Abstract
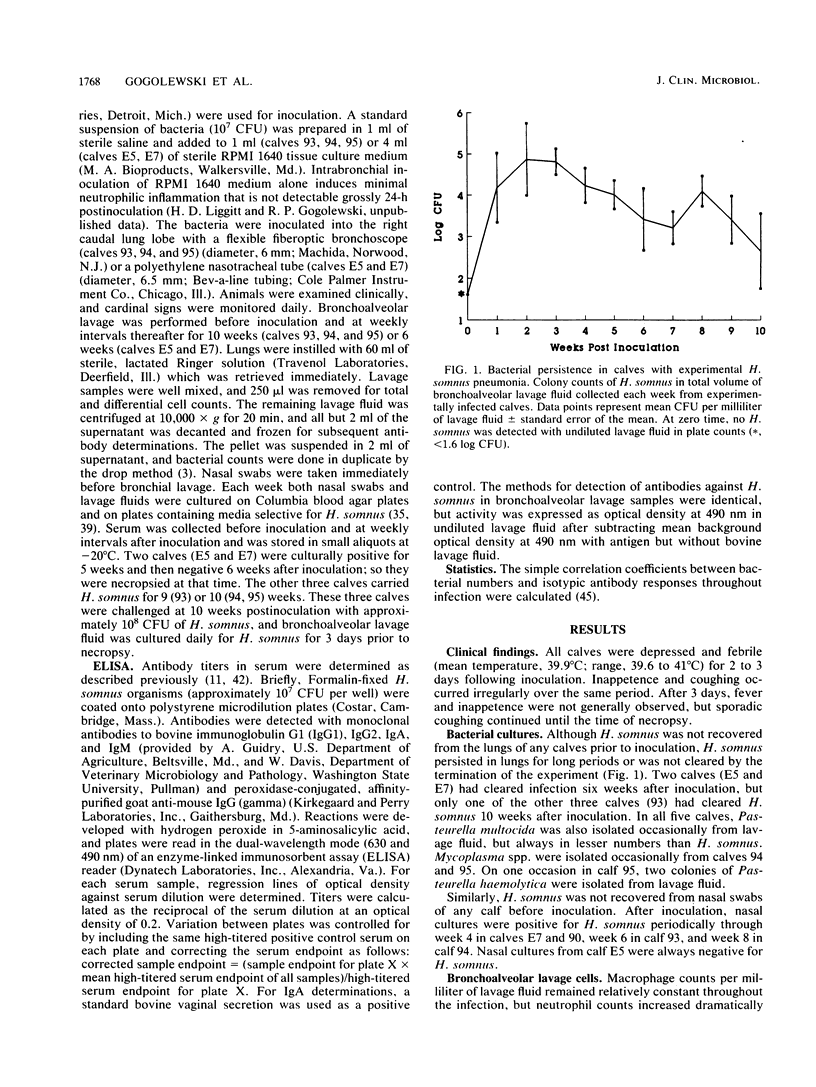
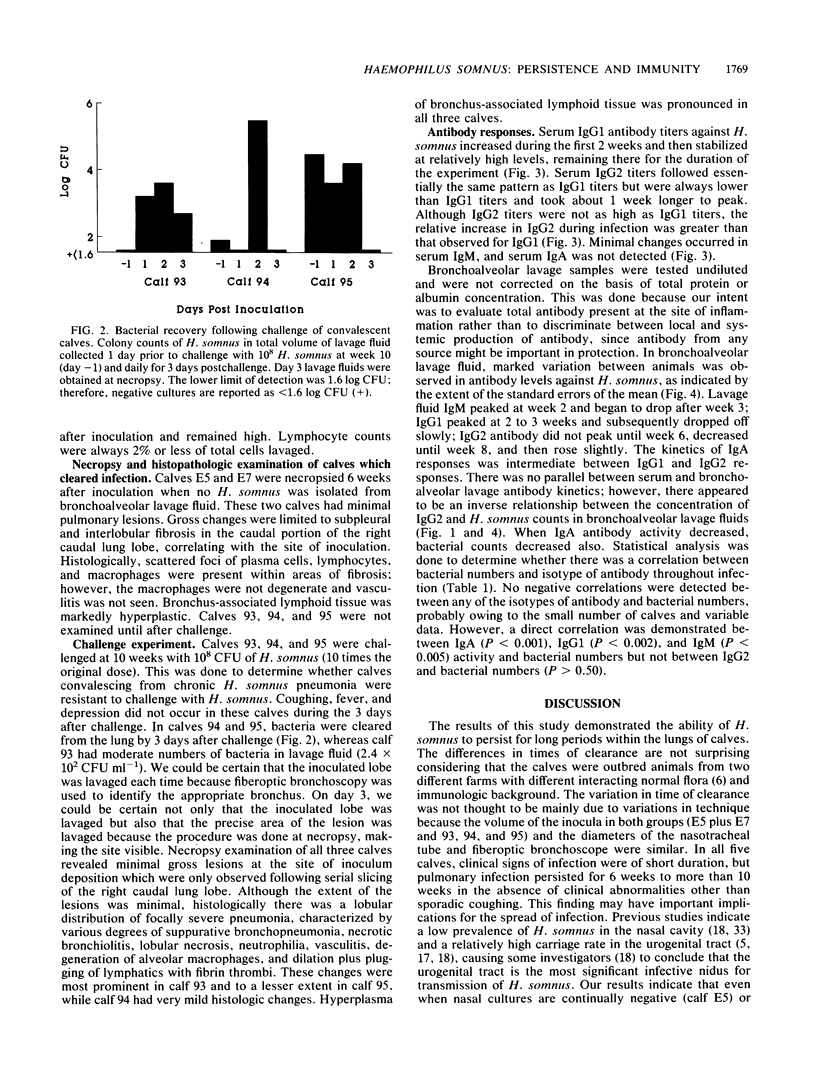
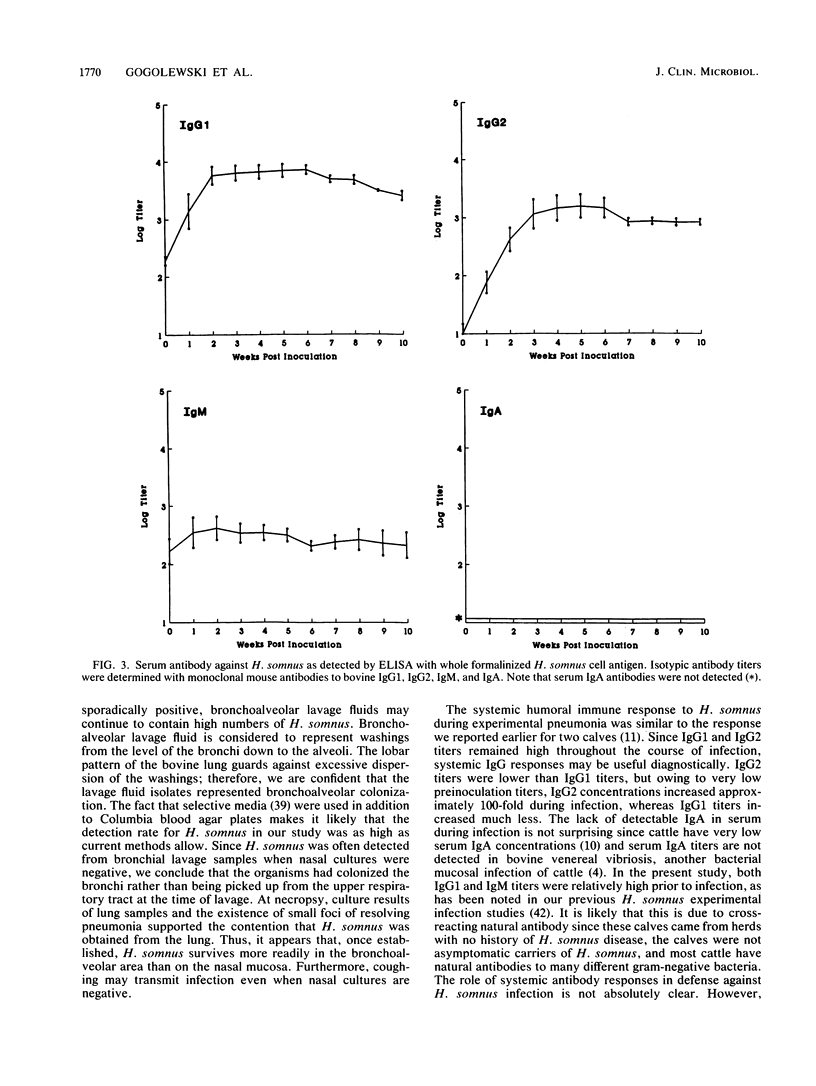
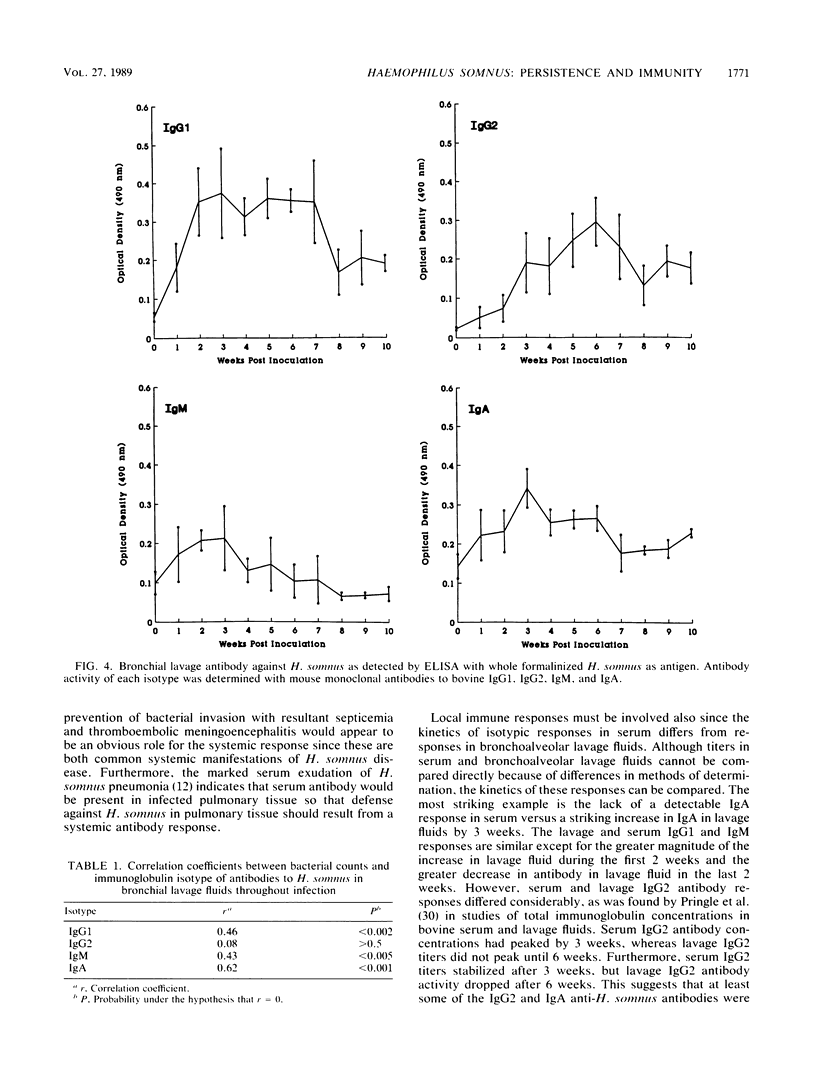
Chronic experimental Haemophilus somnus pneumonia was produced in five 8- to 12-week-old calves to investigate host-parasite relationships in the respiratory tract. Calves were depressed and pyrexic and coughed intermittently for 3 days and then recovered except for sporadic coughing. Bacteria persisted in the lung for 6 to 10 weeks or more. Immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1), IgG2, and IgM but no IgA antibodies specific for H. somnus were detected in serum. Bronchoalveolar lavage samples contained detectable IgG1, IgG2, IgM, and IgA antibodies specific for H. somnus throughout most of the experiment. The kinetics of the isotypic antibody response against H. somnus in serum and bronchoalveolar lavage fluids differed, suggesting that both local and systemic antibody responses had occurred. Persistence of pulmonary infection for 10 weeks or more in the presence of antibody may be due to an inappropriate distribution of isotypes, toxicity of H. somnus for bovine macrophages, and perhaps other factors. Three of the calves were challenged with a 10-fold-higher dose of H. somnus at 10 weeks after the original inoculation. Immunity against H. somnus was indicated by the rapid clearance of bacteria from the lungs and the presence of minimal pneumonia at necropsy 3 days after bacterial challenge.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews J. J., Anderson T. D., Slife L. N., Stevenson G. W. Microscopic lesions associated with the isolation of Haemophilus somnus from pneumonic bovine lungs. Vet Pathol. 1985 Mar;22(2):131–136. doi: 10.1177/030098588502200206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chladek D. W. Bovine abortion associated with Haemophilus somnus. Am J Vet Res. 1975 Jul;36(7):1041–1041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbeil L. B., Blau K., Prieur D. J., Ward A. C. Serum susceptibility of Haemophilus somnus from bovine clinical cases and carriers. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Aug;22(2):192–198. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.2.192-198.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbeil L. B., Duncan J. R., Schurig G. G., Hall C. E., Winter A. J. Bovine venereal vibriosis: variations in immunoglobulin class of antibodies in genital secretions and serum. Infect Immun. 