Abstract
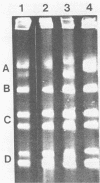
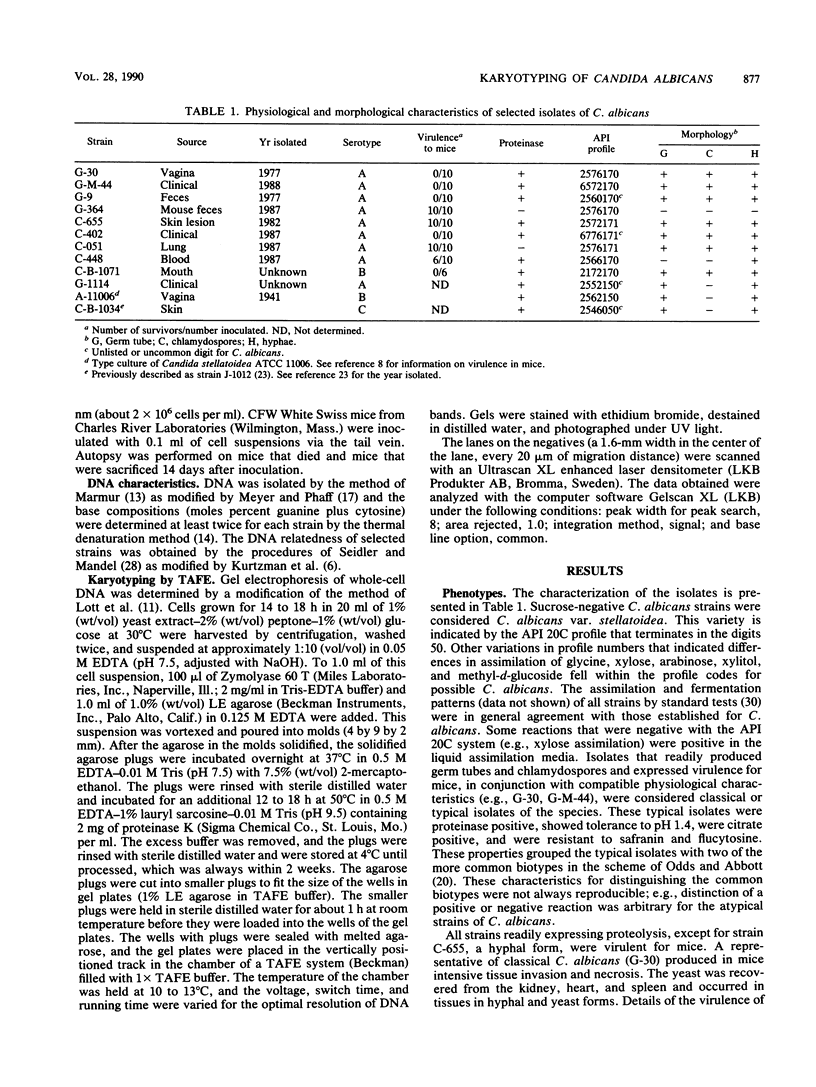
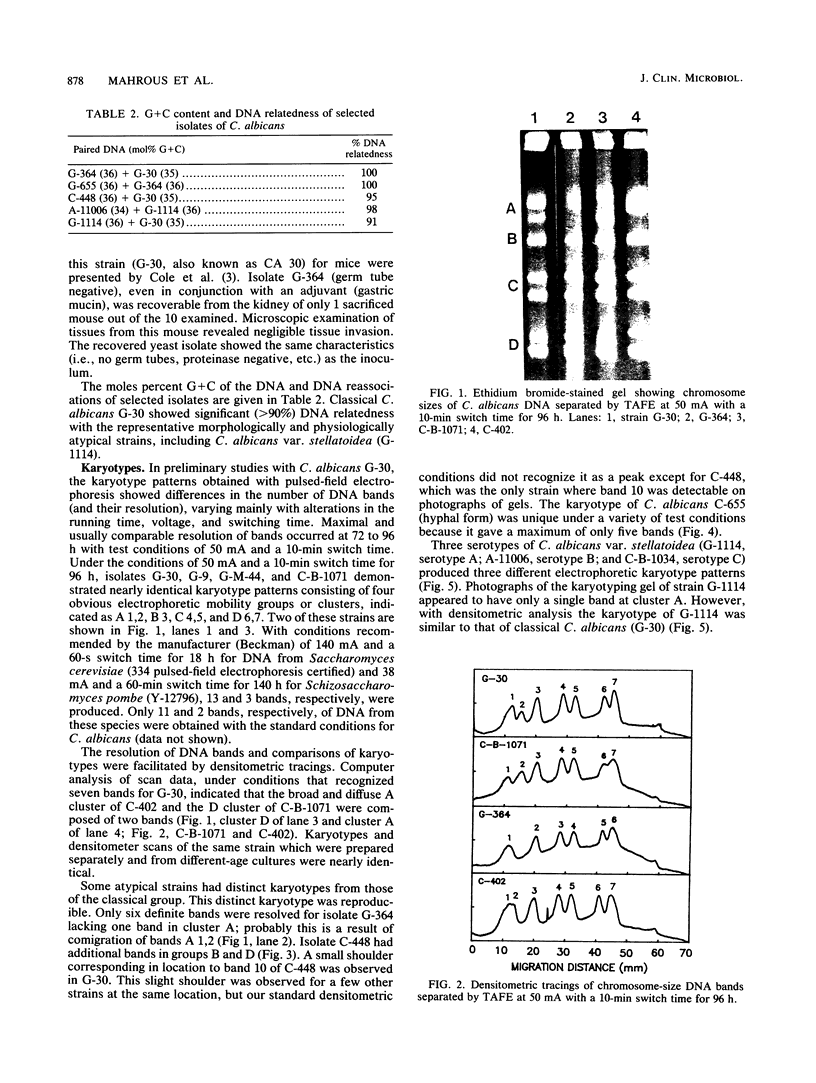
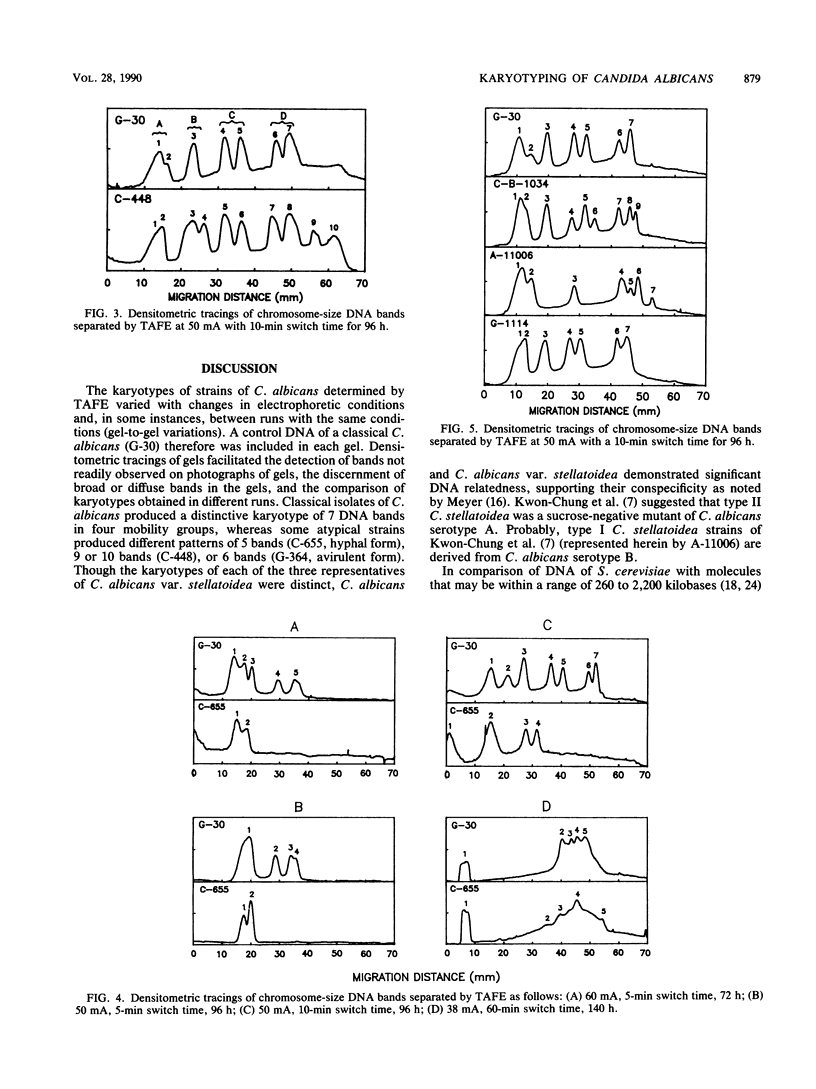
Electrophoretic karyotypes of atypical isolates of Candida albicans, e.g., strains that were germ tube negative, failed to express proteinase activity, demonstrated low virulence for mice, formed hyperchlamydoconidia, produced hyperhyphae, or were sucrose negative (including the type strain of Candida stellatoidea), were compared with those of typical C. albicans. Karyotypes of whole-cell DNA of classical C. albicans examined with transverse alternating-field electrophoresis under specific conditions were composed of seven DNA bands with a specific migration pattern. Certain atypical strains and representatives of the three serotypes of C. stellatoidea produced discrete karyotypes with 5 to 10 bands. All isolates demonstrated a significant degree of DNA relatedness, suggesting their conspecificity. Densitometric tracings of DNA bands provided an objective and standardized method for comparing bands within the gels.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cole G. T., Seshan K. R., Pope L. M., Yancey R. J. Morphological aspects of gastrointestinal tract invasion by Candida albicans in the infant mouse. J Med Vet Mycol. 1988 Jun;26(3):173–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASENCLEVER H. F., MITCHELL W. O. Antigenic studies of Candida. I. Observation of two antigenic groups in Candida albicans. J Bacteriol. 1961 Oct;82:570–573. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.4.570-573.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J., Riggsby W. S., Uphoff R. A., Hicks J. B., Whelan W. L., Reiss E., Magee B. B., Wickes B. L. Genetic differences between type I and type II Candida stellatoidea. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):527–532. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.527-532.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J., Wickes B. L., Merz W. G. Association of electrophoretic karyotype of Candida stellatoidea with virulence for mice. Infect Immun. 1988 Jul;56(7):1814–1819. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.7.1814-1819.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasker B. A., Carle G. F., Kobayashi G. S., Medoff G. Comparison of the separation of Candida albicans chromosome-sized DNA by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis techniques. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 25;17(10):3783–3793. