Abstract
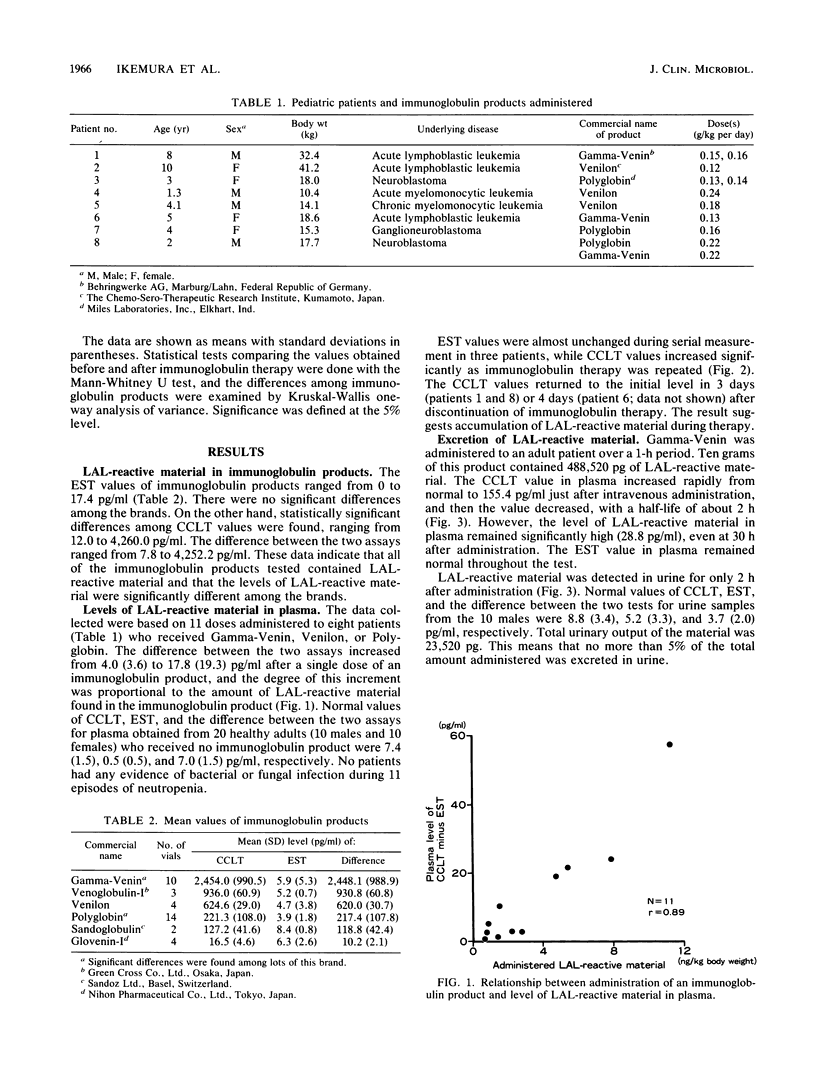
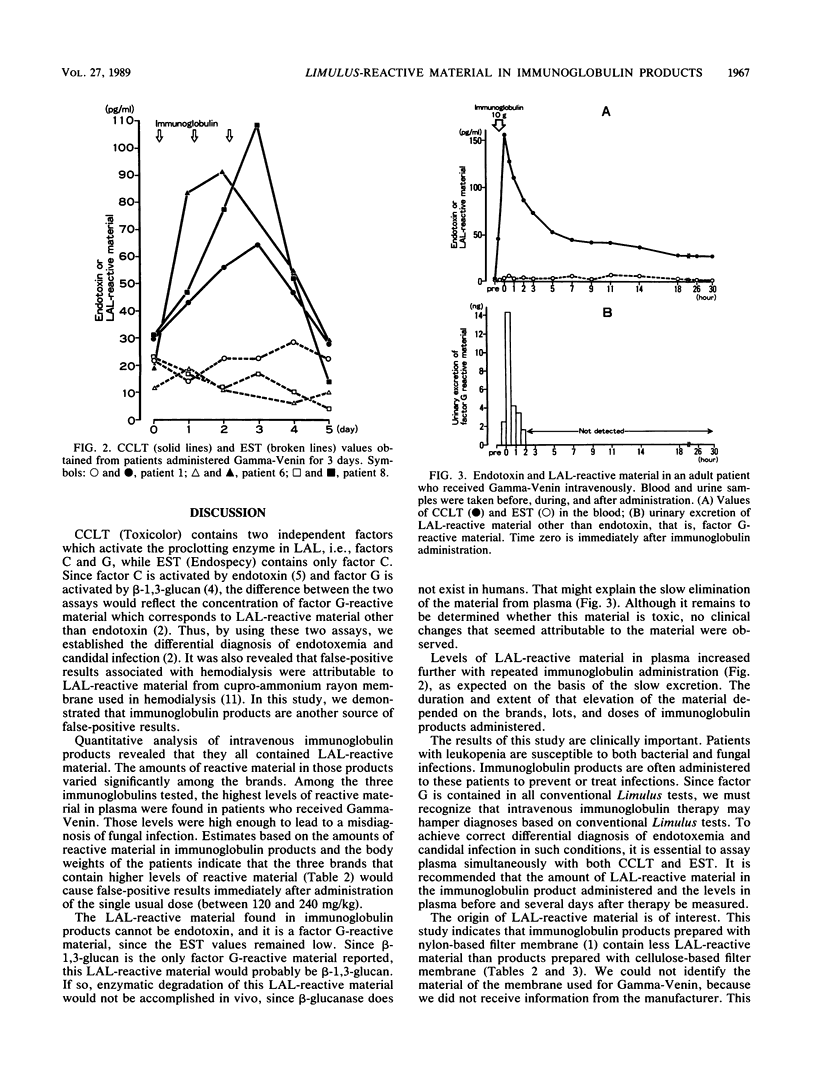
Limulus amebocyte lysate (LAL)-reactive material other than endotoxin was detected in the plasma and urine of patients after intravenous immunoglobulin therapy. Thirty-seven vials of six different immunoglobulin products were analyzed for the LAL-reactive material by combined use of a conventional chromogenic Limulus test and a chromogenic endotoxin-specific test. The amount of LAL-reactive material in reconstituted immunoglobulin solutions ranged from a mean (standard deviation) of 10.2 (2.1) to 2,448.1 (988.9) pg/ml, and there were statistically significant differences among the six brands. The levels of LAL-reactive material in plasma increased in proportion to the amounts contained in the immunoglobulin products administered. The material accumulated in the blood with repeated administration. Urinary excretion of the material was less than 5% of the total amount administered. Such material seems to be derived from the cellulose-based membranes used during preparation of the blood products. Thus, interpretation of Limulus test results of patients receiving immunoglobulin therapy requires special consideration.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
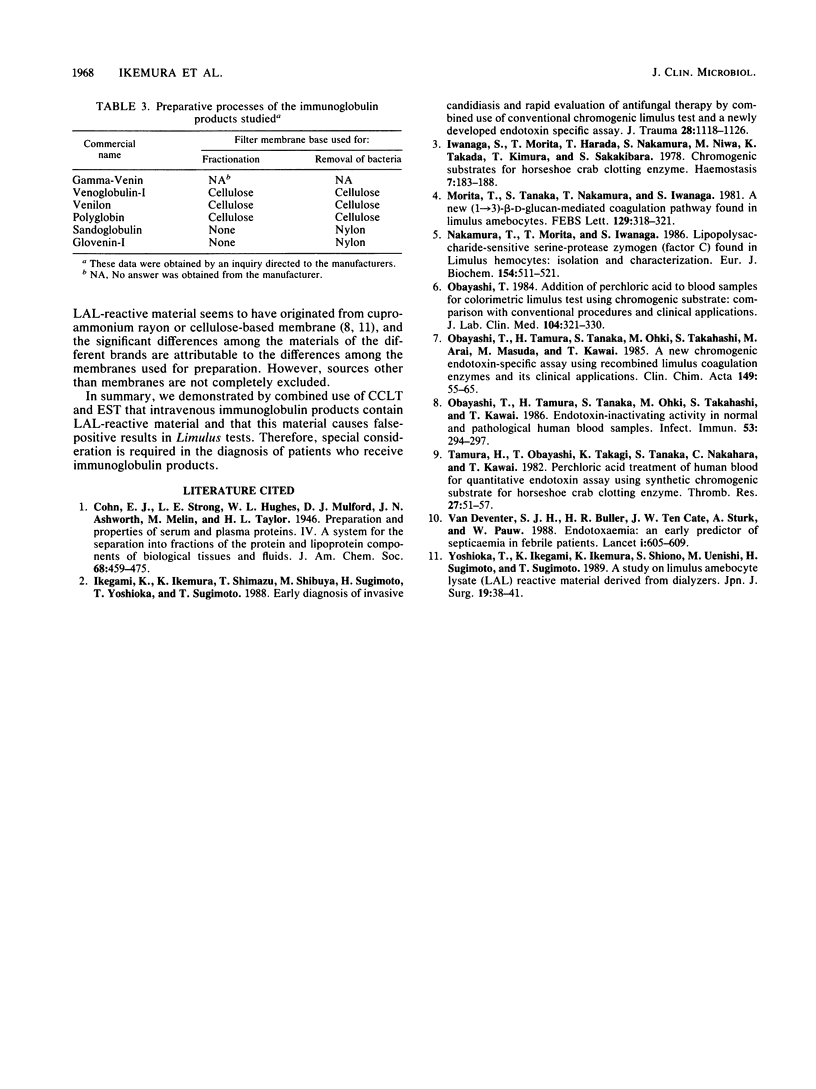
