Abstract
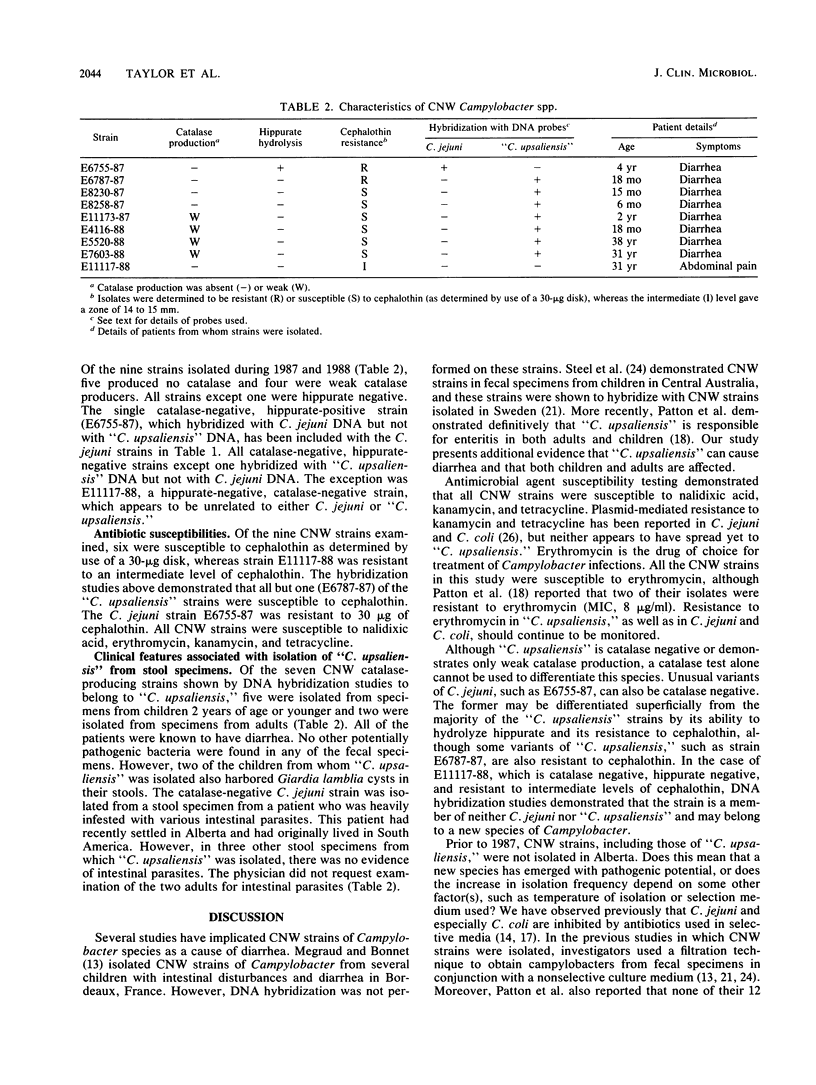
During 1987 and 1988, nine strains of catalase-negative or -weak Campylobacter species were isolated in Alberta, Canada. DNA hybridization studies demonstrated that seven strains were "Campylobacter upsaliensis," one strain was highly homologous with Campylobacter jejuni DNA, and one strain was a campylobacter unrelated to the other two species. All "C. upsaliensis" strains were hippurate negative, and six of seven were susceptible to cephalothin. The unusual variant of C. jejuni was hippurate positive and cephalothin resistant, whereas the unclassified strain was hippurate negative and resistant to intermediate levels of cephalothin. All patients from whom "C. upsaliensis" was isolated had diarrhea. Five of the patients were children two years old or younger, and two were adults. In this study, all catalase-negative and -weak strains were isolated from stool specimens by using a charcoal-based selective medium containing 32 micrograms of cefaperazone per ml and which was described by Hutchinson and Bolton (D. N. Hutchinson and F. J. Bolton, J. Clin. Pathol. 37:956-957, 1984).
