Abstract
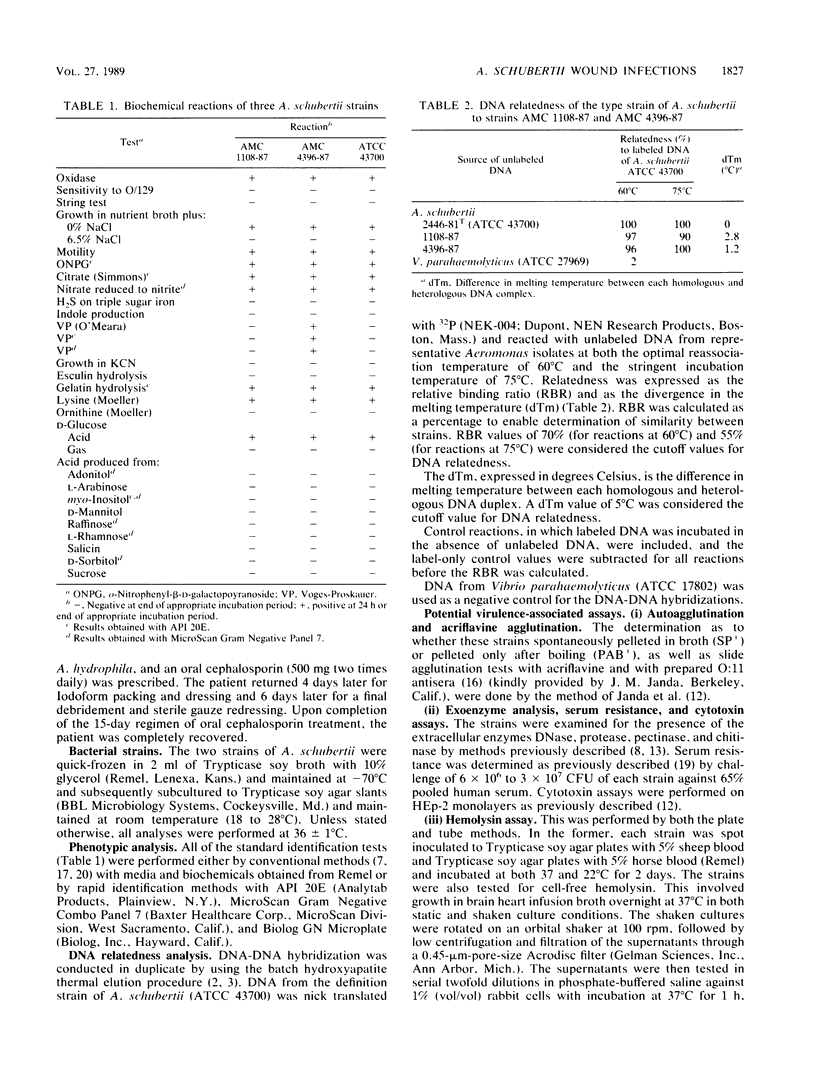
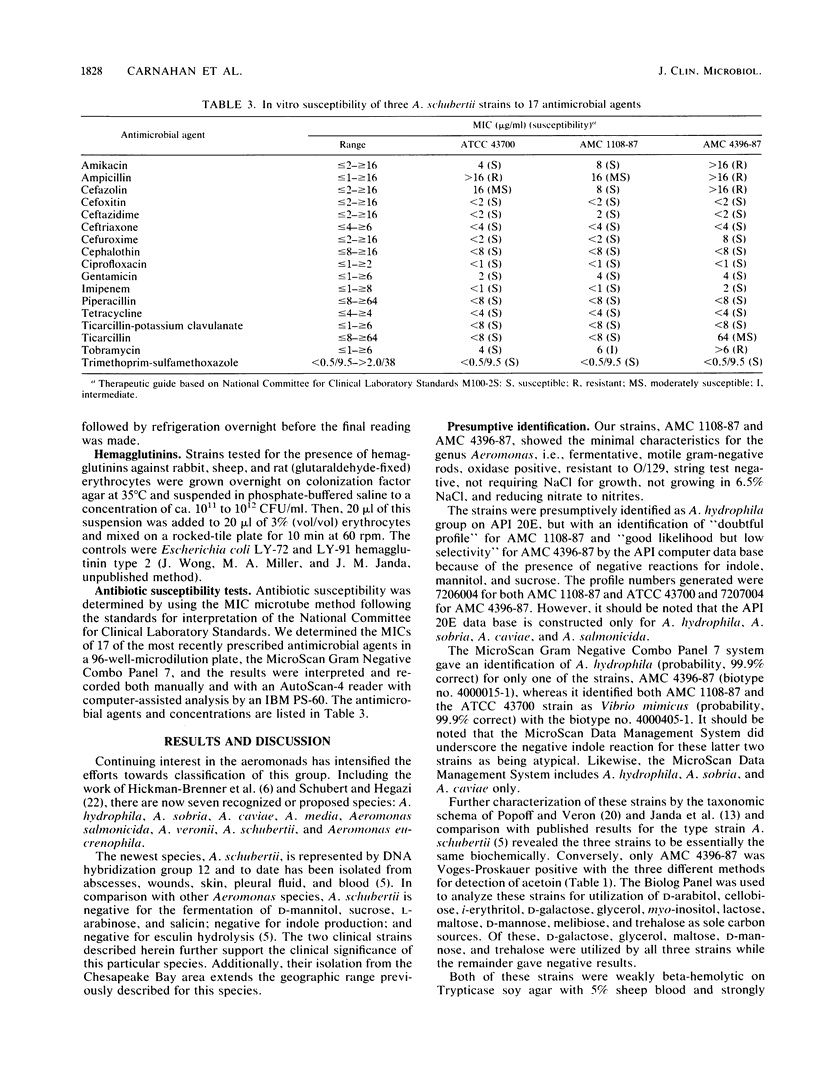
Recent studies have resulted in the proposal of a new species, Aeromonas schubertii (mannitol, sucrose, and indole negative), formerly termed Enteric Group 501, on the basis of the study of seven strains isolated from the southeastern and southwestern United States and Puerto Rico. We have isolated two phenotypically similar A. schubertii strains from infected human wounds sustained in the Chesapeake Bay area. Their identification was confirmed by DNA-DNA hybridization to the Centers for Disease Control definition strain 2446-81 (ATCC 43700) for group 12. The strains were further examined for the presence of virulence-associated markers: hemolysin, hemagglutinins, cytotoxin production, agglutination in acriflavine, resistance to normal human serum, and autoagglutination phenotype. Both strains were positive for hemolysin by the plate assay, cytotoxin production at 1:10, and DNase and protease. They were resistant to human serum and negative for acriflavine agglutination, and only one of the strains was autoagglutination positive. Both strains were negative for cell-free hemolysin, hemagglutinins, pectinase, and chitinase. These isolations of A. schubertii further extend its previously described geographic distribution and reinforce its role as a primary causative agent of cellulitis with possible increased antimicrobial resistance.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brenner D. J., Fanning G. R., Rake A. V., Johnson K. E. Batch procedure for thermal elution of DNA from hydroxyapatite. Anal Biochem. 1969 Apr 4;28(1):447–459. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90199-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. J., McWhorter A. C., Knutson J. K., Steigerwalt A. G. Escherichia vulneris: a new species of Enterobacteriaceae associated with human wounds. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):1133–1140. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.1133-1140.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman-Brenner F. W., Fanning G. R., Arduino M. J., Brenner D. J., Farmer J. J., 3rd Aeromonas schubertii, a new mannitol-negative species found in human clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Aug;26(8):1561–1564. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.8.1561-1564.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman-Brenner F. W., MacDonald K. L., Steigerwalt A. G., Fanning G. R., Brenner D. J., Farmer J. J., 3rd Aeromonas veronii, a new ornithine decarboxylase-positive species that may cause diarrhea. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 May;25(5):900–906. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.5.900-906.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janda J. M. Biochemical and exoenzymatic properties of Aeromonas species. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1985 May;3(3):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(85)90034-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janda J. M., Bottone E. J. Pseudomonas aeruginosa enzyme profiling: predictor of potential invasiveness and use as an epidemiological tool. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jul;14(1):55–60. