Abstract
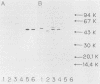
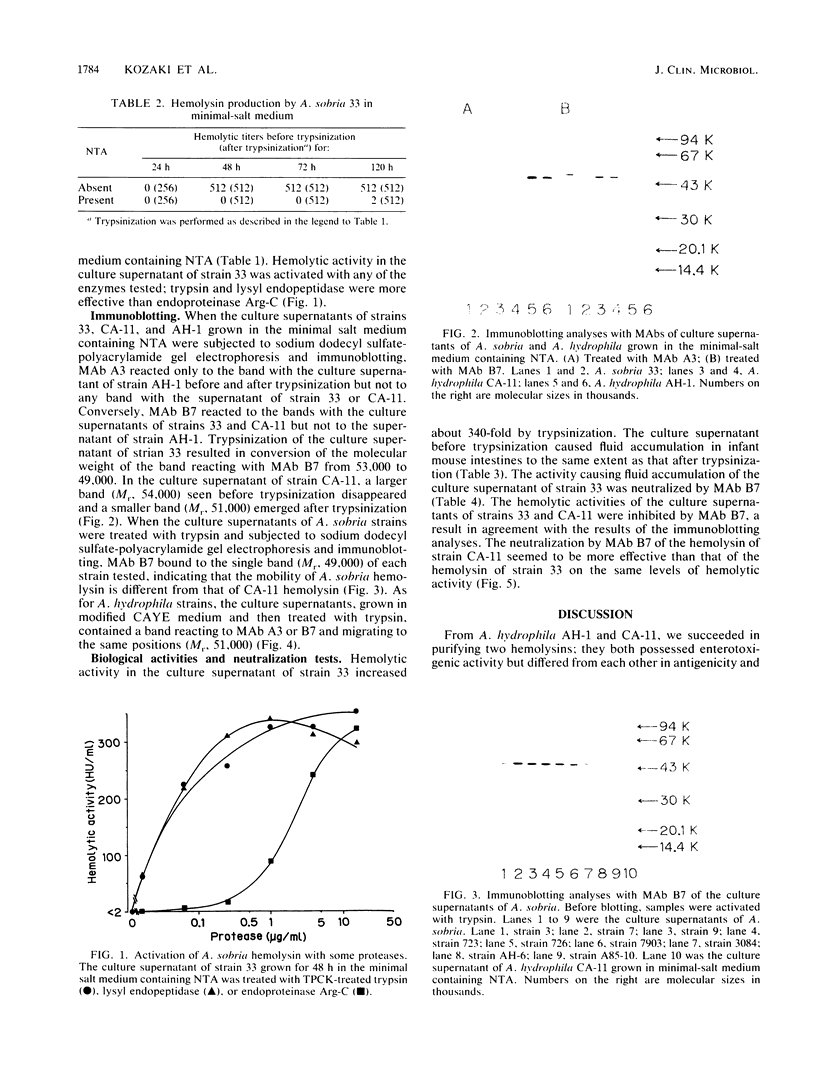
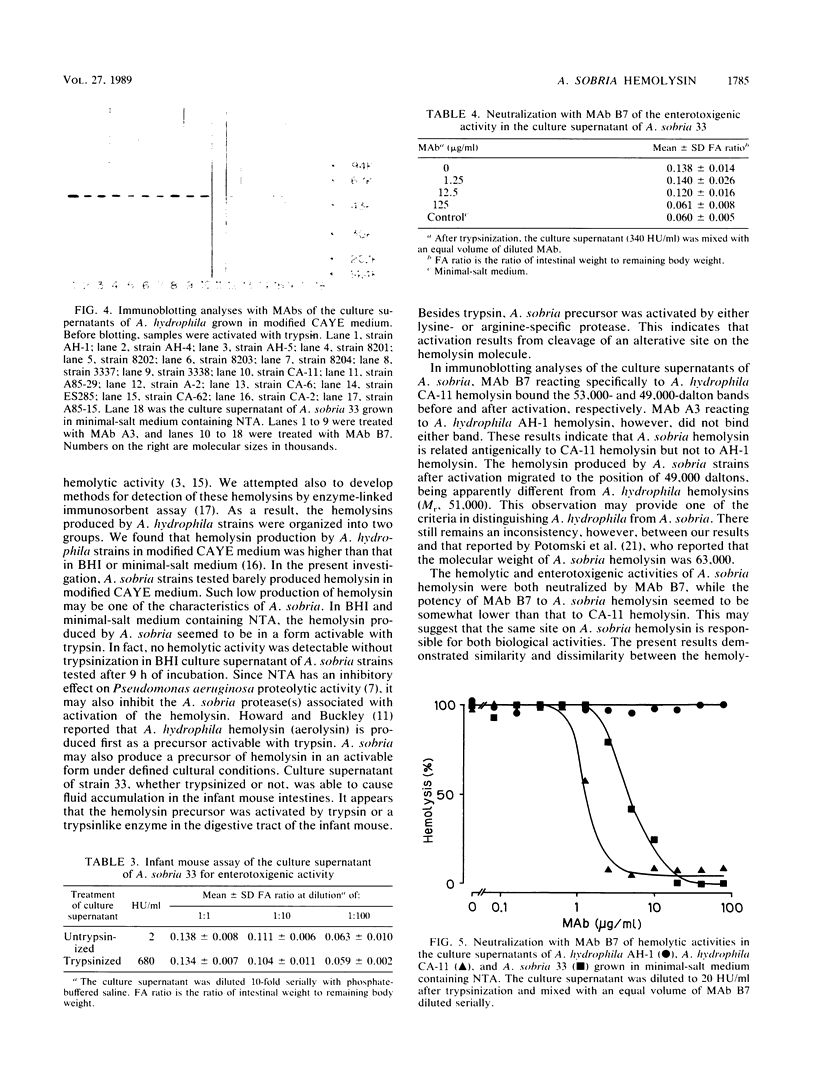
Aeromonas sobria produces hemolysin in a form activable with trypsin under defined cultural conditions. In immunoblotting analyses with the culture supernatant of A. sobria, the monoclonal antibody reacting specifically to Aeromonas hydrophila CA-11 hemolysin bound to the 53,000- and 49,000-dalton bands before and after trypsinization, respectively. The monoclonal antibody reacting to A. hydrophila AH-1 hemolysin did not bind either band. A. sobria hemolysin is, therefore, related antigenically to CA-11 hemolysin, while the molecular weights before and after activation differ from those of A. hydrophila hemolysins, being 54,000 and 51,000, respectively. The hemolytic and enterotoxigenic activities of A. sobria hemolysin were both neutralized by the monoclonal antibody against CA-11 hemolysin. It seems, therefore, that the same site on A. sobria hemolysin is responsible for both biological activities.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agger W. A., McCormick J. D., Gurwith M. J. Clinical and microbiological features of Aeromonas hydrophila-associated diarrhea. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jun;21(6):909–913. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.6.909-913.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asao T., Kinoshita Y., Kozaki S., Uemura T., Sakaguchi G. Purification and some properties of Aeromonas hydrophila hemolysin. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):122–127. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.122-127.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asao T., Kozaki S., Kato K., Kinoshita Y., Otsu K., Uemura T., Sakaguchi G. Purification and characterization of an Aeromonas hydrophila hemolysin. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Aug;24(2):228–232. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.2.228-232.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke V., Gracey M., Robinson J., Peck D., Beaman J., Bundell C. The microbiology of childhood gastroenteritis: Aeromonas species and other infective agents. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jul;148(1):68–74. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.1.68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke V., Robinson J., Atkinson H. M., Gracey M. Biochemical characteristics of enterotoxigenic Aeromonas spp. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jan;15(1):48–52. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.1.48-52.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callahan L. T., 3rd Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin: purification by preparative polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and the development of a highly specific antitoxin serum. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):55–61. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.55-61.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean A. G., Ching Y. C., Williams R. G., Harden L. B. Test for Escherichia coli enterotoxin using infant mice: application in a study of diarrhea in children in Honolulu. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):407–411. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R. L., Fainstein V., Elting L., Hopfer R. L., Bodey G. P. Bacteremia caused by Aeromonas species in hospitalized cancer patients. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 May-Jun;7(3):314–320. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.3.314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hostacká A., Ciznár I., Korych B., Karolcek J. Toxic factors of Aeromonas hydrophila and Plesiomonas shigelloides. