Abstract
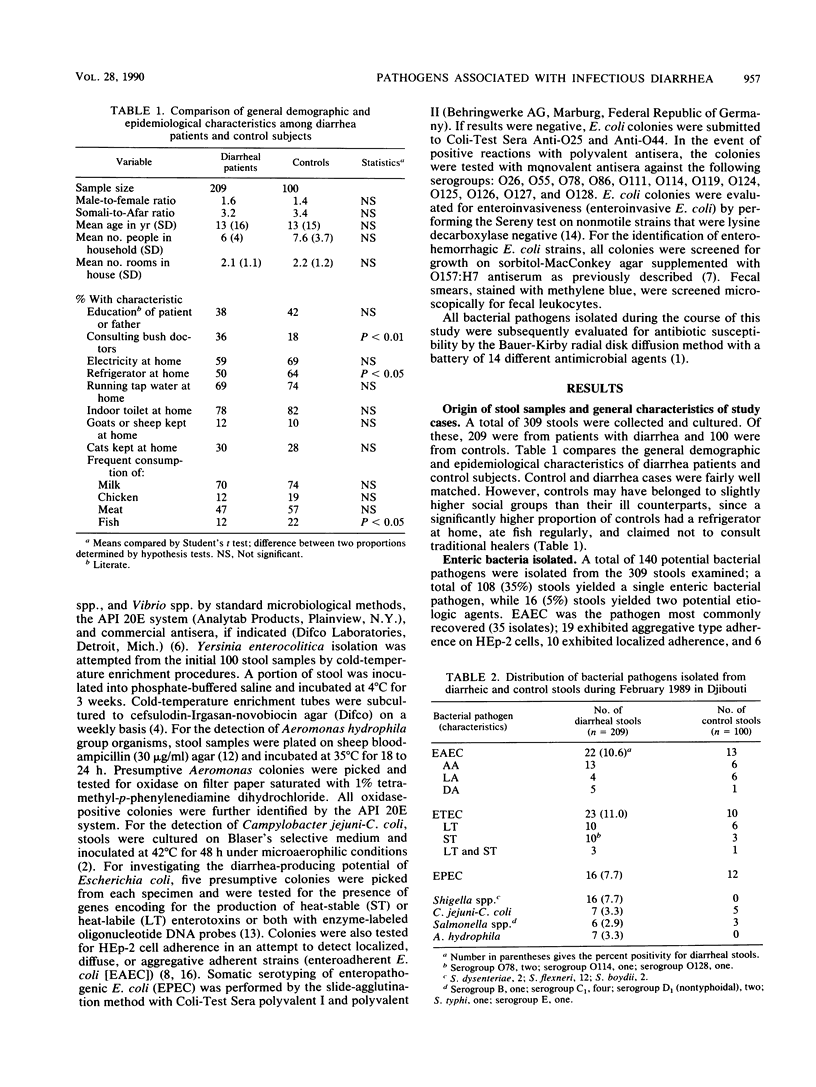
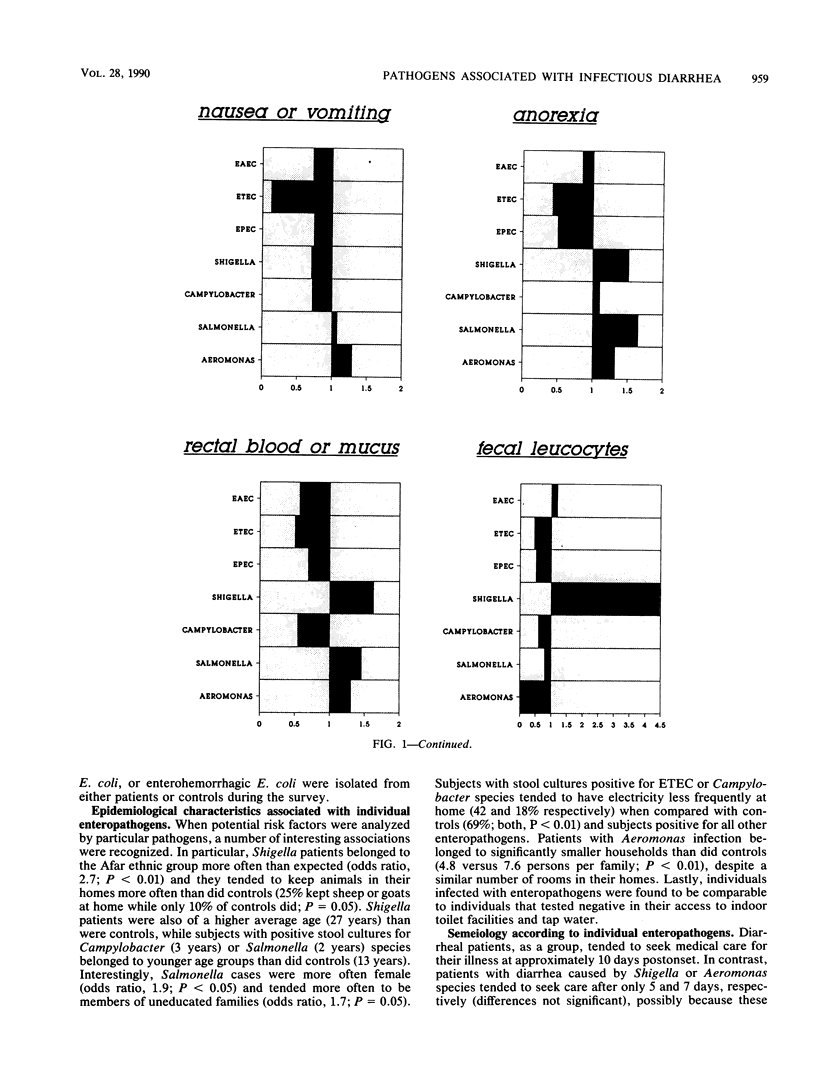
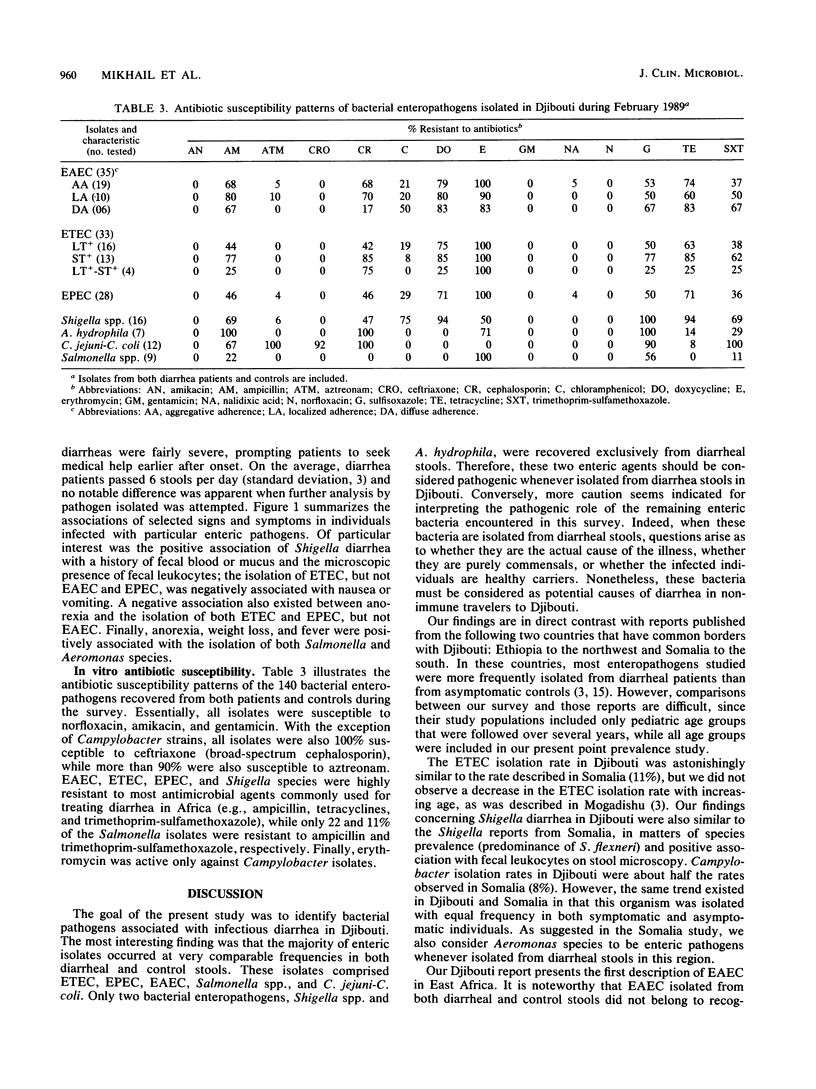
During a survey examining the causes of diarrhea in the East African country of Djibouti, 140 bacterial pathogens were recovered from 209 diarrheal and 100 control stools. The following pathogens were isolated at comparable frequencies from both diarrheal and control stools: enteroadherent Escherichia coli (EAEC) (10.6 versus 13%), enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC) (11 versus 10%), enteropathogenic E. coli (EPEC) (7.7 versus 12%), Salmonella spp. (2.9 versus 3%), and Campylobacter jejuni-C. coli (3.3 versus 5%). Surprisingly, the EAEC strains isolated did not correspond to well-recognized EPEC serogroups. No Yersinia spp., enteroinvasive E. coli, or enterohemorrhagic E. coli were isolated during the course of this study. Only the following two genera were recovered from diarrheal stools exclusively: Shigella spp. (7.7%) and Aeromonas hydrophila group organisms (3.3%). Shigella flexneri was the most common Shigella species isolated. Patients with Shigella species were of a higher average age than were controls (27 versus 13 years), while subjects with Campylobacter or Salmonella species belonged to younger age groups (2.6 and 1.6 years, respectively). Salmonella cases were more often in females. Shigella diarrhea was associated with fecal blood or mucus and leukocytes. ETEC was not associated with nausea or vomiting. Anorexia, weight loss, and fever were associated with the isolation of Salmonella and Aeromonas species. EAEC, ETEC, EPEC, and Shigella species were resistant to most drugs used for treating diarrhea in Africa, while the antibiotic most active against all bacteria tested was norfloxacin. We conclude that in Djibouti in 1989, Shigella and Aeromonas species must be considered as potential pathogens whenever they are isolated from diarrheal stools and that norfloxacin should be considered the drug of choice in adults for treating severe shigellosis and for diarrhea prophylaxis in travelers.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Glass R. I., Huq M. I., Stoll B., Kibriya G. M., Alim A. R. Isolation of Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni from Bangladeshi children. