Abstract
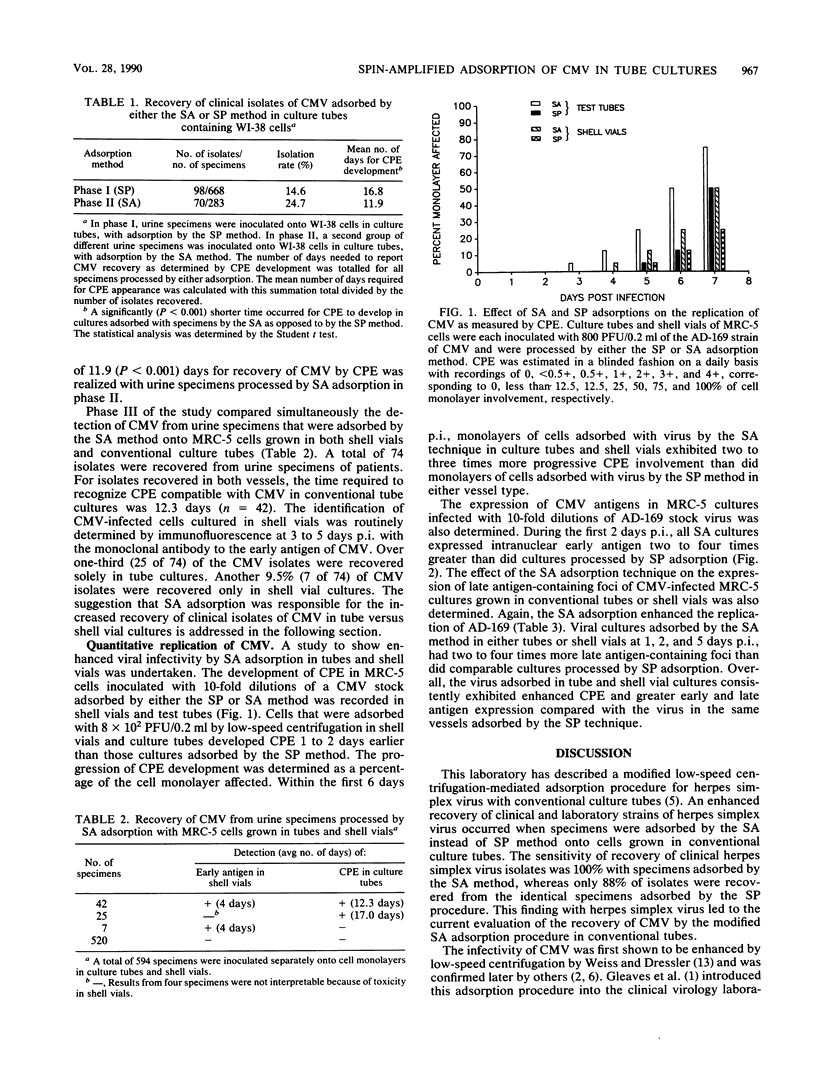
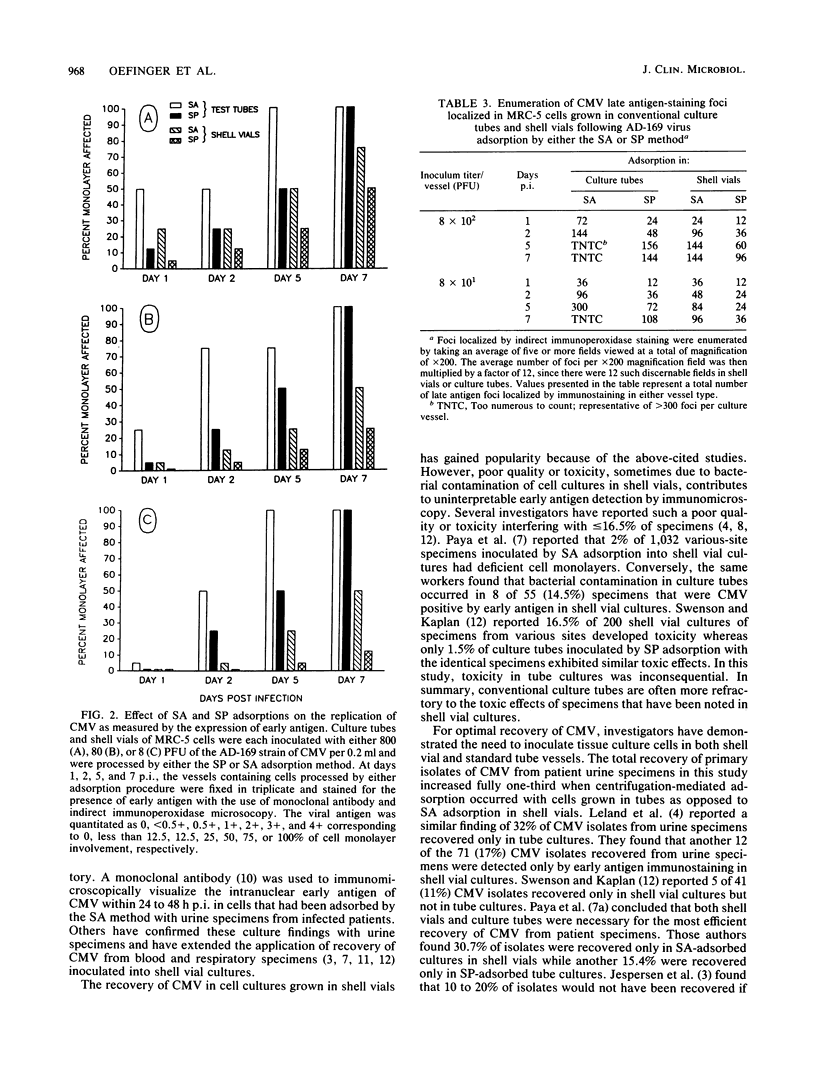
Low-speed centrifugation-mediated adsorption was evaluated as an enhancement of infectivity of clinical and laboratory strains of cytomegalovirus (CMV) occurring with cells grown in conventional culture tubes. The time required for reporting of primary isolates of CMV from urine specimens adsorbed onto monolayers of WI-38 cells in culture tubes was calculated. Of 668 specimens adsorbed by the stationary phase (SP) method, 98 were positive by cytopathic effect (CPE) that required an average of 16.8 days for recovery in culture. However, the appearance of CPE required a shorter average time of 11.9 days for 70 CMV strains isolated from 283 specimens adsorbed in tube cultures by the spin-amplified (SA) method. In another phase of clinical CMV recovery, urine specimens were adsorbed by the SA method onto cell cultures grown in both shell vials and test tubes. Of 594 specimens inoculated, a total of 74 were positive by either CPE in test tubes or immunostaining-localized early antigen in shell vials. Approximately one-third of these CMV isolates were recovered only by CPE from specimens adsorbed by the SA method in test-tube cultures. In a related study to further evaluate differences between adsorption methods, the AD-169 laboratory strain of CMV was adsorbed by SP and SA methods onto MRC-5 cells grown in both culture vessels. Early antigen detection by immunomicroscopy was found in the infected cells at least 2 to 4 days prior to the appearance of CPE, regardless of adsorption procedure. In both vessels, the replication of AD-169 virus in cultures adsorbed by the SA method consistently exceeded that of virus adsorbed by the SP procedure. CPE occurred 24 to 48 h earlier and progressed two to four times more extensively; early antigen was expressed two- to fourfold greater within 24 to 48 h postinfection; and foci of infected cells containing late antigen were two to four times greater in number at 1, 2, and 5 days postinfection. Overall, the replication and enhancement of infectivity of laboratory and clinical strains of CMV as determined by CPE and early and late antigen expression occurred most efficiently with specimens adsorbed by the SA method onto cultures grown in conventional tubes or shell vials.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gleaves C. A., Smith T. F., Shuster E. A., Pearson G. R. Rapid detection of cytomegalovirus in MRC-5 cells inoculated with urine specimens by using low-speed centrifugation and monoclonal antibody to an early antigen. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jun;19(6):917–919. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.6.917-919.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson J. B., Misra V., Mosmann T. R. Cytomegalovirus infectivity: analysis of the phenomenon of centrifugal enhancement of infectivity. Virology. 1976 Jul 1;72(1):235–243. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90326-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jespersen D. J., Drew W. L., Gleaves C. A., Meyers J. D., Warford A. L., Smith T. F. Multisite evaluation of a monoclonal antibody reagent (Syva) for rapid diagnosis of cytomegalovirus in the shell vial assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jul;27(7):1502–1505. