Abstract
Idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis (IPH) is a rare cause of diffuse alveolar hemorrhage with unknown etiology. In the present report, the presentations of two sisters are described: one sister had IPH, eosinophilia and a high serum immunoglobulin E (IgE) level; and the other had IPH, pneumothorax, eosinophilia and a high serum IgE level. Both cases had quite unusual presentations. The first patient was 23 years of age, and had suffered from dry cough and progressive dyspnea for four years. Her hemoglobin level was 60 g/L, total serum IgE level was 900 U/mL and eosinophilia was 9%. Her chest radiography revealed diffuse infiltration. She died due to respiratory failure. The second patient was 18 years of age. She had also suffered from dry cough and gradually increasing dyspnea for two years. She had partial pneumothorax in the right lung and diffuse infiltration in other pulmonary fields on chest radiography. Her hemoglobin level was 99 g/L, total serum IgE level was 1200 U/mL and eosinophilia was 8%. IPH was diagnosed by open lung biopsy. All these findings suggested that familial or allergic factors, as well as immunological factors, might have contributed to the etiology of IPH.
Keywords: Eosinophilia, Familial factors, Hemosiderosis, Pneumothorax
Abstract
L’hémosidérose pulmonaire idiopathique (HPI) est une cause rare d’hémorragie alvéolaire diffuse à l’étiologie inconnue. Dans le présent article, les auteurs décrivent la présentation de deux sœurs : l’une souffrait d’HPI, d’éosinophilie et d’un taux élevé d’immunoglobuline E (IgE) sérique et l’autre, d’HPI, d’un pneumothorax, d’une éosinophilie et d’un taux élevé d’IgE sérique. Les deux cas avaient une présentation très inhabituelle. La première patiente avait 23 ans et était incommodée par une toux sèche et une dyspnée évolutive depuis quatre ans. Son taux d’hémoglobine était de 60 g/L, son taux d’IgE sérique total, de 900 U/mL, et son éosinophilie, de 9 %. La radiographie pulmonaire révélait une infiltration diffuse. Elle est morte d’une insuffisance respiratoire. La deuxième patiente avait 18 ans. Elle souffrait également d’une toux sèche et d’une dyspnée croissante depuis deux ans. Elle avait un pneumothorax partiel dans un poumon et une infiltration diffuse dans les autres champs pulmonaires selon la radiographie pulmonaire. Son taux d’hémoglobine était de 99 g/L, son taux d’IgE sérique total, de 1 200 U/mL, et son éosinophilie, de 8 %. L’HPI a été diagnostiquée par une biopsie pulmonaire ouverte. Toutes ces observations indiquent que des facteurs familiaux ou allergiques, en plus des facteurs immunologiques, pourraient avoir contribué à l’étiologie de l’HPI.
Idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis (IPH) is a rare disease, characterized by recurrent or chronic hemoptysis, iron deficiency anemia and diffuse parenchymal infiltration on chest radiography. Although the etiology of IPH remains unknown, it is considered to be an immune-mediated disease (1–4) that occurs frequently in children. The clinical course of the disease includes two phases. First, an acute phase, ‘IPH exacerbation’, corresponds to intra-alveolar bleeding episodes manifested by cough, dyspnea, hemoptysis and sometimes respiratory failure. The second phase, known as the chronic phase, is characterized by a slow resolution of previous symptoms, with or without treatment (1,2).
The anemia is typically microcytic and hypochromic (5,6). Radiographic changes range from minimal infiltrates resembling pneumonia to massive pulmonary involvement. Late diagnosis of IPH may occur at a stage when pulmonary fibrosis has already developed, consequently yielding a poorer prognosis (7). Absolute diagnosis is based on hemosiderin-laden macrophages without any evidence of pulmonary vasculitis, nonspecific granulomatous inflammation or deposition of immunoglobulins in respiratory secretion or biopsy materials. If this is not possible, IPH is diagnosed by the characteristic clinical and radiographic findings, in addition to excluding the other causes of diffuse alveolar hemorrhage (3,4,6).
CASE PRESENTATIONS
Case 1
A 23-year-old woman presented to the hospital with worsening dyspnea and a nonproductive cough that had been present for the previous four years, gradually increasing in intensity. She took vitamin pills for anemia and had received several blood transfusions. She also had been treated repeatedly for lower respiratory tract infections.
The general status of the patient was poor, with severe dyspnea and pallor on admission. Her respiratory rate was 35 breaths/min, with intercostal and subcostal retractions. Breathing sounds were decreased on both sides, with accompanying rales in the middle and lower bilateral zones, but the sounds were more prominent in the left lung. There were no signs of lymphadenopathy or organomegaly.