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Dec;12(6):744–747. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.6.744-747.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiss J. Selective culturing of Yersinia enterocolitica at a low temperature. Scand J Infect Dis. 1975;7(4):249–251. doi: 10.3109/inf.1975.7.issue-4.05. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomes T. A., Blake P. A., Trabulsi L. R. Prevalence of Escherichia coli strains with localized, diffuse, and aggregative adherence to HeLa cells in infants with diarrhea and matched controls. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Feb;27(2):266–269. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.2.266-269.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March S. B., Ratnam S. Sorbitol-MacConkey medium for detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 associated with hemorrhagic colitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 May;23(5):869–872. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.5.869-872.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathewson J. J., Johnson P. C., DuPont H. L., Morgan D. R., Thornton S. A., Wood L. V., Ericsson C. D. A newly recognized cause of travelers' diarrhea: enteroadherent Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1985 Mar;151(3):471–475. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.3.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathewson J. J., Johnson P. C., DuPont H. L., Satterwhite T. K., Winsor D. K. Pathogenicity of enteroadherent Escherichia coli in adult volunteers. J Infect Dis. 1986 Sep;154(3):524–527. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.3.524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathewson J. J., Oberhelman R. A., Dupont H. L., Javier de la Cabada F., Garibay E. V. Enteroadherent Escherichia coli as a cause of diarrhea among children in Mexico. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Oct;25(10):1917–1919. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.10.1917-1919.