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.10.3783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lott T. J., Boiron P., Reiss E. An electrophoretic karyotype for Candida albicans reveals large chromosomes in multiples. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Aug;209(1):170–174. doi: 10.1007/BF00329854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARMUR J., DOTY P. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its thermal denaturation temperature. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jul;5:109–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee B. B., Koltin Y., Gorman J. A., Magee P. T. Assignment of cloned genes to the seven electrophoretically separated Candida albicans chromosomes. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4721–4726. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz W. G., Connelly C., Hieter P. Variation of electrophoretic karyotypes among clinical isolates of Candida albicans. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 May;26(5):842–845. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.5.842-845.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer S. A., Phaff H. J. Deoxyribonucleic acid base composition in yeasts. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):52–56. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.52-56.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer R. K., Schild D. Genetic map of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, edition 9. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Sep;49(3):181–213. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.3.181-213.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noolandi J., Slater G. W., Lim H. A., Viovy J. L. Generalized tube model of biased reptation for gel electrophoresis of DNA. Science. 1989 Mar 17;243(4897):1456–1458. doi: 10.1126/science.2928779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odds F. C., Abbott A. B. A simple system for the presumptive identification of Candida albicans and differentiation of strains within the species. Sabouraudia. 1980 Dec;18(4):301–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odds F. C., Abbott A. B. Modification and extension of tests for differentiation of Candida species and strains. Sabouraudia. 1983 Mar;21(1):79–81. doi: 10.1080/00362178385380111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odds F. C., Auger P., Krogh P., Neely A. N., Segal E. Biotyping of Candida albicans: results of an international collaborative survey. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jul;27(7):1506–1509. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.7.1506-1509.