Abstract
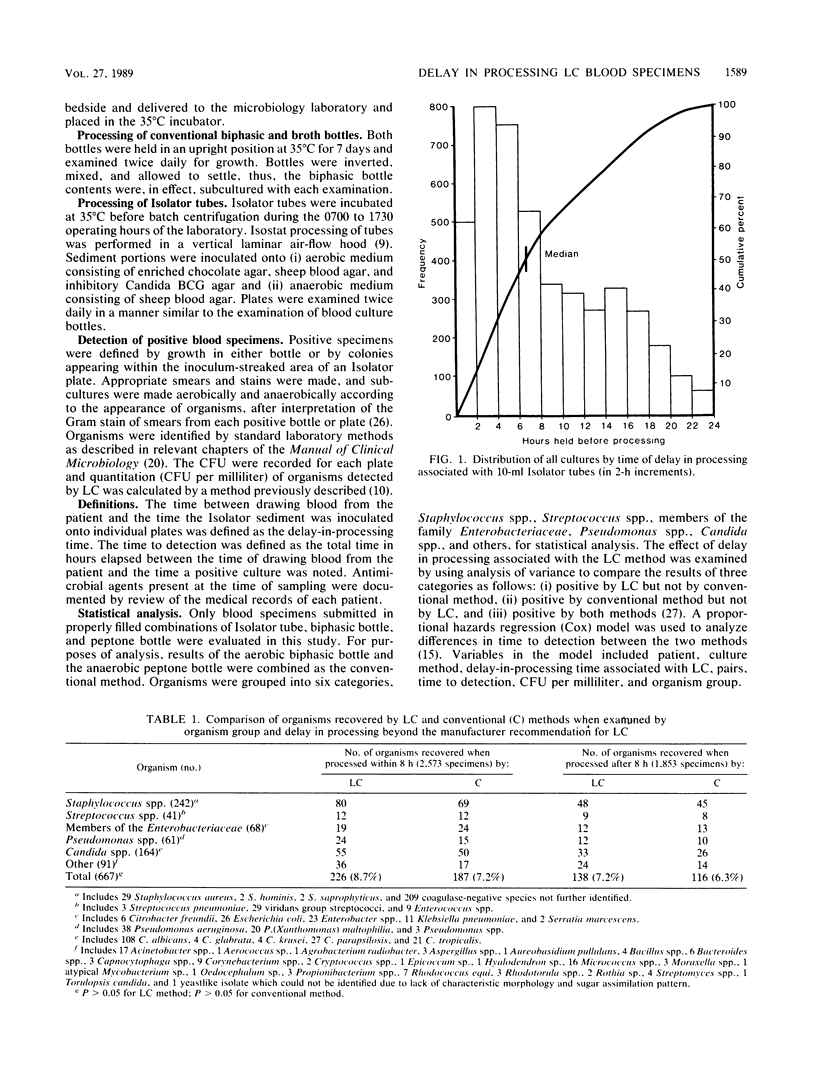
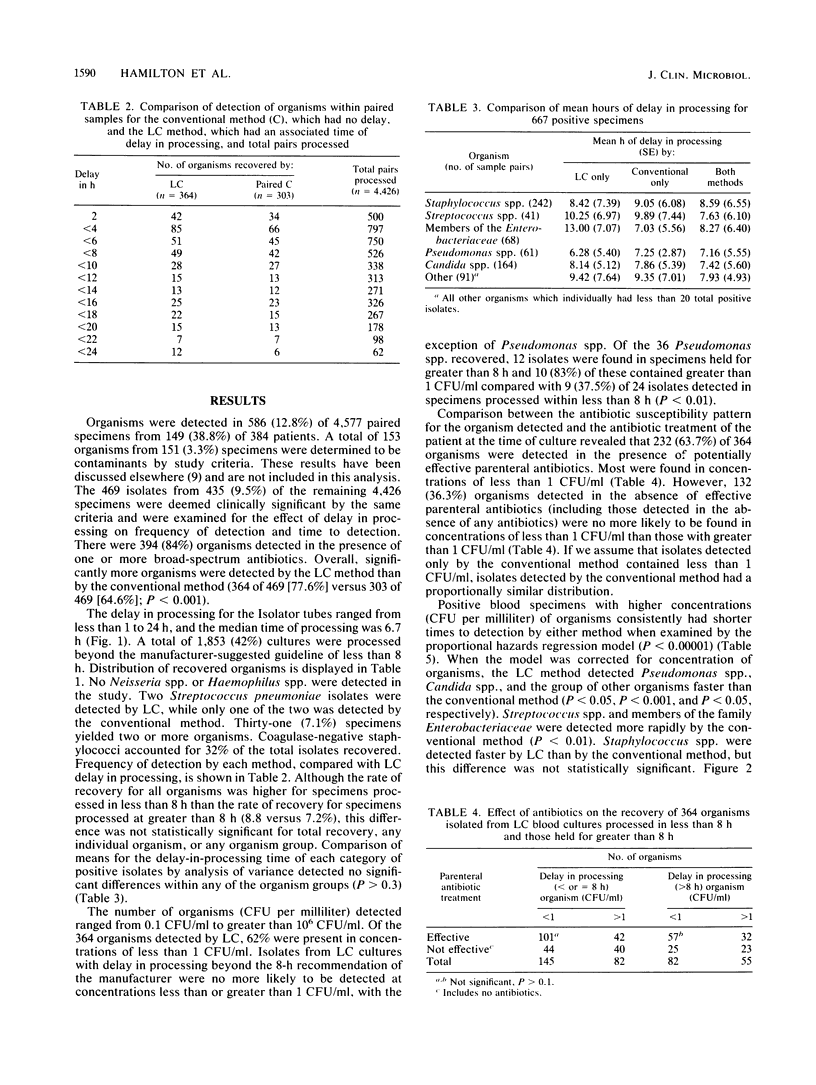
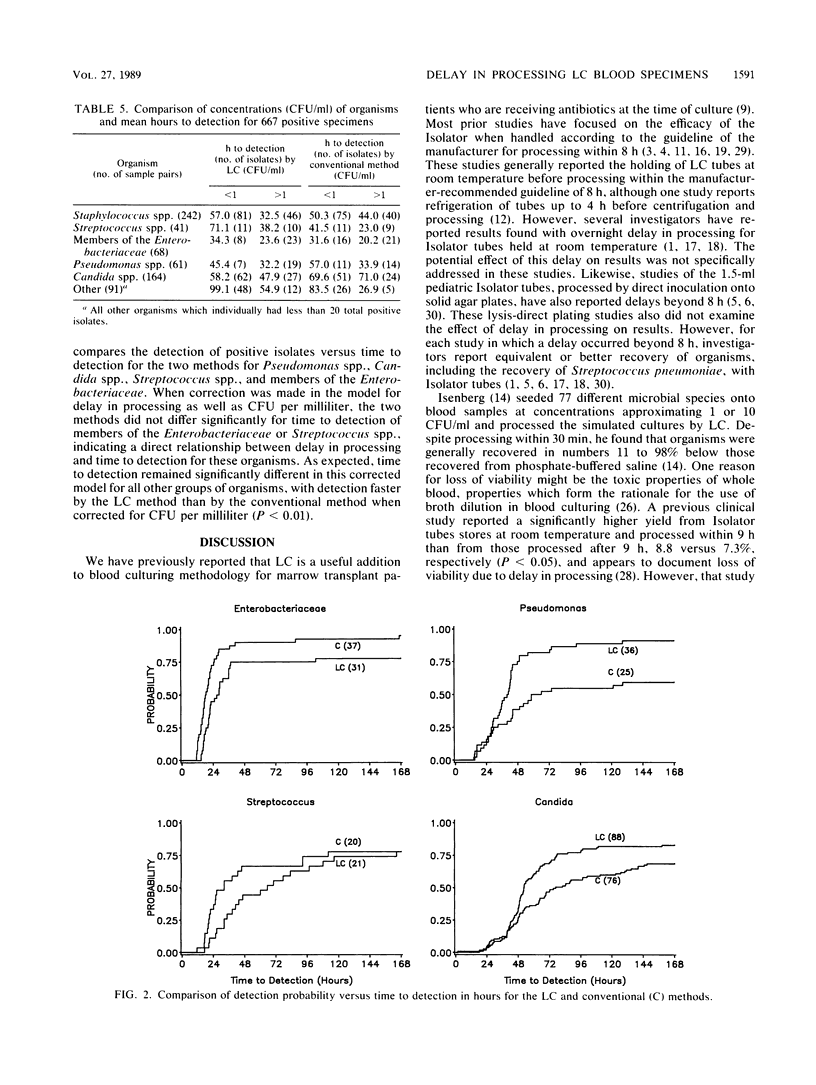
The effect of delay in processing on results of lysis-centrifugation (LC; Isolator) blood cultures was assessed in 4,577 paired blood specimens. Blood specimens were obtained at all hours from 384 febrile marrow transplant patients with indwelling venous catheters and were processed by the LC technique and by a conventional two-bottle method. Most patients (84%) were receiving broad-spectrum antibiotics at the time of blood culture. Specimens were delivered to the laboratory, where Isolator tubes were held at 35 degrees C and processed in batches between 0700 and 1730 h daily. This procedure resulted in a delay beyond the manufacturer-suggested processing time of less than 8 h for 1,853 (42%) of the LC cultures. There was no overall difference in the recovery of organisms present in LC cultures processed after being held for 8 to 24 h compared with the conventional two-bottle method. LC methodology had shorter time to detection than the conventional method for detection of Candida spp. and Pseudomonas spp. (P less than 0.05). However, time to detection for Streptococcus spp. and members of the family Enterobacteriaceae, responsible for 16.3% of total isolates, was prolonged significantly by delay in processing when compared with the conventional two-bottle method (P less than 0.01). Results of this study support the recommendation of the manufacturer for processing of Isolator tubes within 8 h or less. Although one can safely delay processing beyond 8 h in terms of total recovery of organisms, such delays were associated with longer time to detection for certain important potentially pathogenic organisms which accounted for a sizeable proportion of blood culture isolates from marrow transplant patients.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bille J., Edson R. S., Roberts G. D. Clinical evaluation of the lysis-centrifugation blood culture system for the detection of fungemia and comparison with a conventional biphasic broth blood culture system. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):126–128. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.126-128.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodey G. P., Bolivar R., Fainstein V., Jadeja L. Infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Mar-Apr;5(2):279–313. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.2.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brannon P., Kiehn T. E. Clinical comparison of lysis-centrifugation and radiometric resin systems for blood culture. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Nov;24(5):886–887. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.5.886-887.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brannon P., Kiehn T. E. Large-scale clinical comparison of the lysis-centrifugation and radiometric systems for blood culture. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Dec;22(6):951–954. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.6.951-954.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campos J. M., Spainhour J. R. Comparison of the Isolator 1.5 Microbial Tube with a conventional blood culture broth system for detection of bacteremia in children. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1985 Mar;3(2):167–174. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(85)90027-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey R. B. Clinical comparison of the Isolator 1.5 microbial tube and the BACTEC radiometric system for detection of bacteremia in children. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 May;19(5):634–638. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.5.634-638.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashman J. S., Boshard R., Matsen J. M. Viability of organisms held in the isolator blood culture system for 15 h and their rapid detection by acridine orange staining. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Sep;18(3):709–712. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.3.709-712.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Counts G. W., Schwartz R. W., Ulness B. K., Hamilton D. J., Rosok M. J., Cunningham M. D., Tam M. R., Darveau R. P. Evaluation of an immunofluorescent-antibody test for rapid identification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in blood cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jun;26(6):1161–1165. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.6.1161-1165.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry N. K., Grewell C. M., Van Grevenhof P. E., Ilstrup D. M., Washington J. A., 2nd Comparison of lysis-centrifugation with a biphasic blood culture medium for the recovery of aerobic and facultatively anaerobic bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Sep;20(3):413–416. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.3.413-416.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry N. K., McLimans C. A., Wright A. J., Thompson R. L., Wilson W. R., Washington J. A., 2nd Microbiological and clinical evaluation of the isolator lysis-centrifugation blood culture tube. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 May;17(5):864–869. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.5.864-869.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman R. O., Buckner C. D., Clift R. A., Sanders J. E., Stewart P., Thomas E. D. A modified right atrial catheter for access to the venous system in marrow transplant recipients. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1979 Jun;148(6):871–875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg J. A., Manzella J. P., McConville J. H. Clinical laboratory comparison of the 10-ml isolator blood culture system with BACTEC radiometric blood culture media. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Oct;20(4):618–623. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.4.618-623.