Abstract
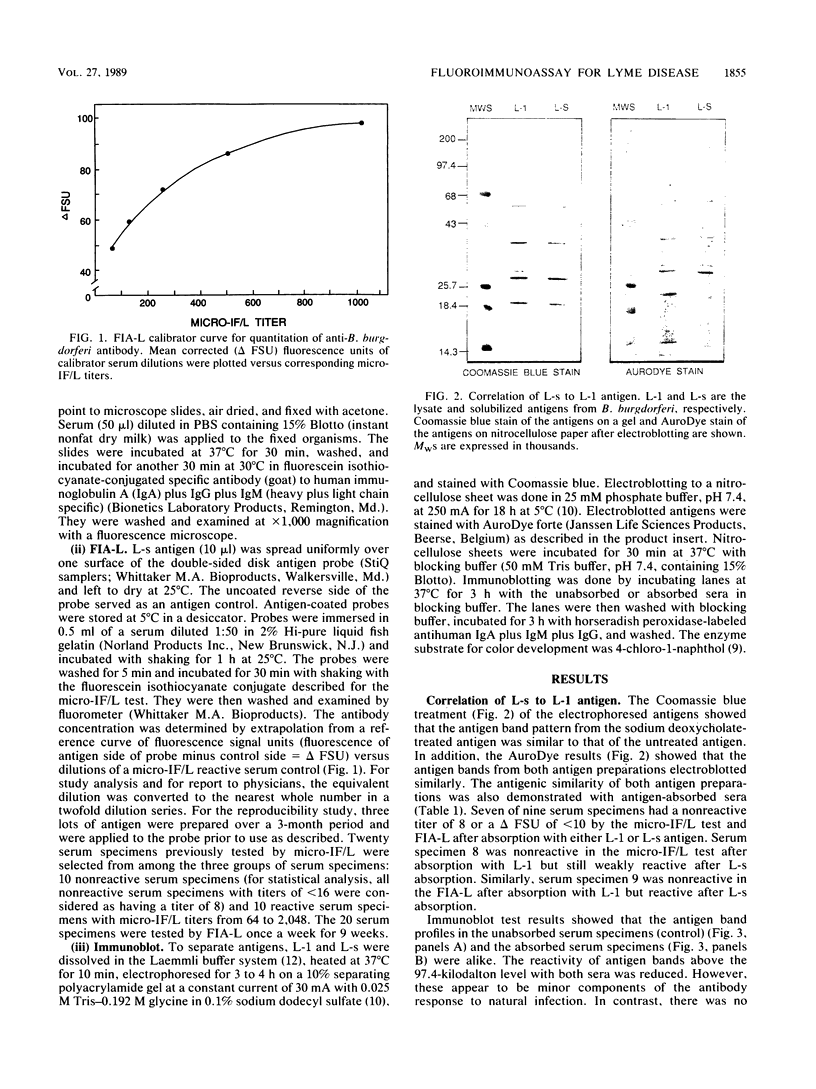
Sodium deoxycholate-solubilized Borrelia burgdorferi antigen was prepared for use in a solid-phase fluoroimmunoassay (FIA-L) to detect antibodies in Lyme disease. Serum specimens were tested by FIA-L and by a microimmunofluorescence test. The FIA-L results are comparable to those of the standard microimmunofluorescence test. The overall agreement was 0.98. Moreover, the FIA-L procedure is simple and rapid; fluorescence is objectively determined and is proportional to antibody titer.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbour A. G. Isolation and cultivation of Lyme disease spirochetes. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):521–525. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Benach J. L., Grunwaldt E., Davis J. P. Lyme disease-a tick-borne spirochetosis? Science. 1982 Jun 18;216(4552):1317–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.7043737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W. Discovery of the Lyme disease spirochete and its relation to tick vectors. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):515–520. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J. L., Benach J. L. Isolation of antigenic components from the Lyme disease spirochete: their role in early diagnosis. J Infect Dis. 1987 Apr;155(4):756–765. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.4.756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craft J. E., Fischer D. K., Shimamoto G. T., Steere A. C. Antigens of Borrelia burgdorferi recognized during Lyme disease. Appearance of a new immunoglobulin M response and expansion of the immunoglobulin G response late in the illness. J Clin Invest. 1986 Oct;78(4):934–939. doi: 10.1172/JCI112683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grizzle J. E., Allen D. M. Analysis of growth and dose response curves. Biometrics. 1969 Jun;25(2):357–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodzicki R. L., Steere A. C. Comparison of immunoblotting and indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using different antigen preparations for diagnosing early Lyme disease. J Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;157(4):790–797. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.4.790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes R., Niday E., Gordon J. A dot-immunobinding assay for monoclonal and other antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):142–147. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90677-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hechemy K. E., Raoult D., Eisemann C., Han Y. S., Fox J. A. Detection of antibodies to Rickettsia conorii with a latex agglutination test in patients with Mediterranean spotted fever. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jan;153(1):132–135. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.1.132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnarelli L. A., Anderson J. F. Early detection and persistence of antibodies to Borrelia burgdorferi in persons with Lyme disease. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1987 Feb;263(3):392–399. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(87)80098-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnarelli L. A., Meegan J. M., Anderson J. F., Chappell W. A. Comparison of an indirect fluorescent-antibody test with an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for serological studies of Lyme disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Aug;20(2):181–184. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.2.181-184.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennell D. R., Wand P. J., Schell R. F. Evaluation of a quantitative fluorescence immunoassay (FIAX) for detection of serum antibody to Borrelia burgdorferi. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Nov;25(11):2218–2220. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.11.2218-2220.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philip R. N., Casper E. A., Ormsbee R. A., Peacock M. G., Burgdorfer W. Microimmunofluorescence test for the serological study of rocky mountain spotted fever and typhus. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Jan;3(1):51–61. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.1.51-61.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell H., Sampson J. S., Schmid G. P., Wilkinson H. W., Plikaytis B. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and indirect immunofluorescence assay for Lyme disease. J Infect Dis. 1984 Mar;149(3):465–470. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.3.465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrestha M., Grodzicki R. L., Steere A. C. Diagnosing early Lyme disease. Am J Med. 1985 Feb;78(2):235–240. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(85)90432-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Grodzicki R. L., Kornblatt A. N., Craft J. E., Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W., Schmid G. P., Johnson E., Malawista S. E. The spirochetal etiology of Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 31;308(13):733–740. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303313081301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Malawista S. E., Snydman D. R., Shope R. E., Andiman W. A., Ross M. R., Steele F. M. Lyme arthritis: an epidemic of oligoarticular arthritis in children and adults in three connecticut communities. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Jan-Feb;20(1):7–17. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]