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okubo Y., Honma Y., Suzuki S. Relationship between phosphate content and serological activities of the mannans of Candida albicans strains NIH A-207, NIH B-792, and J-1012. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):677–680. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.677-680.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perfect J. R., Magee B. B., Magee P. T. Separation of chromosomes of Cryptococcus neoformans by pulsed field gel electrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2624–2627. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2624-2627.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polonelli L., Archibusacci C., Sestito M., Morace G. Killer system: a simple method for differentiating Candida albicans strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 May;17(5):774–780. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.5.774-780.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüchel R., Tegeler R., Trost M. A comparison of secretory proteinases from different strains of Candida albicans. Sabouraudia. 1982 Sep;20(3):233–244. doi: 10.1080/00362178285380341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer S., Stevens D. A. Application of DNA typing methods to epidemiology and taxonomy of Candida species. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Apr;25(4):675–679. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.4.675-679.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidler R. J., Mandel M. Quantitative aspects of deoxyribonucleic acid renaturation: base composition, state of chromosome replication, and polynucleotide homologies. J Bacteriol. 1971 May;106(2):608–614. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.2.608-614.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet C. E., Kaufman L. Application of agglutinins for the rapid and accurate identification of medically important Candida species. Appl Microbiol. 1970 May;19(5):830–836. doi: 10.1128/am.19.5.830-836.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warnock D. W., Speller C. D., Milne J. D., Hilton A. L., Kershaw P. I. Epidemiological investigation of patients with vulvovaginal candidosis. Application of a resistogram method for strain differentiation of Candida albicans. Br J Vener Dis. 1979 Oct;55(5):357–361. doi: 10.1136/sti.55.5.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whelan W. L., Magee P. T. Natural heterozygosity in Candida albicans. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):896–903. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.896-903.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]