Laboratory examinations of the patient’s blood found a hemoglobin level of 60 g/L, a hematocrit ratio of 0.17, a leukocyte count of 7.56×106/L (9% eosinophils), and a platelet count of 296×109/L. The measurement of mean corpuscular volume was 66 fL, mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH) was 20 pg, MCH concentration was 300 g/L and red cell distribution width was 18%. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate was 32 mm/h and C-reactive protein level was 4.5 mg/L. Blood chemistry was normal. Room-air arterial blood gas analysis on admission showed that the partial pressure of oxygen was 52 mmHg, the oxygen saturation was 79% and the partial pressure of carbon dioxide was 33 mmHg. Chest x-ray and high-resolution computed tomography examination showed bilateral alveolar infiltrates (Figure 1). The patient, whose general status was not good, was treated for respiratory insufficiency and anemia. Intravenous fluid and nasal oxygen therapy were started. On the second day of hospitalization, her respiratory distress increased. After blood was taken for laboratory investigations, she was transfused with concentrated erythrocytes. According to the results obtained from pretransfusion blood specimens, serum bilirubin levels were normal. The direct Coombs test was negative, and coagulation test results were within normal ranges. The electrophoresis of hemoglobin was also normal, and the serum iron profile was consistent with iron deficiency (serum iron 5.32 μmol/L, unsaturated iron-binding capacity 103.82 μmol/L, ferritin 5.04 pmol/L). The total serum IgE level was 900 U/mL. The urinary sediment examination was normal. Tests of antiglomerular basement membrane antibodies, antinuclear antibodies, anticardiolipin antibodies, rheumatoid factor, perinuclear antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies and cytoplasmic antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies were negative.
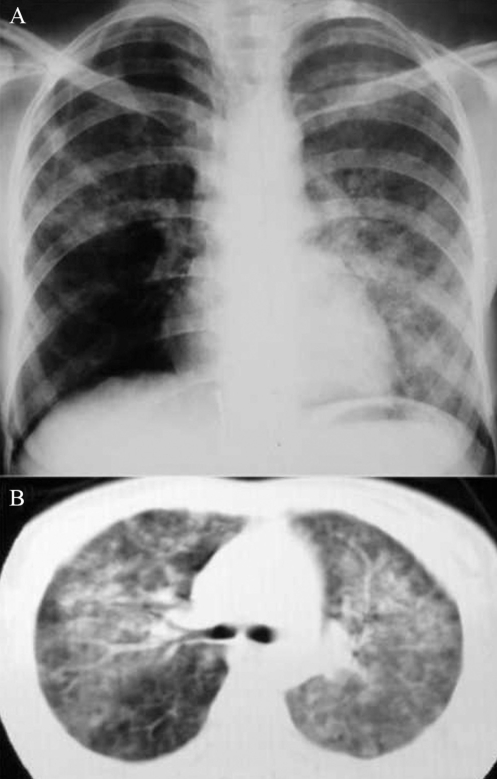
Figure 1).
Case 1. Chest radiograph (A) and computed tomography scan (B) of the chest. Bilateral alveolar infiltration was suggestive of intra-alveolar hemorrhage
She was diagnosed as having IPH by clinical and laboratory findings, and by exclusion of other causes of intra-alveolar hemorrhage. To confirm presumptive diagnosis of IPH, a lung biopsy was planned. However, the respiratory distress of the patient worsened, and respiratory arrest occurred. She could not be resuscitated. The family did not give consent for an autopsy.
Case 2
The second patient presented to the hospital approximately six months after the first patient; she was the 18-year-old sister of the previous patient. She complained of dyspnea, right chest pain, cough, fatigue and rapid exhaustion, and she was treated several times for iron deficiency anemia and bronchitis. She was dyspneic and slightly pale on admission. She had intercostal retractions. On auscultation, the respiratory sounds were severely decreased in the right hemithorax, and rales were heard in the basal bilateral regions. There were no signs of lymphadenopathy or organomegaly.
Laboratory examinations of the patient’s blood found a hemoglobin level of 99 g/L, a hematocrit ratio of 0.28, a leukocyte count of 9.56×106/L (8% eosinophils) and a platelet count of 355×109/L. The measurement of mean corpuscular volume was 66.2 fL, MCH was 20.6 pg, MCH concentration was 322 g/L and red cell distribution width was 18.2%. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate was 39 mm/h and C-reactive protein level was 6.2 mg/L. Blood chemistry was normal. Room-air arterial blood gas analysis on admission showed that the partial pressure of oxygen was 68 mmHg, the oxygen saturation was 86% and the partial pressure of carbon dioxide was 40 mmHg. On chest x-ray and high-resolution computed tomography, there was partial pneumothorax in the right lung, as well as extensive interstitial infiltration and fibrosis, which became more intense in the bilateral hilar regions (Figure 2).