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M. T., Buck G. E., Fojtasek M. F. Evaluation of a lysis-centrifugation and biphasic bottle blood culture system during routine use. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Sep;18(3):554–557. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.3.554-557.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M. T., Fojtasek M. F., Abbott T. M., Hale D. C., Dizikes J. R., Boshard R., Buck G. E., Martin W. J., Matsen J. M. Clinical evaluation of a lysis-centrifugation technique for the detection of septicemia. JAMA. 1983 Oct 28;250(16):2185–2188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiehn T. E., Wong B., Edwards F. F., Armstrong D. Comparative recovery of bacteria and yeasts from lysis-centrifugation and a conventional blood culture system. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;18(2):300–304. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.2.300-304.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie R., Reimer L. G. Effect of antimicrobials on blood cultures in endocarditis. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1987 Nov;8(3):165–172. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(87)90167-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody J. A., Fasching C. E., Shanholtzer C. J., Gerding D. N., Peterson L. R. Evaluation of new blood culture processing systems. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Sep;20(3):351–356. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.3.351-356.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pazin G. J., Saul S., Thompson M. E. Blood culture positivity: suppression by outpatient antibiotic therapy in patients with bacterial endocarditis. Arch Intern Med. 1982 Feb;142(2):263–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzo P. A., Robichaud K. J., Gill F. A., Witebsky F. G., Levine A. S., Deisseroth A. B., Glaubiger D. L., Maclowry J. D., Magrath I. T., Poplack D. G. Duration of empiric antibiotic therapy in granulocytopenic patients with cancer. Am J Med. 1979 Aug;67(2):194–200. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(79)90390-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockman L., Roberts G. D., Ilstrup D. M. Effect of storage of the du Pont lysis-centrifugation system on recovery of bacteria and fungi in a prospective clinical trial. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):283–285. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.283-285.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R. C., Henry N. K., Washington J. A., 2nd, Thompson R. L. Lysis-centrifugation blood culture technique. Clinical impact in Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. Arch Intern Med. 1986 Dec;146(12):2341–2343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch D. F., Scribner R. K., Hensel D. Evaluation of a lysis direct plating method for pediatric blood cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jun;21(6):955–958. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.6.955-958.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


