Abstract
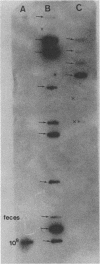
A DNA probe, M13 mpHAW71, that detects Mycobacterium paratuberculosis in the fecal material of infected animals was developed for use in the diagnosis of Johne's disease. The probe detected as few as 10(5) M. paratuberculosis when hybridized under stringent conditions to total genomic DNA purified from bovine fecal material. When the probe was used diagnostically, it did not differentiate members of the Mycobacterium avium-M. intracellulare-M. paratuberculosis complex. Compared with culturing, the DNA probe identified 34.4% more mycobacterium-containing fecal samples, and testing took only 72 h to complete.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aksamit A. J., Major E. O., Ghatak N. R., Sidhu G. S., Parisi J. E., Guccion J. G. Diagnosis of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy by brain biopsy with biotin labeled DNA:DNA in situ hybridization. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1987 Sep;46(5):556–566. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198709000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baess I. Deoxyribonucleic acid relatedness among species of slowly-growing mycobacteria. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1979 Aug;87(4):221–226. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1979.tb02430.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baess I. Isolation and purification of deoxyribonucleic acid from mycobacteria. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1974 Dec;82(6):780–784. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1974.tb02375.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendixen P. H. Immunological reactions caused by infection with Mycobacterium paratuberculosis. A review. Nord Vet Med. 1978 Apr-May;30(4-5):163–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camphausen R. T., Jones R. L., Brennan P. J. A glycolipid antigen specific to Mycobacterium paratuberculosis: structure and antigenicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3068–3072. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaparas S. D. The immunology of mycobacterial infections. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1982;9(2):139–197. doi: 10.3109/10408418209104488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiodini R. J. Biochemical characteristics of various strains of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Jul;47(7):1442–1445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiodini R. J., Van Kruiningen H. J., Merkal R. S. Ruminant paratuberculosis (Johne's disease): the current status and future prospects. Cornell Vet. 1984 Jul;74(3):218–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb J. J., Wickenden C., Snell M. E., Hulme B., Malcolm A. D., Coleman D. V. Use of hybridot assay to screen for BK and JC polyomaviruses in non-immunosuppressed patients. J Clin Pathol. 1987 Jul;40(7):777–781. doi: 10.1136/jcp.40.7.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donald B. Occurrence of mycobacteria in normal bovine lymph nodes. Aust Vet J. 1983 Aug;60(8):256–257. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1983.tb05984.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Embury S. H., Scharf S. J., Saiki R. K., Gholson M. A., Golbus M., Arnheim N., Erlich H. A. Rapid prenatal diagnosis of sickle cell anemia by a new method of DNA analysis. N Engl J Med. 1987 Mar 12;316(11):656–661. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198703123161103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill E. B., Wayne L. G., Gross W. M. Purification of mycobacterial deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1972 Dec;112(3):1033–1039. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.3.1033-1039.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley S. S., Splitter G. A., Welch R. A. Rapid lysis technique for mycobacterial species. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Nov;25(11):2227–2229. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.11.2227-2229.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuritza A. P., Getty C. E., Shaughnessy P., Hesse R., Salyers A. A. DNA probes for identification of clinically important Bacteroides species. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Feb;23(2):343–349. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.2.343-349.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LARSEN A. B., KOPECKY K. E. STUDIES ON THE INTRAVENOUS ADMINISTRATION OF JOHNIN TO DIAGNOSE JOHNE'S DISEASE. Am J Vet Res. 1965 May;26:673–675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen A. B., Merkal R. S., Cutlip R. C. Age of cattle as related to resistance to infection with Mycobacterium paratuberculosis. Am J Vet Res. 1975 Mar;36(3):255–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews P. R., McDiarmid A., Collins P., Brown A. The dependence of some strains of Mycobacterium avium on mycobactin for initial and subsequent growth. J Med Microbiol. 1978 Feb;11(1):53–57. doi: 10.1099/00222615-11-1-53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merkal R. S., Thurston J. R. Comparison of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis and other mycobacteria, using standard cytochemical tests. Am J Vet Res. 1966 Mar;27(117):519–521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley S. L., Echeverria P., Seriwatana J., Tirapat C., Chaicumpa W., Sakuldaipeara T., Falkow S. Identification of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli by colony hybridization using three enterotoxin gene probes. J Infect Dis. 1982 Jun;145(6):863–869. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.6.863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musial C. E., Tice L. S., Stockman L., Roberts G. D. Identification of mycobacteria from culture by using the Gen-Probe Rapid Diagnostic System for Mycobacterium avium complex and Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Oct;26(10):2120–2123. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.10.2120-2123.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M. C., McMillan C., Coyle M. B. Whole chromosomal DNA probes for rapid identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium avium complex. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jul;25(7):1239–1243. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.7.1239-1243.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salyers A. A., Lynn S. P., Gardner J. F. Use of randomly cloned DNA fragments for identification of Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):287–293. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.287-293.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Totten P. A., Holmes K. K., Handsfield H. H., Knapp J. S., Perine P. L., Falkow S. DNA hybridization technique for the detection of Neisseria gonorrhoeae in men with urethritis. J Infect Dis. 1983 Sep;148(3):462–471. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.3.462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]