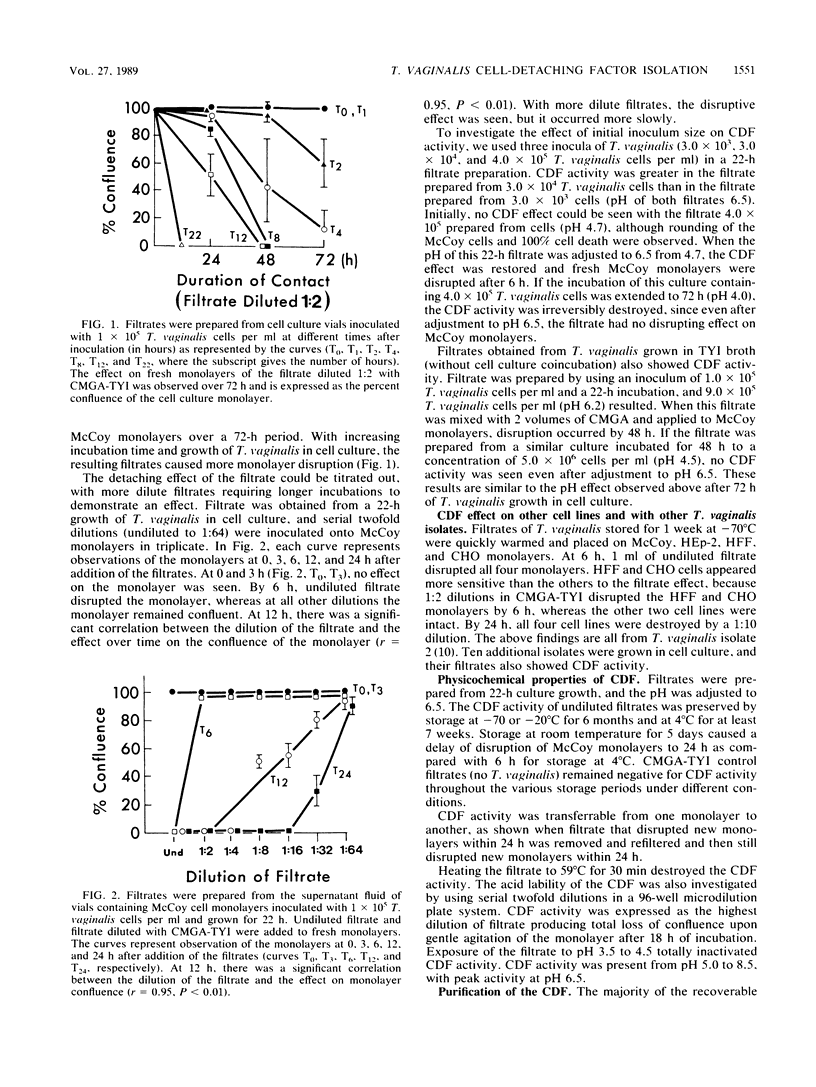
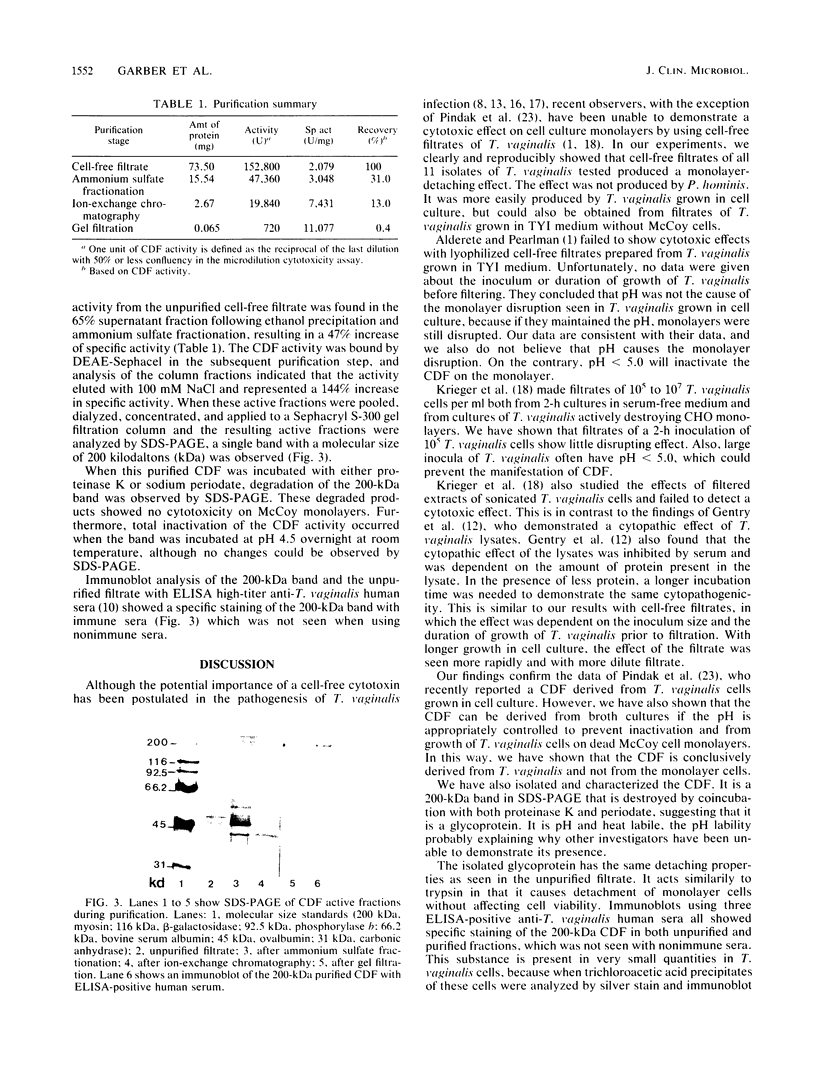

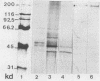
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alderete J. F., Pearlman E. Pathogenic Trichomonas vaginalis cytotoxicity to cell culture monolayers. Br J Vener Dis. 1984 Apr;60(2):99–105. doi: 10.1136/sti.60.2.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. T. Trichomoniasis. Practitioner. 1972 Nov;209(253):639–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTIAN R. T., MILLER N. F., LUDOVICI P. P., RILEY G. M. A study of Trichomonas vaginalis in human cell culture. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1963 Apr 1;85:947–954. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(16)35599-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall R. D. Trichomonal infections of the genital tract. Med Clin North Am. 1972 Sep;56(5):1203–1209. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)32345-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIAMOND L. S. The establishment of various trichomonads of animals and man in axenic cultures. J Parasitol. 1957 Aug;43(4):488–490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duerst R. E., Frantz C. N. A sensitive assay of cytotoxicity applicable to mixed cell populations. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Sep 3;82(1):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90222-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farris V. K., Honigberg B. M. Behavior and pathogenicity of Trichomonas vaginalis Donné in chick liver cell cultures. J Parasitol. 1970 Oct;56(5):849–882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fouts A. C., Kraus S. J. Trichomonas vaginalis: reevaluation of its clinical presentation and laboratory diagnosis. J Infect Dis. 1980 Feb;141(2):137–143. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.2.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber G. E., Proctor E. M., Bowie W. R. Immunogenic proteins of Trichomonas vaginalis as demonstrated by the immunoblot technique. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):250–253. