Abstract
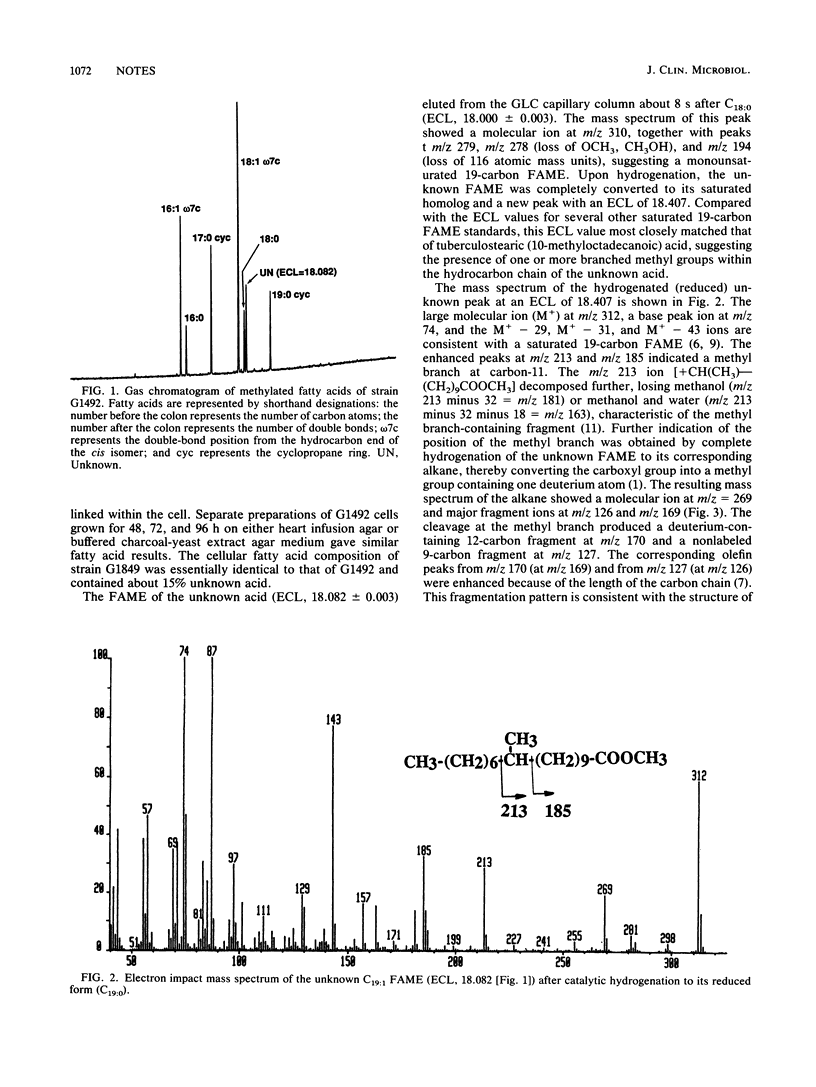
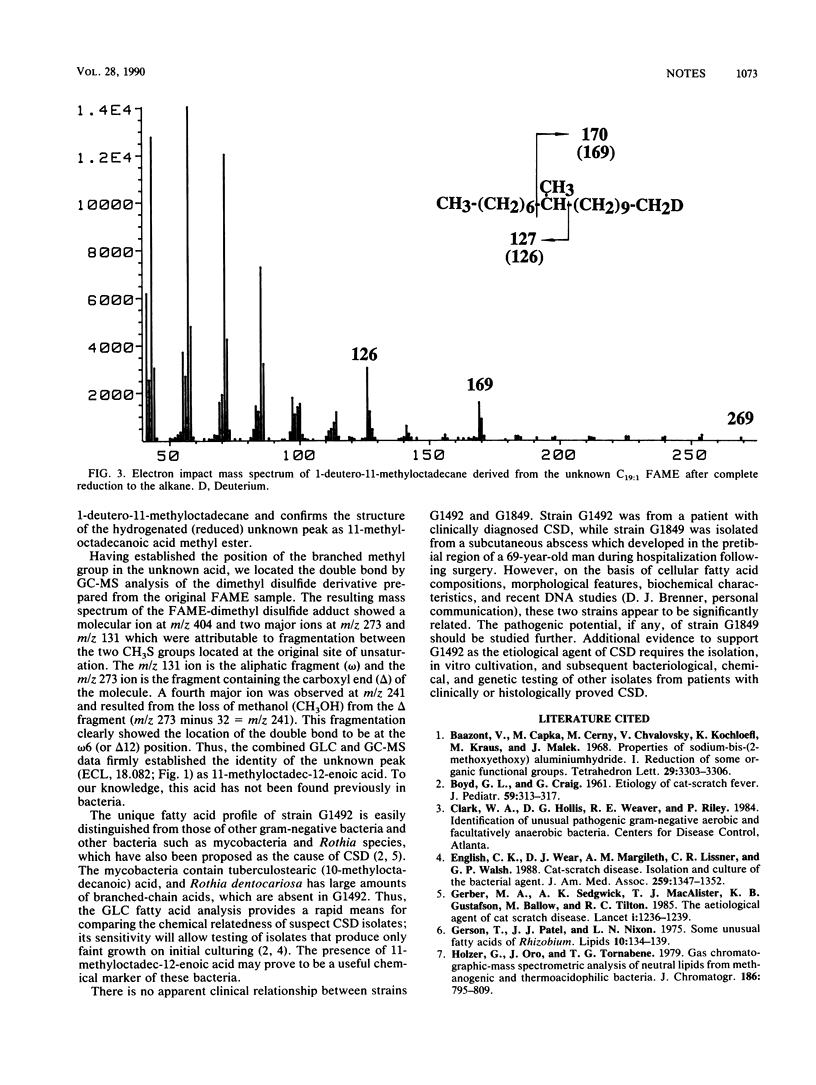
The cellular fatty acid composition of a gram-negative bacterium associated with cat scratch disease was determined by capillary gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). The fatty acid profile of this organism was distinct from those of other bacteria we have tested and was characterized by an unknown acid which was identified as 11-methyloctadec-12-enoic acid. The position of the branched methyl group in this acid was established by GC-MS of the reduced acid, and the location of the double bond was confirmed by GC-MS analysis of dimethyl disulfide derivatives. Another clinical isolate with no known relationship to cat scratch disease but with similar morphological and biochemical features had a similar fatty acid profile, including 11-methyloctadec-12-enoic acid.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- English C. K., Wear D. J., Margileth A. M., Lissner C. R., Walsh G. P. Cat-scratch disease. Isolation and culture of the bacterial agent. JAMA. 1988 Mar 4;259(9):1347–1352. doi: 10.1001/jama.259.9.1347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber M. A., Sedgwick A. K., MacAlister T. J., Gustafson K. B., Ballow M., Tilton R. C. The aetiological agent of cat scratch disease. Lancet. 1985 Jun 1;1(8440):1236–1239. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92311-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerson T., Patel J. J., Nixon L. N. Some unusual fatty acids of Rhizobium. Lipids. 1975 Mar;10(3):134–139. doi: 10.1007/BF02534150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert M. A., Moss C. W. Cellular fatty acid compositions and isoprenoid quinone contents of 23 Legionella species. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Mar;27(3):465–473. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.3.465-473.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W. Gas-liquid chromatography as an analytical tool in microbiology. J Chromatogr. 1981 Jan 9;203:337–347. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)80305-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W., Lambert-Fair M. A. Location of double bonds in monounsaturated fatty acids of Campylobacter cryaerophila with dimethyl disulfide derivatives and combined gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jul;27(7):1467–1470. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.7.1467-1470.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