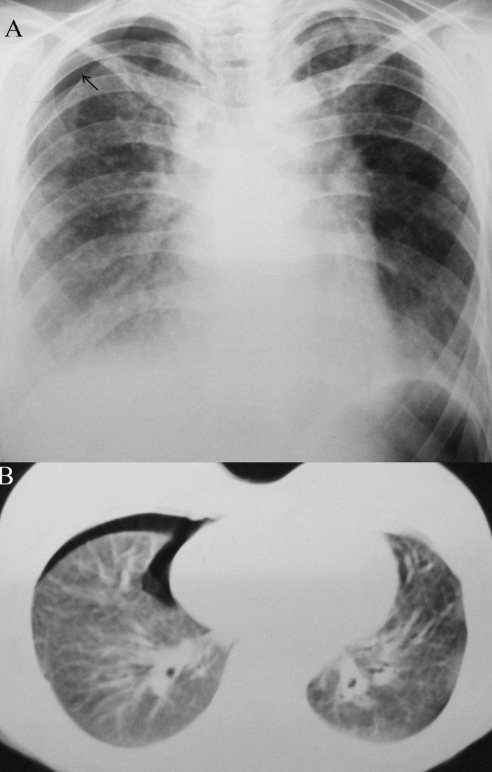
Figure 2).
Case 2. Chest radiograph (A) and computed tomography scan (B) of the chest, illustrating right partial pneumothorax and bilateral infiltrates
Serum bilirubin levels were normal. The direct Coombs test was negative, and coagulation test results were within normal limits. Electrophoresis of hemoglobin was normal. Her serum iron profile was consistent with iron deficiency (serum iron 3.4 μmol/L, unsaturated iron-binding capacity 98.8 μmol/L, ferritin 6.04 pmol/L). Tests of antiglomerular basement membrane antibodies, antinuclear antibodies, anticardiolipin antibodies, rheumatoid factor, perinuclear antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies and cytoplasmic antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies were negative. The urinary sediment examination was normal. The total serum IgE level was 1200 U/mL. Pulmonary function tests, as a percentage of predicted normal values, were measured: forced vital capacity, 29% of predicted; forced expiratory volume in 1 s, 28% of predicted; ratio of forced expiratory volume in 1 s to forced vital capacity, 1.09; and diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide, 59% of predicted. Sputum and bronchial secretions did not reveal findings of infection or colonization with fungi. Echocardiography was within normal limits. The examination of serum-specific IgE level against allergens such as cow’s milk, gluten and casein did not reveal any abnormal results. The patient was treated with conservative symptomatic management, including pain relief, antibiotherapy and nasal oxygen administration for pneumothorax, and findings of pneumothorax disappeared on the chest x-ray on the fifth day of treatment.
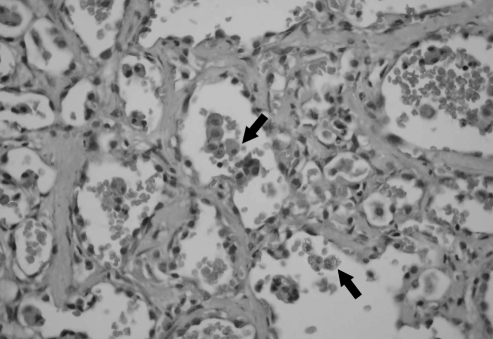
Diagnosis of IPH was made following an open lung biopsy showing intra-alveolar hemorrhage, hemosiderin-laden macrophages and fibrosis without findings of vasculitis (Figure 3). The patient was administered methylprednisolone at a daily dose of 2 mg/kg. During the follow-up period, her symptoms partially improved; however, radiological and lung function tests did not reveal significant improvement.
Figure 3).
Open lung biopsy, showing mild nonspecific thickening of alveolar septae, fibrosis and hemosiderin-laden macrophages within the alveolar spaces (arrows). Original magnification ×200
DISCUSSION
Although IPH is a pediatric disease, it has also been reported in adults (8,9). Our patients were young adults. Patient 1 was diagnosed in the acute phase and patient 2 in the chronic phase of the disease. Radiological findings were more intense in the hilar region in both patients, whereas the presence of pneumothorax in the second patient was an interesting finding. The second patient was diagnosed by open lung biopsy. The first patient was unable to undergo a biopsy procedure because of impaired general status, with prominent respiratory distress and severe anemia, and her diagnosis was made on the basis of clinical and radiological findings, as well as exclusion of other causes of intra-alveolar hemorrhage.
Although IPH is defined as one of the causes of recurrent hemoptysis, it has been reported without hemoptysis, especially in adult patients (6,10).