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishra S., Nair G. B., Bhadra R. K., Sikder S. N., Pal S. C. Comparison of selective media for primary isolation of Aeromonas species from human and animal feces. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Nov;25(11):2040–2043. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.11.2040-2043.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oprandy J. J., Thornton S. A., Gardiner C. H., Burr D., Batchelor R., Bourgeois A. L. Alkaline phosphatase-conjugated oligonucleotide probes for enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in travelers to South America and West Africa. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jan;26(1):92–95. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.1.92-95.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva R. M., Toledo M. R., Trabulsi L. R. Biochemical and cultural characteristics of invasive Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 May;11(5):441–444. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.5.441-444.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stintzing G., Bäck E., Tufvesson B., Johnsson T., Wadström T., Habte D. Seasonal fluctuations in the occurrence of enterotoxigenic bacteria and rotavirus in paediatric diarrhoea in Addis Ababa. Bull World Health Organ. 1981;59(1):67–73. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vial P. A., Robins-Browne R., Lior H., Prado V., Kaper J. B., Nataro J. P., Maneval D., Elsayed A., Levine M. M. Characterization of enteroadherent-aggregative Escherichia coli, a putative agent of diarrheal disease. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jul;158(1):70–79. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.1.70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaki A. M., DuPont H. L., el Alamy M. A., Arafat R. R., Amin K., Awad M. M., Bassiouni L., Imam I. Z., el Malih G. S., el Marsafie A. The detection of enteropathogens in acute diarrhea in a family cohort population in rural Egypt. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1986 Sep;35(5):1013–1022. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1986.35.1013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


