Abstract
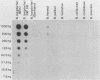
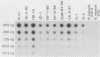
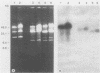
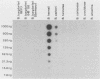
Fragments of plasmid DNA from Borrelia burgdorferi and B. hermsii were cloned and tested for specificity as hybridization probes to identify these two species of pathogenic spirochetes. Three fragments from the 49-kilobase-pair linear plasmid of B. burgdorferi were tested: a 500-base-pair (bp) HindIII fragment (probe 49A), a 445-bp PstI-HindIII fragment (probe 3G), and a 320-bp HindIII fragment (probe 16H). When hybridized to purified DNA or whole spirochetes, all of the probes distinguished B. burgdorferi from the other species examined, including B. hermsii, B. parkeri, B. turicatae, B. coriaceae, B. crocidurae, and B. anserina. Probe 49A was the most useful, however, hybridizing with all strains of B. burgdorferi originating from both North America and Europe while not cross-hybridizing with B. hermsii. A 790-bp HindIII fragment of B. hermsii DNA hybridized with DNA and whole spirochetes of this species and also with B. parkeri, confirming the close relatedness of these two species. These probes provide a new method of identifying these Borrelia species once the organisms have been grown in culture.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F. Biology of Borrelia species. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Dec;50(4):381–400. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.4.381-400.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Heiland R. A., Howe T. R. Heterogeneity of major proteins in Lyme disease borreliae: a molecular analysis of North American and European isolates. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):478–484. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Isolation and cultivation of Lyme disease spirochetes. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):521–525. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Plasmid analysis of Borrelia burgdorferi, the Lyme disease agent. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Mar;26(3):475–478. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.3.475-478.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Tessier S. L., Hayes S. F. Variation in a major surface protein of Lyme disease spirochetes. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):94–100. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.94-100.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker R. H., Jr, Suebsaeng L., Rooney W., Alecrim G. C., Dourado H. V., Wirth D. F. Specific DNA probe for the diagnosis of Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Science. 1986 Mar 21;231(4744):1434–1436. doi: 10.1126/science.3513309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissett M. L., Hill W. Characterization of Borrelia burgdorferi strains isolated from Ixodes pacificus ticks in California. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Dec;25(12):2296–2301. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.12.2296-2301.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Benach J. L., Grunwaldt E., Davis J. P. Lyme disease-a tick-borne spirochetosis? Science. 1982 Jun 18;216(4552):1317–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.7043737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoogstraal H. Ticks and spirochetes. Acta Trop. 1979 Jun;36(2):133–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe T. R., LaQuier F. W., Barbour A. G. Organization of genes encoding two outer membrane proteins of the Lyme disease agent Borrelia burgdorferi within a single transcriptional unit. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):207–212. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.207-212.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huppertz H. I., Sticht-Groh V., Schwan T. Borderline antibody response in initial stages of lymphocytic meningitis does not rule out borreliosis. Lancet. 1986 Dec 20;2(8521-22):1468–1469. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92789-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde F. W., Johnson R. C. Genetic relationship of lyme disease spirochetes to Borrelia, Treponema, and Leptospira spp. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Aug;20(2):151–154. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.2.151-154.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kukla B. A., Majiwa P. A., Young J. R., Moloo S. K., ole-MoiYoi O. K. Use of species-specific DNA probes for detection and identification of trypanosome infection in tsetse flies. Parasitology. 1987 Aug;95(Pt 1):1–16. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000057498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane R. S., Burgdorfer W., Hayes S. F., Barbour A. G. Isolation of a spirochete from the soft tick, Ornithodoros coriaceus: a possible agent of epizootic bovine abortion. Science. 1985 Oct 4;230(4721):85–87. doi: 10.1126/science.3898367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonough K. A., Schwan T. G., Thomas R. E., Falkow S. Identification of a Yersinia pestis-specific DNA probe with potential for use in plague surveillance. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Dec;26(12):2515–2519. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.12.2515-2519.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson K., Blair C., Padmanabhan R., Beaty B. Detection of dengue virus type 2 in Aedes albopictus by nucleic acid hybridization with strand-specific RNA probes. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Mar;26(3):579–581. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.3.579-581.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piesman J., Mather T. N., Sinsky R. J., Spielman A. Duration of tick attachment and Borrelia burgdorferi transmission. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Mar;25(3):557–558. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.3.557-558.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plasterk R. H., Simon M. I., Barbour A. G. Transposition of structural genes to an expression sequence on a linear plasmid causes antigenic variation in the bacterium Borrelia hermsii. Nature. 1985 Nov 21;318(6043):257–263. doi: 10.1038/318257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M. C., Moncla B., Kenny G. E. Chromosomal DNA probes for the identification of Bacteroides species. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Jun;133(6):1423–1430. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-6-1423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan T. G., Burgdorfer W. Antigenic changes of Borrelia burgdorferi as a result of in vitro cultivation. J Infect Dis. 1987 Nov;156(5):852–853. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.5.852-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan T. G., Burgdorfer W., Garon C. F. Changes in infectivity and plasmid profile of the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi, as a result of in vitro cultivation. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1831–1836. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1831-1836.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan T. G., Burgdorfer W., Schrumpf M. E., Karstens R. H. The urinary bladder, a consistent source of Borrelia burgdorferi in experimentally infected white-footed mice (Peromyscus leucopus). J Clin Microbiol. 1988 May;26(5):893–895. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.5.893-895.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Grodzicki R. L., Kornblatt A. N., Craft J. E., Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W., Schmid G. P., Johnson E., Malawista S. E. The spirochetal etiology of Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 31;308(13):733–740. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303313081301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Malawista S. E., Snydman D. R., Shope R. E., Andiman W. A., Ross M. R., Steele F. M. Lyme arthritis: an epidemic of oligoarticular arthritis in children and adults in three connecticut communities. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Jan-Feb;20(1):7–17. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoenner H. G. Biology of Borrelia hermsii in Kelly medium. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Oct;28(4):540–543. doi: 10.1128/am.28.4.540-543.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoenner H. G., Dodd T., Larsen C. Antigenic variation of Borrelia hermsii. J Exp Med. 1982 Nov 1;156(5):1297–1311. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.5.1297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenover F. C. Diagnostic deoxyribonucleic acid probes for infectious diseases. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1988 Jan;1(1):82–101. doi: 10.1128/cmr.1.1.82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]