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRYNER J. H., FRANK A. H. A preliminary report on the identification of Vibrio fetus. Am J Vet Res. 1955 Jan;16(58):76–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devlin H. R., McIntyre L. Campylobacter fetus subsp. fetus in homosexual males. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Oct;18(4):999–1000. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.4.999-1000.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds P., Patton C. M., Barrett T. J., Morris G. K., Steigerwalt A. G., Brenner D. J. Biochemical and genetic characteristics of atypical Campylobacter fetus subsp. fetus strains isolated from humans in the United States. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jun;21(6):936–940. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.6.936-940.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds P., Patton C. M., Griffin P. M., Barrett T. J., Schmid G. P., Baker C. N., Lambert M. A., Brenner D. J. Campylobacter hyointestinalis associated with human gastrointestinal disease in the United States. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Apr;25(4):685–691. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.4.685-691.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezaki T., Takeuchi N., Liu S. L., Kai A., Yamamoto H., Yabuuchi E. Small-scale DNA preparation for rapid genetic identification of Campylobacter species without radioisotope. Microbiol Immunol. 1988;32(2):141–150. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1988.tb01373.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georges-Courbot M. C., Baya C., Beraud A. M., Meunier D. M., Georges A. J. Distribution and serotypes of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli in enteric Campylobacter strains isolated from children in the Central African Republic. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Mar;23(3):592–594. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.3.592-594.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson D. N., Bolton F. J. Improved blood free selective medium for the isolation of campylobacter jejuni from faecal specimens. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Aug;37(8):956–957. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.8.956-b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang M. N., Ederer G. M. Rapid hippurate hydrolysis method for presumptive identification of group B streptococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jan;1(1):114–115. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.1.114-115.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., Penner J. L., Fleming P. C., Williams A., Hennessy J. N. The serotype and biotype distribution of clinical isolates of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli over a three-year period. J Infect Dis. 1983 Feb;147(2):243–246. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.2.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARMUR J., DOTY P. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its thermal denaturation temperature. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jul;5:109–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Megraud F., Bonnet F. Unusual campylobacters in human faeces. J Infect. 1986 May;12(3):275–276. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(86)94398-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng L. K., Stiles M. E., Taylor D. E. Classification of Campylobacter strains using DNA probes. Mol Cell Probes. 1987 Sep;1(3):233–243. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(87)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng L. K., Stiles M. E., Taylor D. E. DNA probes for identification of tetracycline resistance genes in Campylobacter species isolated from swine and cattle. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Nov;31(11):1669–1674. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.11.1669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng L. K., Stiles M. E., Taylor D. E. Inhibition of Campylobacter coli and Campylobacter jejuni by antibiotics used in selective growth media. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Oct;22(4):510–514. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.4.510-514.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng L. K., Taylor D. E., Stiles M. E. Characterization of freshly isolated Campylobacter coli strains and suitability of selective media for their growth. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Mar;26(3):518–523. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.3.518-523.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton C. M., Shaffer N., Edmonds P., Barrett T. J., Lambert M. A., Baker C., Perlman D. M., Brenner D. J. Human disease associated with "Campylobacter upsaliensis" (catalase-negative or weakly positive Campylobacter species) in the United States. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jan;27(1):66–73. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.1.66-73.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner J. L. The genus Campylobacter: a decade of progress. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1988 Apr;1(2):157–172. doi: 10.1128/cmr.1.2.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simor A. E., Wilcox L. Enteritis associated with Campylobacter laridis. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jan;25(1):10–12. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.1.10-12.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis: a "new" disease. Br Med J. 1977 Jul 2;2(6078):9–11. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6078.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele T. W., Sangster N., Lanser J. A. DNA relatedness and biochemical features of Campylobacter spp. isolated in central and South Australia. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jul;22(1):71–74. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.1.71-74.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauxe R. V., Patton C. M., Edmonds P., Barrett T. J., Brenner D. J., Blake P. A. Illness associated with Campylobacter laridis, a newly recognized Campylobacter species. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Feb;21(2):222–225. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.2.222-225.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. E., Courvalin P. Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in Campylobacter species. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Aug;32(8):1107–1112. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.8.1107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. E., Ng L. K., Lior H. Susceptibility of Campylobacter species to nalidixic acid, enoxacin, and other DNA gyrase inhibitors. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Nov;28(5):708–710. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.5.708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. S., Cahoon F. E., Hodge D. S. Rate of Campylobacter spp. isolation in three regions of Ontario, Canada, from 1978 to 1985. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Nov;24(5):876–878. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.5.876-878.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