- Ikegami K., Ikemura K., Shimazu T., Shibuya M., Sugimoto H., Yoshioka T., Sugimoto T. Early diagnosis of invasive candidiasis and rapid evaluation of antifungal therapy by combined use of conventional chromogenic limulus test and a newly developed endotoxin specific assay. J Trauma. 1988 Aug;28(8):1118–1126. doi: 10.1097/00005373-198808000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwanaga S., Morita T., Harada T., Nakamura S., Niwa M., Takada K., Kimura T., Sakakibara S. Chromogenic substrates for horseshoe crab clotting enzyme. Its application for the assay of bacterial endotoxins. Haemostasis. 1978;7(2-3):183–188. doi: 10.1159/000214260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Morita T., Iwanaga S. Lipopolysaccharide-sensitive serine-protease zymogen (factor C) found in Limulus hemocytes. Isolation and characterization. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Feb 3;154(3):511–521. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09427.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obayashi T. Addition of perchloric acid to blood samples for colorimetric limulus test using chromogenic substrate: comparison with conventional procedures and clinical applications. J Lab Clin Med. 1984 Sep;104(3):321–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obayashi T., Tamura H., Tanaka S., Ohki M., Takahashi S., Arai M., Masuda M., Kawai T. A new chromogenic endotoxin-specific assay using recombined limulus coagulation enzymes and its clinical applications. Clin Chim Acta. 1985 Jun 30;149(1):55–65. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(85)90273-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obayashi T., Tamura H., Tanaka S., Ohki M., Takahashi S., Kawai T. Endotoxin-inactivating activity in normal and pathological human blood samples. Infect Immun. 1986 Aug;53(2):294–297. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.2.294-297.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura H., Obayashi T., Takagi K., Tanaka S., Nakahara C., Kawai T. Perchloric acid treatment of human blood for quantitative endotoxin assay using synthetic chromogenic substrate for horseshoe crab clotting enzyme. Thromb Res. 1982 Jul 1;27(1):51–57. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(82)90277-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka T., Ikegami K., Ikemura K., Shiono S., Uenishi M., Sugimoto H., Sugimoto T. A study on limulus amebocyte lysate (LAL) reactive material derived from dialyzers. Jpn J Surg. 1989 Jan;19(1):38–41. doi: 10.1007/BF02471564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Deventer S. J., Buller H. R., ten Cate J. W., Sturk A., Pauw W. Endotoxaemia: an early predictor of septicaemia in febrile patients. Lancet. 1988 Mar 19;1(8586):605–609. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91412-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


