Abstract
An ear punch biopsy method for the detection and isolation of Borrelia burgdorferi from rodents was developed. The ear punch biopsy proved to be extremely sensitive, detecting spirochetes in 100% (11 of 11) of laboratory hamsters infected by tick bite and 95.8% (23 of 24) of hamsters infected by intraperitoneal inoculation. When cultured at 4 to 6 weeks postinfection, 92 to 100% of the ear punches taken from individual hamsters yielded viable spirochetes. B. burgdorferi was detected in sequential cultures from animals as early as 4 days postinfection and as late as 20 weeks postinfection. A total of 86% (6 of 7) of field-collected white-footed mice (Peromyscus leucopus) which were positive for B. burgdorferi as determined by xenodiagnosis were also positive by the ear punch method. The ear punch biopsy method allows individual rodents to be sampled for B. burgdorferi serially over a long period and thus should prove useful for both field and laboratory experiments.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
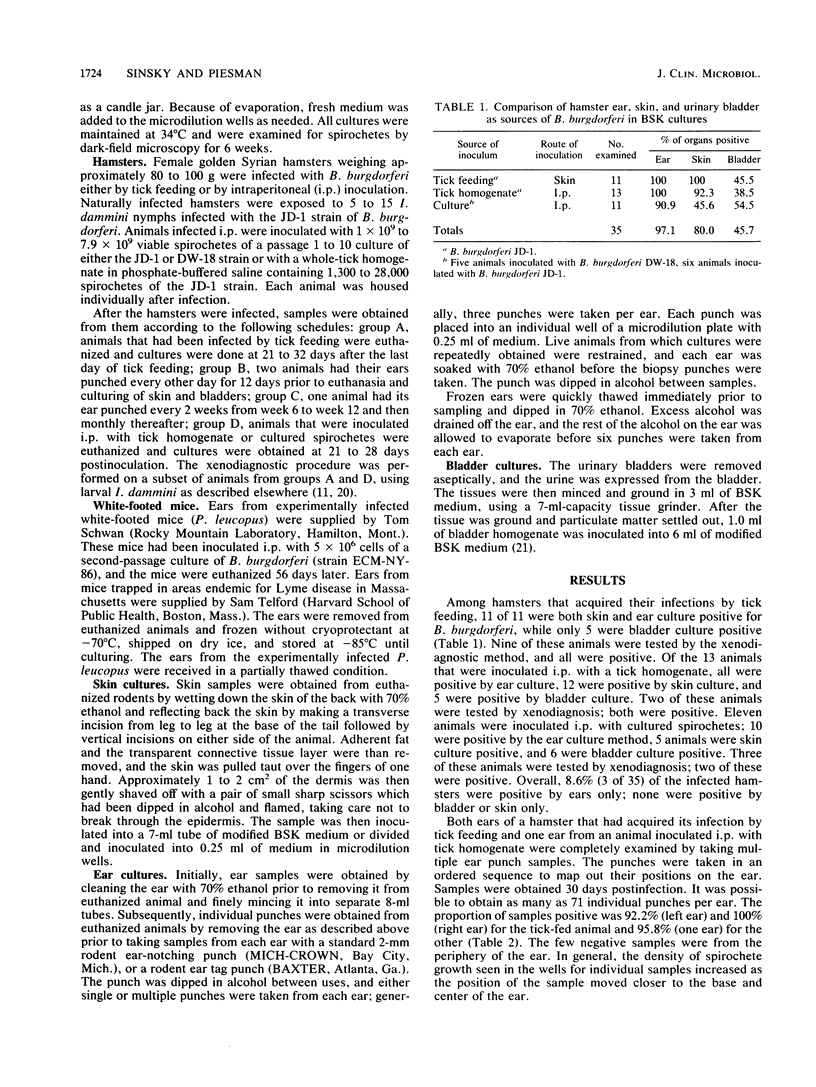
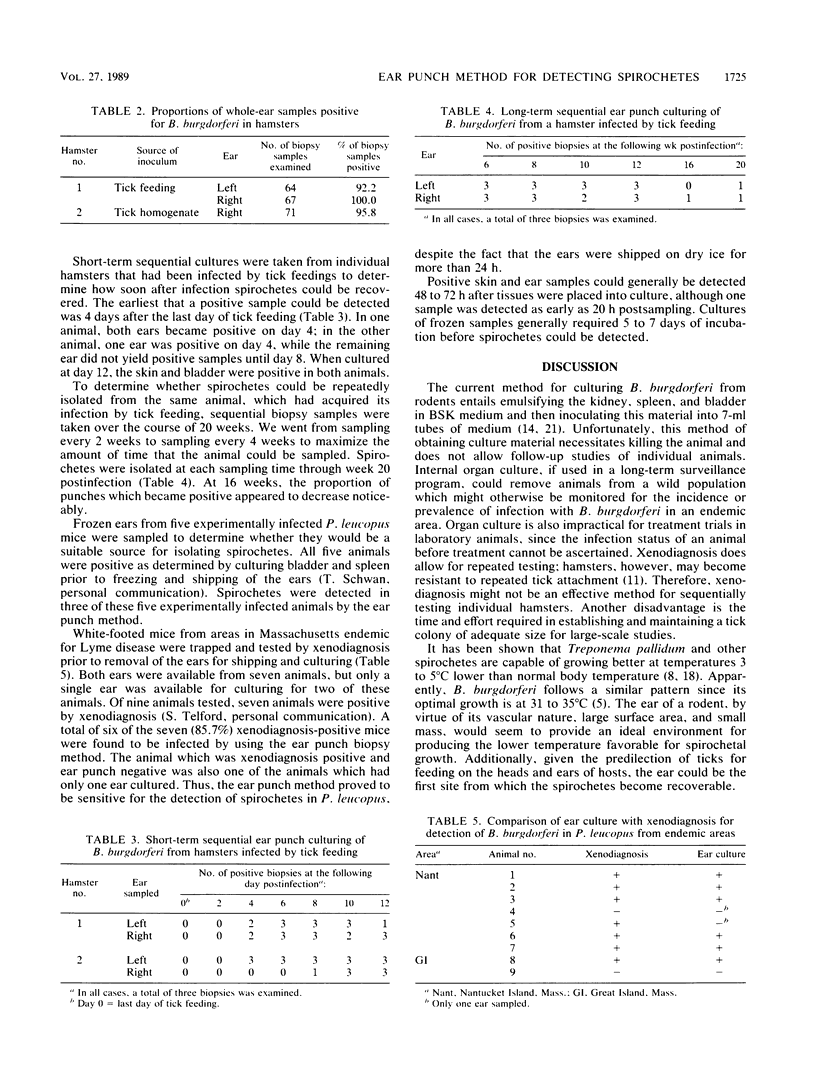
- Anderson J. F., Johnson R. C., Magnarelli L. A., Hyde F. W. Identification of endemic foci of Lyme disease: isolation of Borrelia burgdorferi from feral rodents and ticks (Dermacentor variabilis). J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jul;22(1):36–38. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.1.36-38.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. F., Johnson R. C., Magnarelli L. A. Seasonal prevalence of Borrelia burgdorferi in natural populations of white-footed mice, Peromyscus leucopus. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;25(8):1564–1566. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.8.1564-1566.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asbrink E., Hovmark A. Early and late cutaneous manifestations in Ixodes-borne borreliosis (erythema migrans borreliosis, Lyme borreliosis). Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:4–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31833.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asbrink E., Olsson I., Hovmark A. Erythema chronicum migrans Afzelius in Sweden. A study on 231 patients. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1986 Dec;263(1-2):229–236. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(86)80126-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Isolation and cultivation of Lyme disease spirochetes. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):521–525. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold S. W., Moody K. D., Terwilliger G. A., Duray P. H., Jacoby R. O., Steere A. C. Experimental Lyme arthritis in rats infected with Borrelia burgdorferi. J Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;157(4):842–846. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.4.842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benach J. L., Bosler E. M., Hanrahan J. P., Coleman J. L., Habicht G. S., Bast T. F., Cameron D. J., Ziegler J. L., Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W. Spirochetes isolated from the blood of two patients with Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 31;308(13):740–742. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303313081302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosler E. M., Coleman J. L., Benach J. L., Massey D. A., Hanrahan J. P., Burgdorfer W., Barbour A. G. Natural Distribution of the Ixodes dammini spirochete. Science. 1983 Apr 15;220(4594):321–322. doi: 10.1126/science.6836274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Benach J. L., Grunwaldt E., Davis J. P. Lyme disease-a tick-borne spirochetosis? Science. 