Neither of our two patients described hemoptysis; therefore, cases of IPH without hemoptysis may be a diagnostic challenge. Although our patients did not describe hemoptysis, they had iron deficiency anemia and had probably swallowed the expelled blood (6). Therefore, patients with diffuse pulmonary infiltration but without hemoptysis should be examined for iron deficiency anemia and IPH should be considered as a possible diagnosis. On the other hand, iron deficiency anemia with or without hemoptysis should raise the suspicion of a problem in the respiratory system, and a chest x-ray should be taken if necessary. It should be kept in mind that respiratory symptoms may be indistinct despite prominent radiological findings or vice versa (5).
The etiology of IPH has been suspected to be autoimmune, allergic, genetic or environmental in different theories (3). The increased incidence of IPH in some autoimmune diseases is suggestive of an autoimmune theory (11). The disease is not hereditary; however, a small number of familial cases have been reported (12). As a result, the contribution of familial and genetic factors has been discussed. Because our two patients are sisters, the present cases may add support to the literature of a role of genetic or environmental factors in the etiology of IPH.
Despite reports stating that gluten-sensitive enteropathy (10) and sensitivity to cow’s milk (13) may accompany IPH, such associations were not detected in our patients. In some of these studies, elevations were reported in wheat-specific IgE and cow milk-specific IgE. The serum-specific levels of IgE were normal in both of the patients, and no specific allergens were detected in the skin prick tests of the second patient. However, the total serum IgE levels were high in both patients. Possible reasons for IgE elevation, such as parasitic infestation, malignancy and drug usage, were excluded. Therefore, it was possible that other sensitivities were accompanying or contributing to the etiology. Eosinophilia in the peripheral blood has been reported in patients with IPH (6). Both of our patients exhibited eosinophilia in the blood. These findings suggest that immunological factors contributed to the etiology.
Many interstitial lung diseases such as eosinophilic granuloma, tuberous sclerosis and lymphangioleiomyomatosis may cause pneumothorax. To our knowledge, there is only one case of IPH in the literature presenting with spontaneous pneumothorax (8). Our second patient presented with spontaneous pneumothorax and was diagnosed as having IPH on further investigations. Thus, our case is the second patient with IPH in the literature presenting with spontaneous pneumothorax. Therefore, we suggest keeping IPH in mind when the etiology of spontaneous pneumothorax is under investigation.
CONCLUSIONS
The features of the patients that may possibly contribute to the literature are the presence of IPH in the two sisters, the admission of the second patient with pneumothorax, the lack of hemoptysis, and the elevated serum IgE levels and eosinophil counts.
REFERENCES
- 1.Ferrari GF, Fioretto JR, Alves AF, Brandão GS. [Idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis: Case report.] J Pediatr (Rio J) 2000;76:149–52. doi: 10.2223/jped.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Cohen S. Idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis. Am J Med Sci. 1999;317:67–74. doi: 10.1097/00000441-199901000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ioachimescu OC, Sieber S, Kotch A. Idiopathic pulmonary haemosiderosis revisited. Eur Respir J. 2004;24:162–70. doi: 10.1183/09031936.04.00116302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Vinodh BN, Sharma SK, Mukhopadhyay S, Ray R. Idiopathic pulmonary haemosiderosis: Two case reports. Indian J Chest Dis Allied Sci. 2006;48:75–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Dearborn DG. Pulmonary hemosiderosis. In: Behrman RE, Kliegman RM, Jenson HB, editors. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. Philadelphia: WB Saunders Co; 2003. pp. 1455–7. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Saeed MM, Woo MS, MacLaughlin EF, Margetis MF, Keens TG. Prognosis in pediatric idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis. Chest. 1999;116:721–5. doi: 10.1378/chest.116.3.721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Marwaha RK, Garewal G, Kumar V, Sarkar B, Malik N. Microcytic hypochromic anemia in idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis: A diagnostic pitfall. Indian Pediatr. 1994;31:1101–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Nickol KH. Idiopathic pulmonary haemosiderosis presenting with spontaneous pneumothorax. Tubercle. 1960;41:216–8. doi: 10.1016/s0041-3879(60)80082-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kishimoto N, Kondou H. [A case of idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis of adult onset.] Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi. 2000;38:589–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Morgan PG, Turner-Warwick M. Pulmonary haemosiderosis and pulmonary haemorrhage. Br J Dis Chest. 1981;75:225–42. doi: 10.1016/0007-0971(81)90001-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Agata H, Kondo N, Fukutomi O, et al. Pulmonary hemosiderosis with hypersensitivity to buckwheat. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1997;78:233–7. doi: 10.1016/S1081-1206(10)63394-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Breckenridge RL, Jr, Ross JS. Idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis: A report of familial occurrence. Chest. 1979;75:636–9. doi: 10.1378/chest.75.5.636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Pacheco A, Casanova C, Fogue L, Sueiro A. Long-term clinical follow-up of adult idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis and celiac disease. Chest. 1991;99:1525–6. doi: 10.1378/chest.99.6.1525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]