1974 Nov;10(5):1084–1090. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.5.1084-1090.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbeil L. B., Woodward W., Ward A. C., Mickelsen W. D., Paisley L. Bacterial interactions in bovine respiratory and reproductive infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 May;21(5):803–807. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.5.803-807.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corboz L., Pohlenz J. Experimentelle Infektionen mit sogenanntem Haemophilus somnus beim Kalb: Vergleich von Stämmen mit unterschiedlicher Virulenz. Schweiz Arch Tierheilkd. 1976 Oct;118(10):429–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czuprynski C. J., Hamilton H. L. Bovine neutrophils ingest but do not kill Haemophilus somnus in vitro. Infect Immun. 1985 Nov;50(2):431–436. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.2.431-436.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dossett J. H., Kronvall G., Williams R. C., Jr, Quie P. G. Antiphagocytic effects of staphylococcal protein A. J Immunol. 1969 Dec;103(6):1405–1410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan J. R., Wilkie B. N., Hiestand F., Winter A. J. The serum and secretory immunoglobulins of cattle: characterization and quantitation. J Immunol. 1972 Apr;108(4):965–976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gogolewski R. P., Kania S. A., Inzana T. J., Widders P. R., Liggitt H. D., Corbeil L. B. Protective ability and specificity of convalescent serum from calves with Haemophilus somnus pneumonia. Infect Immun. 1987 Jun;55(6):1403–1411. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.6.1403-1411.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gogolewski R. P., Leathers C. W., Liggitt H. D., Corbeil L. B. Experimental Haemophilus somnus pneumonia in calves and immunoperoxidase localization of bacteria. Vet Pathol. 1987 May;24(3):250–256. doi: 10.1177/030098588702400309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heikkilä R., Takala A., Käyhty H., Leinonen M. Latex agglutination test for screening of Haemophilus influenzae type b carriers. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jun;25(6):1131–1133. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.6.1131-1133.