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.7.1502-1505.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leland D. S., Hansing R. L., French M. L. Clinical experience with cytomegalovirus isolation using conventional cell cultures and early antigen detection in centrifugation-enhanced shell vial cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jun;27(6):1159–1162. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.6.1159-1162.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn J. E., Walker D. L. Enhancement of infectivity of murine cytomegalovirus in vitro by centrifugal inoculation. J Virol. 1968 Sep;2(9):853–858. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.9.853-858.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paya C. V., Wold A. D., Ilstrup D. M., Smith T. F. Evaluation of number of shell vial cell cultures per clinical specimen for rapid diagnosis of cytomegalovirus infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Feb;26(2):198–200. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.2.198-200.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paya C. V., Wold A. D., Smith T. F. Detection of cytomegalovirus infections in specimens other than urine by the shell vial assay and conventional tube cell cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 May;25(5):755–757. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.5.755-757.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randazzo D. N., Michalski F. J. Comparison of antibodies for rapid detection of cytomegalovirus. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Feb;26(2):369–370. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.2.369-370.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuster E. A., Beneke J. S., Tegtmeier G. E., Pearson G. R., Gleaves C. A., Wold A. D., Smith T. F. Monoclonal antibody for rapid laboratory detection of cytomegalovirus infections: characterization and diagnostic application. Mayo Clin Proc. 1985 Sep;60(9):577–585. doi: 10.1016/s0025-6196(12)60979-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirk P. R., Griffiths P. D. Use of monoclonal antibodies for the diagnosis of cytomegalovirus infection by the detection of early antigen fluorescent foci (DEAFF) in cell culture. J Med Virol. 1987 Apr;21(4):329–337. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890210405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson P. D., Kaplan M. H. Comparison of two rapid culture methods for detection of cytomegalovirus in clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Dec;25(12):2445–2446. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.12.2445-2446.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISS E., DRESSLER H. R. Centrifugation and Rickettsiae and viruses onto cells and its effect on infection. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Apr;103:691–695. doi: 10.3181/00379727-103-25637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