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.250-253.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber G. E., Sibau L., Ma R., Proctor E. M., Shaw C. E., Bowie W. R. Cell culture compared with broth for detection of Trichomonas vaginalis. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jul;25(7):1275–1279. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.7.1275-1279.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry G. A., Lawrence N., Lushbaugh W. Isolation and differentiation of herpes simplex virus and Trichomonas vaginalis in cell culture. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Aug;22(2):199–204. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.2.199-204.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath J. P. Behaviour and pathogenicity of Trichomonas vaginalis in epithelial cell cultures: a study by light and scanning electron microscopy. Br J Vener Dis. 1981 Apr;57(2):106–117. doi: 10.1136/sti.57.2.106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieger J. N., Ravdin J. I., Rein M. F. Contact-dependent cytopathogenic mechanisms of Trichomonas vaginalis. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):778–786. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.778-786.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lushbaugh W. B., Hofbauer A. F., Pittman F. E. Proteinase activities of Entamoeba histolytica cytotoxin. Gastroenterology. 1984 Jul;87(1):17–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen M. H., Nielsen R. Electron microscopy of Trichomonas vaginalis Donné: interaction with vaginal epithelium in human trichomoniasis. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1975 Aug;83(4):305–320. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1975.tb00107.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pindak F. F., Gardner W. A., Jr, Mora de Pindak M. Growth and cytopathogenicity of Trichomonas vaginalis in tissue cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Apr;23(4):672–678. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.4.672-678.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]