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard R. D., Kaeberle M. L., Roth J. A., Chiang Y. W. Haemophilus somnus-induced interference with bovine neutrophil functions. Vet Microbiol. 1986 Jun;12(1):77–85. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(86)90043-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey J. D., Little P. B., Barnum D. A., Doig P. A., Stephens L. R., Thorsen J. Occurrence of "Haemophilus somnus" in bovine semen and in the prepuce of bulls and steers. Can J Comp Med. 1982 Apr;46(2):215–217. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey J. D., Little P. B., Stephens L. R., Barnum D. A., Doig P. A., Thorsen J. Prevalence and distribution of Haemophilus somnus in the male bovine reproductive tract. Am J Vet Res. 1982 May;43(5):791–795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson J. A., Andrews J. J., Hargis J. W. Experimental Haemophilus somnus pneumonia in calves. Vet Pathol. 1987 Mar;24(2):129–134. doi: 10.1177/030098588702400205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G. A surface component in group A, C, and G streptococci with non-immune reactivity for immunoglobulin G. J Immunol. 1973 Nov;111(5):1401–1406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langone J. J. Protein A of Staphylococcus aureus and related immunoglobulin receptors produced by streptococci and pneumonococci. Adv Immunol. 1982;32:157–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederer J. A., Brown J. F., Czuprynski C. J. "Haemophilus somnus," a facultative intracellular pathogen of bovine mononuclear phagocytes. Infect Immun. 1987 Feb;55(2):381–387. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.2.381-387.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D. C., Schwarz M. I., Matthay R. A., LaForce F. M. Bacteremic hemophilus influenzae pneumonia in adults. A report of 24 cases and a review of the literature. Am J Med. 1977 Feb;62(2):219–224. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(77)90317-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire T. C., Musoke A. J., Kurtti T. Functional properties of bovine IgG1 and IgG2: interaction with complement, macrophages, neutrophils and skin. Immunology. 1979 Oct;38(2):249–256. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musher D. M., Goree A., Baughn R. E., Birdsall H. H. Immunoglobulin A from bronchopulmonary secretions blocks bactericidal and opsonizing effects of antibody to nontypable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):36–40. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.36-40.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musser J. M., Granoff D. M., Pattison P. E., Selander R. K. A population genetic framework for the study of invasive diseases caused by serotype b strains of Haemophilus influenzae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5078–5082. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen K., Stilwell K., Stemshorn B., Duncan R. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (disodium salt)-labile bovine immunoglobulin M Fc binding to Brucella abortus: a cause of nonspecific agglutination. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jul;14(1):32–38. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.1.32-38.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., Verhoef J., Sabath L. D., Quie P. G. Effect of protein A on staphylococcal opsonization. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):760–764. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.760-764.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle J. K., Viel L., Shewen P. E., Willoughby R. A., Martin S. W., Valli V. E. Bronchoalveolar lavage of cranial and caudal lung regions in selected normal calves: cellular, microbiological, immunoglobulin, serological and histological variables. Can J Vet Res. 1988 Apr;52(2):239–248. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard D. G., Shreeve J., Bradley R. The experimental infection of calves with a British strain of Haemophilus somnus. Res Vet Sci. 1979 Jan;26(1):7–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin L. G., Staiman K., Kamani N. Occult bacteremia with nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jul;25(7):1314–1315. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.7.1314-1315.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders J. R., Janzen E. D. Haemophilus somnus infections. II. A Canadian field trial of a commercial bacterin: clinical and serological results. Can Vet J. 1980 Aug;21(8):219–224. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber J. R., Barrus V., Cates K. L., Siber G. R. Functional characterization of human IgG, IgM, and IgA antibody directed to the capsule of Haemophilus influenzae type b. