Abstract
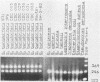
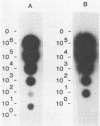
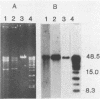
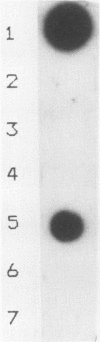
Segments of the ospA gene of Borrelia burgdorferi were amplified by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Oligonucleotide primers used in the reaction flank a 309-base-pair segment within the ospA gene. After 35 cycles of amplification, the product could be detected by agarose gel electrophoresis or dot hybridization with a 32P-labeled probe. This segment was amplified in all strains of B. burgdorferi tested, but it was not detected in other bacterial species. An additional primer pair which has a broad specificity for conserved 16S rRNA sequences that are present in eubacteria amplified a 215-base-pair fragment in all organisms tested. The sensitivity of PCR for the detection of B. burgdorferi in clinical samples was evaluated by seeding blood and urine specimens with B. burgdorferi and subjecting them to amplification. We were able to detect 10 organisms per ml of blood or urine, using PCR with dot hybridization detection. DNA extraction is not required for sample preparation. Blood and urine specimens were obtained from canines with clinical and serologic evidence of Lyme disease and subjected to PCR analysis. Of 17 clinical specimens from 15 animals, one blood specimen showed reactivity in the PCR.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. F., Duray P. H., Magnarelli L. A. Prevalence of Borrelia burgdorferi in white-footed mice and Ixodes dammini at Fort McCoy, Wis. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;25(8):1495–1497. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.8.1495-1497.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. F., Magnarelli L. A., Burgdorfer W., Barbour A. G. Spirochetes in Ixodes dammini and mammals from Connecticut. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1983 Jul;32(4):818–824. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1983.32.818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W., Grunwaldt E., Steere A. C. Antibodies of patients with Lyme disease to components of the Ixodes dammini spirochete. J Clin Invest. 1983 Aug;72(2):504–515. doi: 10.1172/JCI110998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Heiland R. A., Howe T. R. Heterogeneity of major proteins in Lyme disease borreliae: a molecular analysis of North American and European isolates. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):478–484. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Plasmid analysis of Borrelia burgdorferi, the Lyme disease agent. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Mar;26(3):475–478. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.3.475-478.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benach J. L., Bosler E. M., Hanrahan J. P., Coleman J. L., Habicht G. S., Bast T. F., Cameron D. J., Ziegler J. L., Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W. Spirochetes isolated from the blood of two patients with Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 31;308(13):740–742. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303313081302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergström S., Bundoc V. G., Barbour A. G. Molecular analysis of linear plasmid-encoded major surface proteins, OspA and OspB, of the Lyme disease spirochaete Borrelia burgdorferi. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Apr;3(4):479–486. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00194.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Benach J. L., Grunwaldt E., Davis J. P. Lyme disease-a tick-borne spirochetosis? Science. 1982 Jun 18;216(4552):1317–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.7043737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess E. C., Gendron-Fitzpatrick A., Wright W. O. Arthritis and systemic disease caused by Borrelia burgdorferi infection in a cow. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1987 Dec 1;191(11):1468–1470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen K., Neimark H., Rumore P., Steinman C. R. Broad range DNA probes for detecting and amplifying eubacterial nucleic acids. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Jan 1;48(1):19–24. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90139-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciesielski C. A., Markowitz L. E., Horsley R., Hightower A. W., Russell H., Broome C. V. The geographic distribution of Lyme disease in the United States. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:283–288. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31862.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craft J. E., Grodzicki R. L., Steere A. C. Antibody response in Lyme disease: evaluation of diagnostic tests. J Infect Dis. 1984 May;149(5):789–795. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.5.789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duray P. H., Johnson R. C. The histopathology of experimentally infected hamsters with the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1986 Feb;181(2):263–269. doi: 10.3181/00379727-181-42251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe T. R., Mayer L. W., Barbour A. G. A single recombinant plasmid expressing two major outer surface proteins of the Lyme disease spirochete. Science. 1985 Feb 8;227(4687):645–646. doi: 10.1126/science.3969554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu L. C., Bendel R. E., Yoshida A. Direct detection of usual and atypical alleles on the human aldehyde dehydrogenase-2 (ALDH2) locus. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Dec;41(6):996–1001. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen J. W., Steenvoorden A. C., Lyons J., Anger B., Böhlke J. U., Bos J. L., Seliger H., Bartram C. R. RAS gene mutations in acute and chronic myelocytic leukemias, chronic myeloproliferative disorders, and myelodysplastic syndromes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9228–9232. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Hyde F. W., Rumpel C. M. Taxonomy of the Lyme disease spirochetes. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):529–537. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Marek N., Kodner C. Infection of Syrian hamsters with Lyme disease spirochetes. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Dec;20(6):1099–1101. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.6.1099-1101.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok S., Mack D. H., Mullis K. B., Poiesz B., Ehrlich G., Blair D., Friedman-Kien A., Sninsky J. J. Identification of human immunodeficiency virus sequences by using in vitro enzymatic amplification and oligomer cleavage detection. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1690–1694. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1690-1694.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine J. F., Wilson M. L., Spielman A. Mice as reservoirs of the Lyme disease spirochete. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1985 Mar;34(2):355–360. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1985.34.355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lissman B. A., Bosler E. M., Camay H., Ormiston B. G., Benach J. L. Spirochete-associated arthritis (Lyme disease) in a dog. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1984 Jul 15;185(2):219–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnarelli L. A., Anderson J. F., Johnson R. C. Cross-reactivity in serological tests for Lyme disease and other spirochetal infections. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jul;156(1):183–188. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.1.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olive D. M. Detection of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli after polymerase chain reaction amplification with a thermostable DNA polymerase. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Feb;27(2):261–265. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.2.261-265.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reik L., Steere A. C., Bartenhagen N. H., Shope R. E., Malawista S. E. Neurologic abnormalities of Lyme disease. Medicine (Baltimore) 1979 Jul;58(4):281–294. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197907000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan T. G., Burgdorfer W., Schrumpf M. E., Karstens R. H. The urinary bladder, a consistent source of Borrelia burgdorferi in experimentally infected white-footed mice (Peromyscus leucopus). J Clin Microbiol. 1988 May;26(5):893–895. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.5.893-895.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata D. K., Arnheim N., Martin W. J. Detection of human papilloma virus in paraffin-embedded tissue using the polymerase chain reaction. J Exp Med. 1988 Jan 1;167(1):225–230. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.1.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanek G., Burger I., Hirschl A., Wewalka G., Radda A. Borrelia transfer by ticks during their life cycle. Studies on laboratory animals. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1986 Dec;263(1-2):29–33. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(86)80098-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanek G., Pletschette M., Flamm H., Hirschl A. M., Aberer E., Kristoferitsch W., Schmutzhard E. European Lyme borreliosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:274–282. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31861.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Grodzicki R. L., Craft J. E., Shrestha M., Kornblatt A. N., Malawista S. E. Recovery of Lyme disease spirochetes from patients. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):557–560. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Malawista S. E., Bartenhagen N. H., Spieler P. N., Newman J. H., Rahn D. W., Hutchinson G. J., Green J., Snydman D. R., Taylor E. The clinical spectrum and treatment of Lyme disease. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):453–461. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]