Abstract
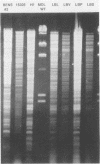
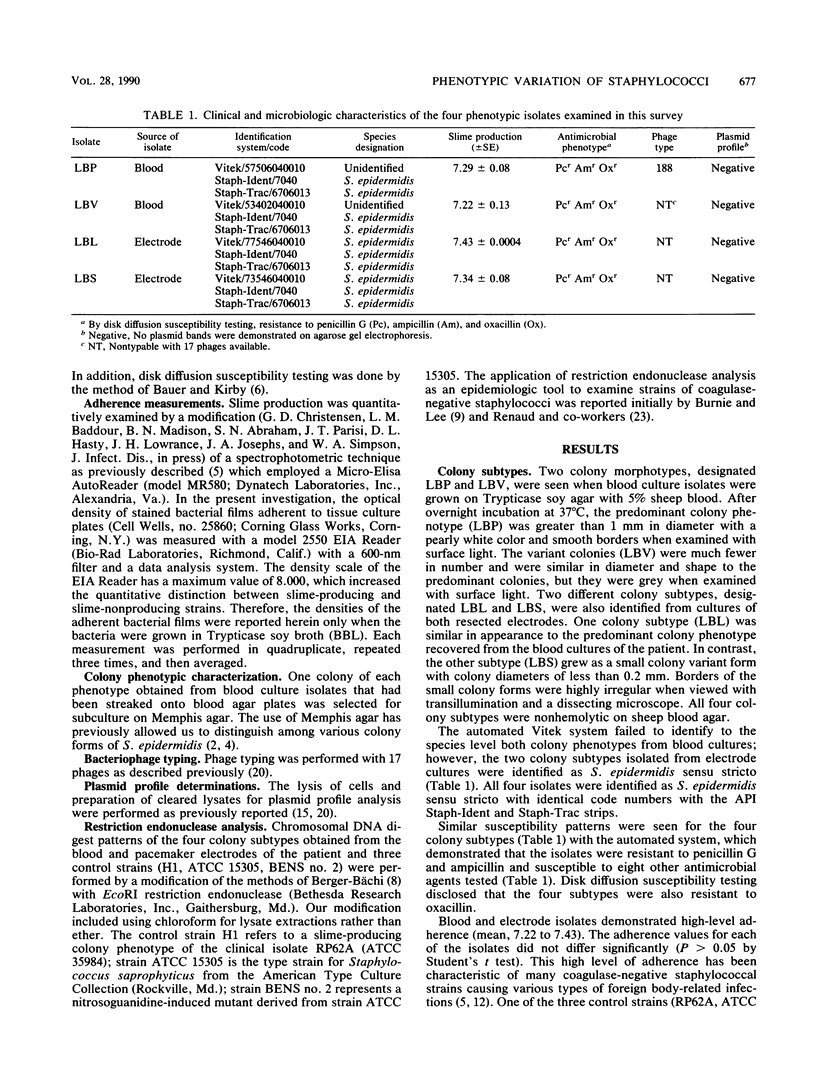
Coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from a patient with a pacemaker electrode infection were extensively evaluated by phenotypic and genotypic characterization. Findings from this evaluation were striking because different colony morphologic subtypes were recovered from blood and resected pacemaker electrodes. Staphylococci from each colony subtype (LBL, LBV, LBP, LBS) were identified as slime-producing strains of Staphylococcus epidermidis sensu stricto. Direct plating of isolates from a restricted electrode revealed a mixture of colony phenotypes when examined on a high-salt, low-glucose medium, Memphis agar. Bacteriophage typing employing 17 different phages and plasmid profile analysis were largely unsuccessful in further characterizing bacterial cells of each of the four colony morphotypes. On the other hand, restriction endonuclease analysis by EcoRI digestion of the chromosomal DNA demonstrated the probable common clonal origin of the four colony phenotypes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baddour L. M., Christensen G. D., Lowrance J. H., Simpson W. A. Pathogenesis of experimental endocarditis. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 May-Jun;11(3):452–463. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.3.452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baddour L. M., Christensen G. D. Prosthetic valve endocarditis due to small-colony staphylococcal variants. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Nov-Dec;9(6):1168–1174. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.6.1168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baddour L. M., Phillips T. N., Bisno A. L. Coagulase-negative staphylococcal endocarditis. Occurrence in patients with mitral valve prolapse. Arch Intern Med. 1986 Jan;146(1):119–121. doi: 10.1001/archinte.146.1.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baddour L. M., Simpson W. A., Weems J. J., Jr, Hill M. M., Christensen G. D. Phenotypic selection of small-colony variant forms of Staphylococcus epidermidis in the rat model of endocarditis. J Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;157(4):757–763. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.4.757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baddour L. M., Smalley D. L., Kraus A. P., Jr, Lamoreaux W. J., Christensen G. D. Comparison of microbiologic characteristics of pathogenic and saprophytic coagulase-negative staphylococci from patients on continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1986 Sep;5(3):197–205. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(86)90002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer A. S., Norman D. C., Kim K. S. Characterization of impermeability variants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated during unsuccessful therapy of experimental endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jan;31(1):70–75. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.1.70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger-Bächi B. Insertional inactivation of staphylococcal methicillin resistance by Tn551. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):479–487. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.479-487.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnie J. P., Lee W. A comparison of DNA and immunoblot fingerprinting of the SII biotype of coagulase negative staphylococci. Epidemiol Infect. 1988 Oct;101(2):203–212. doi: 10.1017/s095026880005411x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers H. F., Miller M. H. Emergence of resistance to cephalothin and gentamicin during combination therapy for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis in rabbits. J Infect Dis. 1987 Mar;155(3):581–585. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.3.581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D., Baddour L. M., Simpson W. A. Phenotypic variation of Staphylococcus epidermidis slime production in vitro and in vivo. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):2870–2877. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.2870-2877.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D., Simpson W. A., Younger J. J., Baddour L. M., Barrett F. F., Melton D. M., Beachey E. H. Adherence of coagulase-negative staphylococci to plastic tissue culture plates: a quantitative model for the adherence of staphylococci to medical devices. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Dec;22(6):996–1006. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.6.996-1006.