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jan;153(1):8–16. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.1.8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slee K. J., Stephens L. R. Selective medium for isolation of Haemophilus somnus from cattle and sheep. Vet Rec. 1985 Feb 23;116(8):215–217. doi: 10.1136/vr.116.8.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L. R., Little P. B., Wilkie B. N., Barnum D. A. Humoral immunity in experimental thromboembolic meningoencephalitis in cattle caused by Haemophilus somnus. Am J Vet Res. 1981 Mar;42(3):468–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L. R., Little P. B., Wilkie B. N., Barnum D. A. Infectious thromboembolic meningoencephalitis in cattle: a review. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1981 Feb 15;178(4):378–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. J., Jr, Baker C. J., Quinones F. J., Hollis D. G., Weaver R. E., Wiss K. Nontypable Haemophilus influenzae (biotype 4) as a neonatal, maternal, and genital pathogen. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Jan-Feb;5(1):123–136. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.1.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. L. Serological response of sheep to live and killed Staphylococcus aureus vaccines. Vaccine. 1987 Dec;5(4):275–278. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(87)90151-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widders P. R., Paisley L. G., Gogolewski R. P., Evermann J. F., Smith J. W., Corbeil L. B. Experimental abortion and the systemic immune response to "Haemophilus somnus" in cattle. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):555–560. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.555-560.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widders P. R., Stokes C. R., Newby T. J., Bourne F. J. Nonimmune binding of equine immunoglobulin by the causative organism of contagious equine metritis, Taylorella equigenitalis. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):417–421. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.417-421.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie B. N., Markham R. J. Bronchoalveolar washing cells and immunoglobulins of clinically normal calves. Am J Vet Res. 1981 Feb;42(2):241–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



