Abstract
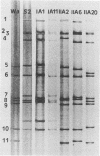
We obtained three stool specimens from each of 371 neonates. Two specimens were obtained between days 1 and 3 after birth, while they were in the hospital, and one specimen was obtained between days 6 and 14 after birth, after they had been discharged from the hospital. Seventy neonates excreted human rotavirus (HRV) while they were in the hospital, and the incidence rate for the cohort was 0.094 episodes per infant day. The incidence rate of community-acquired neonatal infections was markedly reduced to 0.022 episodes per infant day, with eight additional episodes of infection being detected after the infants were discharged from the hospital. Nevertheless, this was higher than the incidence of community-acquired HRV infection of 0.0037 episodes per infant day previously estimated by serology for the same cohort during the subsequent 2 years of infancy. None of the 78 episodes of neonatal HRV infection was accompanied by diarrhea. There were at least 44 distinct electropherotypes of HRV circulating among older infants in the community during the study period, and they comprised at least four different serotypes. Despite the genetic and antigenic diversity of the prevalent HRV isolates, only five electropherotypes with either serotype 2 or 4 specificity were isolated from the neonates, while serotype 1 and 3 viruses were not detected. Two of these electropherotypes, including one which was isolated from 57 of the 78 infants with episodes of infection, were isolated exclusively from the neonates. The other three electropherotypes were also isolated from the older infants; one was a major electropherotype and two were minor electropherotypes which were prevalent among the older infants. These results suggest that distinct populations of HRV cocirculate among neonates and older infants.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert M. J., Unicomb L. E., Barnes G. L., Bishop R. F. Cultivation and characterization of rotavirus strains infecting newborn babies in Melbourne, Australia, from 1975 to 1979. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Sep;25(9):1635–1640. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.9.1635-1640.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop R. F., Barnes G. L., Cipriani E., Lund J. S. Clinical immunity after neonatal rotavirus infection. A prospective longitudinal study in young children. N Engl J Med. 1983 Jul 14;309(2):72–76. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198307143090203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop R. F., Cameron D. J., Veenstra A. A., Barnes G. L. Diarrhea and rotavirus infection associated with differing regimens for postnatal care of newborn babies. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Apr;9(4):525–529. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.4.525-529.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champsaur H., Henry-Amar M., Goldszmidt D., Prevot J., Bourjouane M., Questiaux E., Bach C. Rotavirus carriage, asymptomatic infection, and disease in the first two years of life. II. Serological response. J Infect Dis. 1984 May;149(5):675–682. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.5.675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrystie I. L., Totterdell B. M., Banatvala J. E. Asymptomatic endemic rotavirus infections in the newborn. Lancet. 1978 Jun 3;1(8075):1176–1178. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(78)90967-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulson B. S., Fowler K. J., Bishop R. F., Cotton R. G. Neutralizing monoclonal antibodies to human rotavirus and indications of antigenic drift among strains from neonates. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):14–20. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.14-20.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagbami A. H., Oyejide C. O., Enahoro F. Neonatal rotavirus infection in urban and rural communities in Nigeria. Trop Geogr Med. 1987 Oct;39(4):341–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores J., Midthun K., Hoshino Y., Green K., Gorziglia M., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Conservation of the fourth gene among rotaviruses recovered from asymptomatic newborn infants and its possible role in attenuation. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):972–979. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.972-979.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy A. M., Albrey M. B., Crewe E. B. Rotavirus infections of neonates. Lancet. 1977 Dec 3;2(8049):1149–1150. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(77)91538-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offit P. A., Blavat G., Greenberg H. B., Clark H. F. Molecular basis of rotavirus virulence: role of gene segment 4. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):46–49. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.46-49.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Schael I., Daoud G., White L., Urbina G., Daoud N., Perez M., Flores J. Rotavirus shedding by newborn children. J Med Virol. 1984;14(2):127–136. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890140206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotbart H. A., Nelson W. L., Glode M. P., Triffon T. C., Kogut S. J., Yolken R. H., Hernandez J. A., Levin M. J. Neonatal rotavirus-associated necrotizing enterocolitis: case control study and prospective surveillance during an outbreak. J Pediatr. 1988 Jan;112(1):87–93. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3476(88)80128-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tam J. S., Kum W. W., Lam B., Yeung C. Y., Ng M. H. Molecular epidemiology of human rotavirus infection in children in Hong Kong. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Mar;23(3):660–664. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.3.660-664.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vial P. A., Kotloff K. L., Losonsky G. A. Molecular epidemiology of rotavirus infection in a room for convalescing newborns. J Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;157(4):668–673. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.4.668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walther F. J., Bruggeman C., Daniels-Bosman M. S. Rotavirus infections in high-risk neonates. J Hosp Infect. 1984 Dec;5(4):438–443. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(84)90014-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yam W. C., Lung M. L., Yeung C. Y., Tam J. S., Ng M. H. Escherichia coli associated with childhood diarrheas. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Nov;25(11):2145–2149. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.11.2145-2149.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng B. J., Lam W. P., Yan Y. K., Lo S. K., Lung M. L., Ng M. H. Direct identification of serotypes of natural human rotavirus isolates by hybridization using cDNA probes derived from segment 9 of the rotavirus genome. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Mar;27(3):552–557. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.3.552-557.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng B. J., Lo S. K., Tam J. S., Lo M., Yeung C. Y., Ng M. H. Prospective study of community-acquired rotavirus infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Sep;27(9):2083–2090. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.9.2083-2090.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]