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franson T. R., Sheth N. K., Menon L., Sohnle P. G. Persistent in vitro survival of coagulase-negative staphylococci adherent to intravascular catheters in the absence of conventional nutrients. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Oct;24(4):559–561. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.4.559-561.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenspan A. M., Kay H. R., Berger B. C., Greenberg R. M., Greenspon A. J., Gaughan M. J. Incidence of unwarranted implantation of permanent cardiac pacemakers in a large medical population. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jan 21;318(3):158–163. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198801213180306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutton J. P., Hamory B. H., Parisi J. T., Strausbaugh L. J. Staphylococcus epidermidis arthritis following catheter-induced bacteremia in a neutropenic patient. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1985 Mar;3(2):119–124. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(85)90020-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrie T. J., Nelligan J., Costerton J. W. A scanning and transmission electron microscopic study of an infected endocardial pacemaker lead. Circulation. 1982 Dec;66(6):1339–1341. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.66.6.1339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. H., Edberg S. C., Mandel L. J., Behar C. F., Steigbigel N. H. Gentamicin uptake in wild-type and aminoglycoside-resistant small-colony mutants of Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):722–729. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. H., Wexler M. A., Steigbigel N. H. Single and combination antibiotic therapy of Staphylococcus aureus experimental endocarditis: emergence of gentamicin-resistant mutants. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Sep;14(3):336–343. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.3.336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parisi J. T., Lampson B. C., Hoover D. L., Khan J. A. Comparison of epidemiologic markers for Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jul;24(1):56–60. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.1.56-60.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parisi J. T., Robbins J., Lampson B. C., Hecht D. W. Characterization of a macrolide, lincosamide, and streptogramin resistance plasmid in Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Bacteriol. 1981 Nov;148(2):559–564. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.2.559-564.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier L. L., Jr, Richardson M., Feist M. Virulent gentamicin-induced small colony variants of Staphylococcus aureus. J Lab Clin Med. 1979 Aug;94(2):324–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters G., Saborowski F., Locci R., Pulverer G. Investigations on staphylococcal infection of transvenous endocardial pacemaker electrodes. Am Heart J. 1984 Aug;108(2):359–365. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(84)90625-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renaud F., Freney J., Etienne J., Bes M., Brun Y., Barsotti O., Andre S., Fleurette J. Restriction endonuclease analysis of Staphylococcus epidermidis DNA may be a useful epidemiological marker. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Sep;26(9):1729–1734. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.9.1729-1734.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwalbe R. S., Stapleton J. T., Gilligan P. H. Emergence of vancomycin resistance in coagulase-negative staphylococci. N Engl J Med. 1987 Apr 9;316(15):927–931. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198704093161507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis L. B., MacLowry J. D. Clinically significant differences in antibiograms of morphologic variants of blood culture isolates. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1989 Mar-Apr;12(2):177–179. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(89)90010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade J. S., Cobbs C. G. Infections in cardiac pacemakers. Curr Clin Top Infect Dis. 1988;9:44–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein M. P., Reller L. B., Murphy J. R., Lichtenstein K. A. The clinical significance of positive blood cultures: a comprehensive analysis of 500 episodes of bacteremia and fungemia in adults. I. Laboratory and epidemiologic observations. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Jan-Feb;5(1):35–53. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]