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.1.55-60.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janda J. M., Brenden R. Importance of Aeromonas sobria in Aeromonas bacteremia. J Infect Dis. 1987 Mar;155(3):589–591. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.3.589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janda J. M., Duffey P. S. Mesophilic aeromonads in human disease: current taxonomy, laboratory identification, and infectious disease spectrum. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Sep-Oct;10(5):980–997. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.5.980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janda J. M., Oshiro L. S., Abbott S. L., Duffey P. S. Virulence markers of mesophilic aeromonads: association of the autoagglutination phenomenon with mouse pathogenicity and the presence of a peripheral cell-associated layer. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3070–3077. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3070-3077.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janda J. M., Reitano M., Bottone E. J. Biotyping of Aeromonas isolates as a correlate to delineating a species-associated disease spectrum. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jan;19(1):44–47. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.1.44-47.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J. B., Lockman H., Colwell R. R., Joseph S. W. Aeromonas hydrophila: ecology and toxigenicity of isolates from an estuary. J Appl Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;50(2):359–377. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1981.tb00900.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuijper E. J., Steigerwalt A. G., Schoenmakers B. S., Peeters M. F., Zanen H. C., Brenner D. J. Phenotypic characterization and DNA relatedness in human fecal isolates of Aeromonas spp. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jan;27(1):132–138. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.1.132-138.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leblanc D., Mittal K. R., Olivier G., Lallier R. Serogrouping of motile Aeromonas species isolated from healthy and moribund fish. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jul;42(1):56–60. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.1.56-60.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittal K. R., Lalonde G., Leblanc D., Olivier G., Lallier R. Aeromonas hydrophila in rainbow trout: relation between virulence and surface characteristics. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Dec;26(12):1501–1503. doi: 10.1139/m80-248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paula S. J., Duffey P. S., Abbott S. L., Kokka R. P., Oshiro L. S., Janda J. M., Shimada T., Sakazaki R. Surface properties of autoagglutinating mesophilic aeromonads. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2658–2665. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2658-2665.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popoff M., Véron M. A taxonomic study of the Aeromonas hydrophila-Aeromonas punctata group. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 May;94(1):11–22. doi: 10.1099/00221287-94-1-11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