1982 Jun 18;216(4552):1317–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.7043737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donahue J. G., Piesman J., Spielman A. Reservoir competence of white-footed mice for Lyme disease spirochetes. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1987 Jan;36(1):92–96. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1987.36.92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duray P. H., Johnson R. C. The histopathology of experimentally infected hamsters with the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1986 Feb;181(2):263–269. doi: 10.3181/00379727-181-42251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Kodner C., Russell M. Active immunization of hamsters against experimental infection with Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):897–898. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.897-898.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Marek N., Kodner C. Infection of Syrian hamsters with Lyme disease spirochetes. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Dec;20(6):1099–1101. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.6.1099-1101.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald A. B., Benach J. L., Burgdorfer W. Stillbirth following maternal Lyme disease. N Y State J Med. 1987 Nov;87(11):615–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnarelli L. A., Anderson J. F., Hyland K. E., Fish D., Mcaninch J. B. Serologic analyses of Peromyscus leucopus, a rodent reservoir for Borrelia burgdorferi, in northeastern United States. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jun;26(6):1138–1141. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.6.1138-1141.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnarelli L. A. Serologic diagnosis of Lyme disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:154–161. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31848.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neubert U., Krampitz H. E., Engl H. Microbiological findings in erythema (chronicum) migrans and related disorders. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1986 Dec;263(1-2):237–252. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(86)80127-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piesman J., Mather T. N., Sinsky R. J., Spielman A. Duration of tick attachment and Borrelia burgdorferi transmission. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Mar;25(3):557–558. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.3.557-558.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan T. G., Burgdorfer W., Schrumpf M. E., Karstens R. H. The urinary bladder, a consistent source of Borrelia burgdorferi in experimentally infected white-footed mice (Peromyscus leucopus). J Clin Microbiol. 1988 May;26(5):893–895. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.5.893-895.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Grodzicki R. L., Kornblatt A. N., Craft J. E., Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W., Schmid G. P., Johnson E., Malawista S. E. The spirochetal etiology of Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 31;308(13):733–740. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303313081301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Pachner A. R., Malawista S. E. Neurologic abnormalities of Lyme disease: successful treatment with high-dose intravenous penicillin. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Dec;99(6):767–772. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-6-767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