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1982 Sep;252(4):525–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard S. P., Buckley J. T. Activation of the hole-forming toxin aerolysin by extracellular processing. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):336–340. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.336-340.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janda J. M., Duffey P. S. Mesophilic aeromonads in human disease: current taxonomy, laboratory identification, and infectious disease spectrum. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Sep-Oct;10(5):980–997. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.5.980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J. B., Lockman H., Colwell R. R., Joseph S. W. Aeromonas hydrophila: ecology and toxigenicity of isolates from an estuary. J Appl Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;50(2):359–377. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1981.tb00900.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozaki S., Kato K., Asao T., Kamata Y., Sakaguchi G. Activities of Aeromonas hydrophila hemolysins and their interaction with erythrocyte membranes. Infect Immun. 1987 Jul;55(7):1594–1599. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.7.1594-1599.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozaki S., Kato K., Kurokawa A., Kamata Y., Asao T., Sakaguchi G. Production of monoclonal antibody against Aeromonas hydrophila haemolysin. J Med Microbiol. 1988 Mar;25(3):187–190. doi: 10.1099/00222615-25-3-187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungh A., Wadström T. Aeromonas toxins. Pharmacol Ther. 1981;15(3):339–354. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(81)90049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitarangsi C., Echeverria P., Whitmire R., Tirapat C., Formal S., Dammin G. J., Tingtalapong M. Enteropathogenicity of Aeromonas hydrophila and Plesiomonas shigelloides: prevalence among individuals with and without diarrhea in Thailand. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):666–673. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.666-673.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popoff M., Véron M. A taxonomic study of the Aeromonas hydrophila-Aeromonas punctata group. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 May;94(1):11–22. doi: 10.1099/00221287-94-1-11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potomski J., Burke V., Watson I., Gracey M. Purification of cytotoxic enterotoxin of Aeromonas sobria by use of monoclonal antibodies. J Med Microbiol. 1987 Mar;23(2):171–177. doi: 10.1099/00222615-23-2-171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shotts E. B., Jr, Gaines J. L., Jr, Martin L., Prestwood A. K. Aeromonas-induced deaths among fish and reptiles in an eutrophic inland lake. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1972 Sep 15;161(6):603–607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirinavin S., Likitnukul S., Lolekha S. Aeromonas septicemia in infants and children. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1984 Mar-Apr;3(2):122–125. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198403000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull P. C., Lee J. V., Miliotis M. D., Van de Walle S., Koornhof H. J., Jeffery L., Bryant T. N. Enterotoxin production in relation to taxonomic grouping and source of isolation of Aeromonas species. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):175–180. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.175-180.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]