Abstract
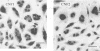
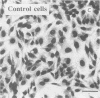
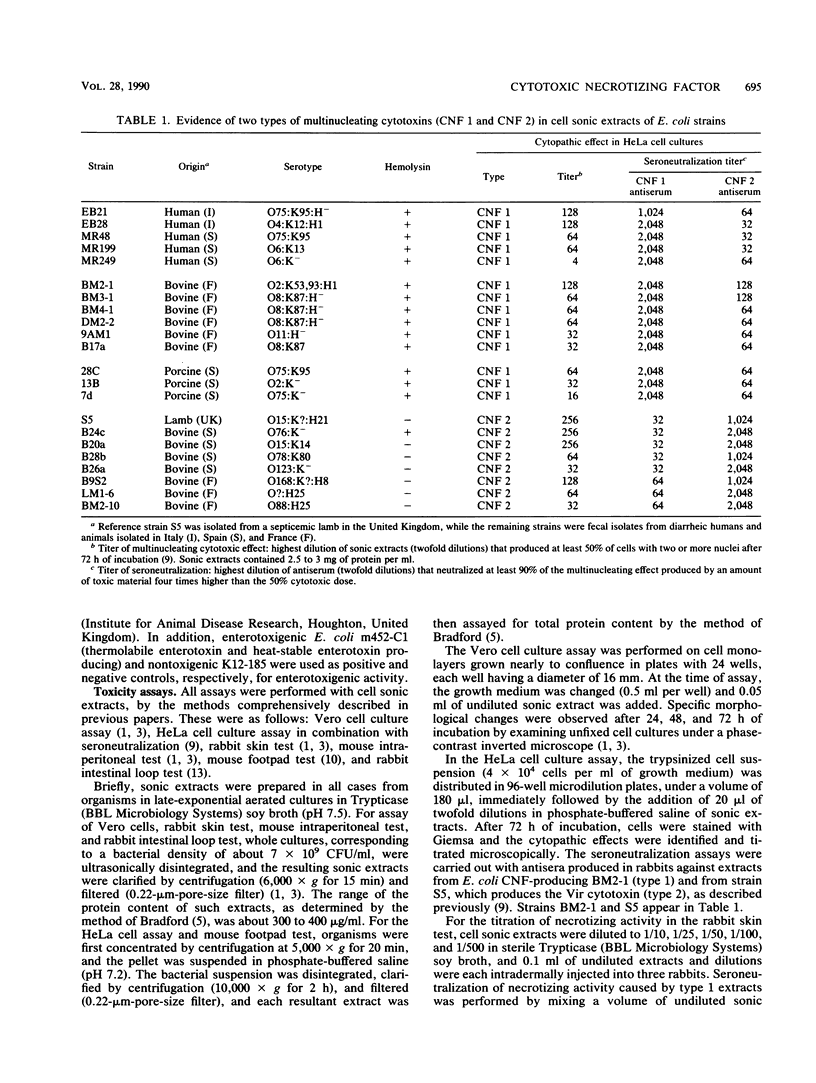
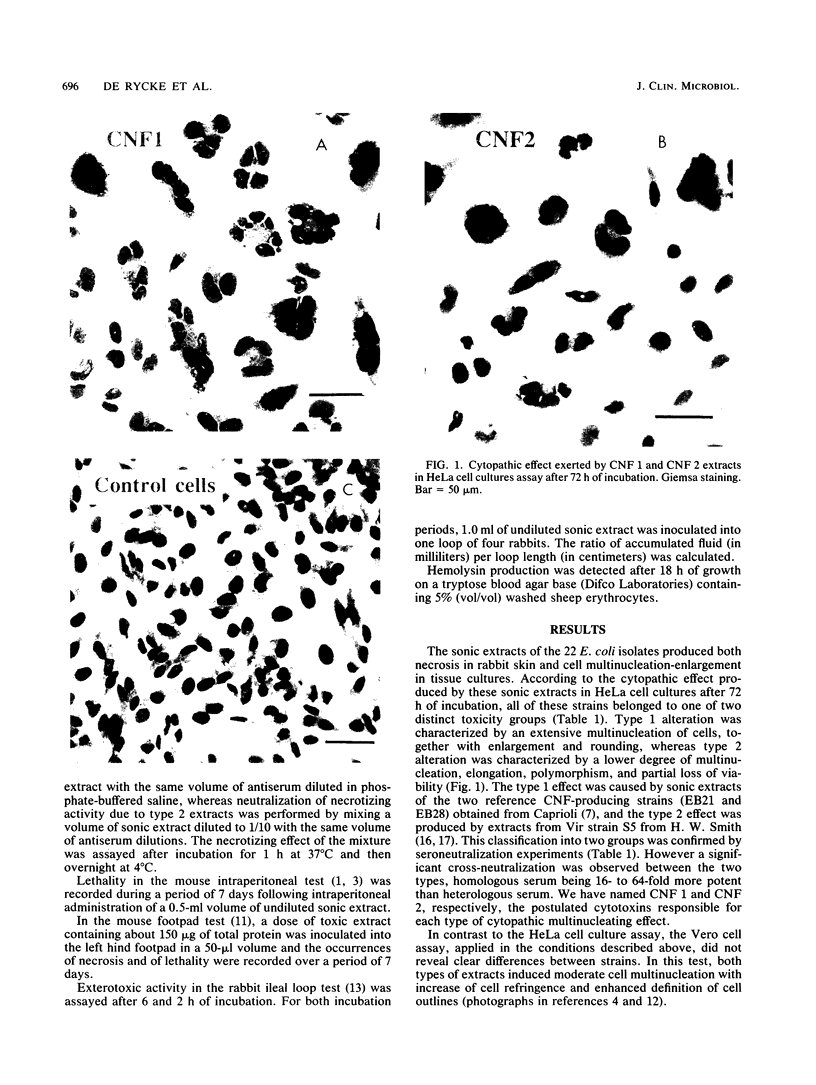
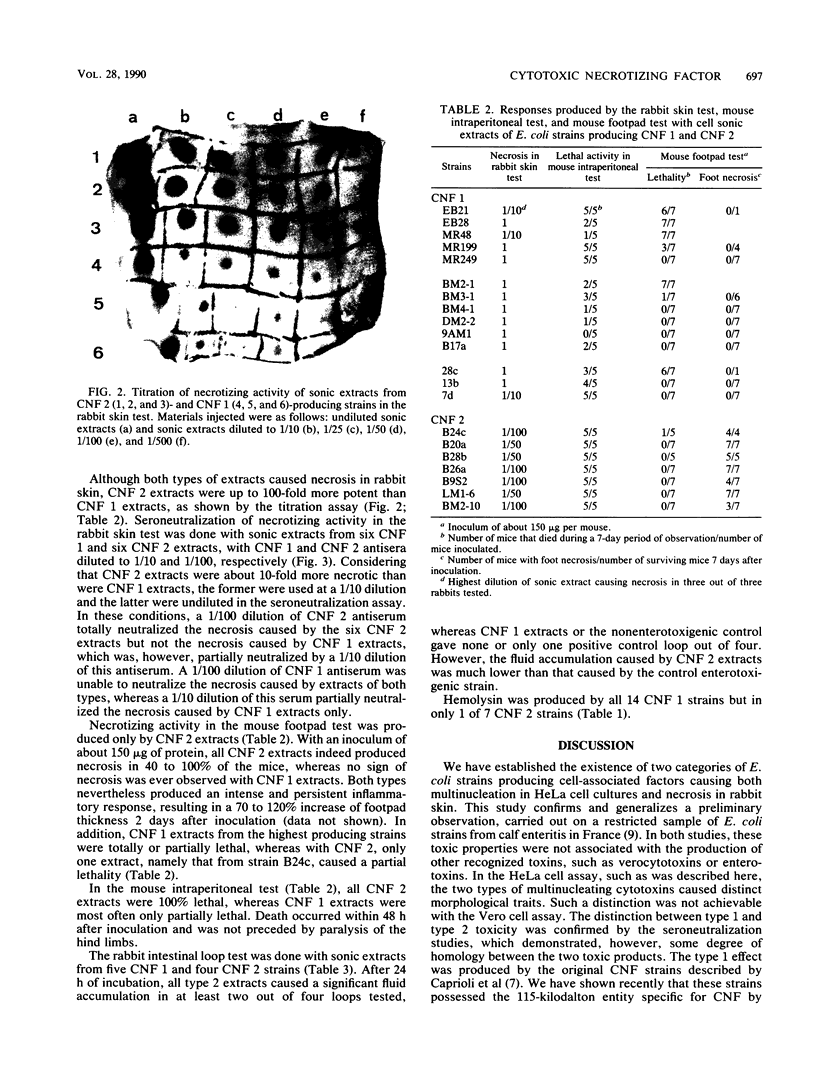
We have characterized the in vitro and in vivo toxic properties of cell sonic extracts from 22 animal and human clinical isolates of Escherichia coli that caused both necrosis in the rabbit skin and multinucleation in tissue cultures, two toxic properties previously reported as being specific for E. coli cytotoxic necrotizing factor (CNF). Two distinct toxic phenotypes were observed. Type 1, which was displayed by originally described CNF strains, was characterized by extensive multinucleation and rounding of cells in HeLa cell culture assays, moderate necrosis in the rabbit skin test, and absence of necrosis in the mouse footpad test. Type 2, which has recently been shown to be associated with E. coli Vir plasmid, was characterized by moderate multinucleation, by polymorphism and elongation of HeLa cells, and by an intense necrotic response in both the rabbit skin test and the mouse footpad test. The distinction between the two cytotoxins accounting for these effects (CNF 1 and CNF 2), together with their partial relatedness, was confirmed by seroneutralization studies of both cytopathic effects and necrosis in the rabbit skin test. In addition, type 2 extracts were more lethal in the mouse intraperitoneal test and induced a moderate, although not totally repetitive, fluid accumulation in the ileal loop test. The original toxic properties of these recently recognized categories of E. coli strains, together with their association with enteritis and septicemia, suggest that these strains may play a significant role in pathology.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bisicchia R., Ciammarughi R., Caprioli A., Falbo V., Ruggeri F. M. Toxin production and haemagglutination in strains of Escherichia coli from diarrhoea in Brescia, Italy. J Hyg (Lond) 1985 Oct;95(2):353–361. doi: 10.1017/s002217240006277x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanco J., Gonzalez E. A., Blanco M., Alonso M. P., Barbadillo M. J. Toxins and serotypes of faecal non-enterotoxigenic and non-enteropathogenic Escherichia coli strains causing mannose-resistant haemagglutination: relation with haemagglutination patterns. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1988 Jul;269(1):43–55. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(88)80083-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanco J., González E. A., García S., Blanco M., Regueiro B., Bernárdez I. Production of toxins by Escherichia coli strains isolated from calves with diarrhoea in galicia (north-western Spain). Vet Microbiol. 1988 Dec;18(3-4):297–311. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(88)90095-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caprioli A., Donelli G., Falbo V., Possenti R., Roda L. G., Roscetti G., Ruggeri F. M. A cell division-active protein from E. coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jan 30;118(2):587–593. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91343-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caprioli A., Falbo V., Roda L. G., Ruggeri F. M., Zona C. Partial purification and characterization of an escherichia coli toxic factor that induces morphological cell alterations. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1300–1306. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1300-1306.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caprioli A., Falbo V., Ruggeri F. M., Baldassarri L., Bisicchia R., Ippolito G., Romoli E., Donelli G. Cytotoxic necrotizing factor production by hemolytic strains of Escherichia coli causing extraintestinal infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jan;25(1):146–149. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.1.146-149.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Rycke J., Guillot J. F., Boivin R. Cytotoxins in non-enterotoxigenic strains of Escherichia coli isolated from feces of diarrheic calves. Vet Microbiol. 1987 Oct;15(1-2):137–150. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(87)90139-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Rycke J., Oswald E., Boivin R. An in vivo assay for the detection of cytotoxic strains of Escherichia coli. Ann Rech Vet. 1989;20(1):39–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Rycke J., Phan-Thanh L., Bernard S. Immunochemical identification and biological characterization of cytotoxic necrotizing factor from Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 May;27(5):983–988. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.5.983-988.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez E. A., Blanco J. Comparison between enterotoxic activity and methanol solubility in heat-stable enterotoxins (STa and STb) from Escherichia coli of human, porcine and bovine origins. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1985 Aug;260(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(85)80092-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaren I., Wray C. Another animal Escherichia coli cytopathic factor. Vet Rec. 1986 Dec 6;119(23):576–577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W., Whipp S. C., Argenzio R. A., Levine M. M., Giannella R. A. Attaching and effacing activities of rabbit and human enteropathogenic Escherichia coli in pig and rabbit intestines. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1340–1351. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1340-1351.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oswald E., De Rycke J., Guillot J. F., Boivin R. Cytotoxic effect of multinucleation in HeLa cell cultures associated with the presence of Vir plasmid in Escherichia coli strains. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Mar;49(1):95–99. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90349-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W. A search for transmissible pathogenic characters in invasive strains of Escherichia coli: the discovery of a plasmid-controlled toxin and a plasmid-controlled lethal character closely associated, or identical, with colicine V. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Jul;83(0):95–111. doi: 10.1099/00221287-83-1-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]