Abstract
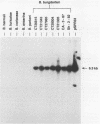
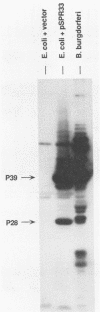
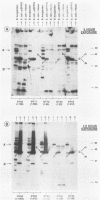
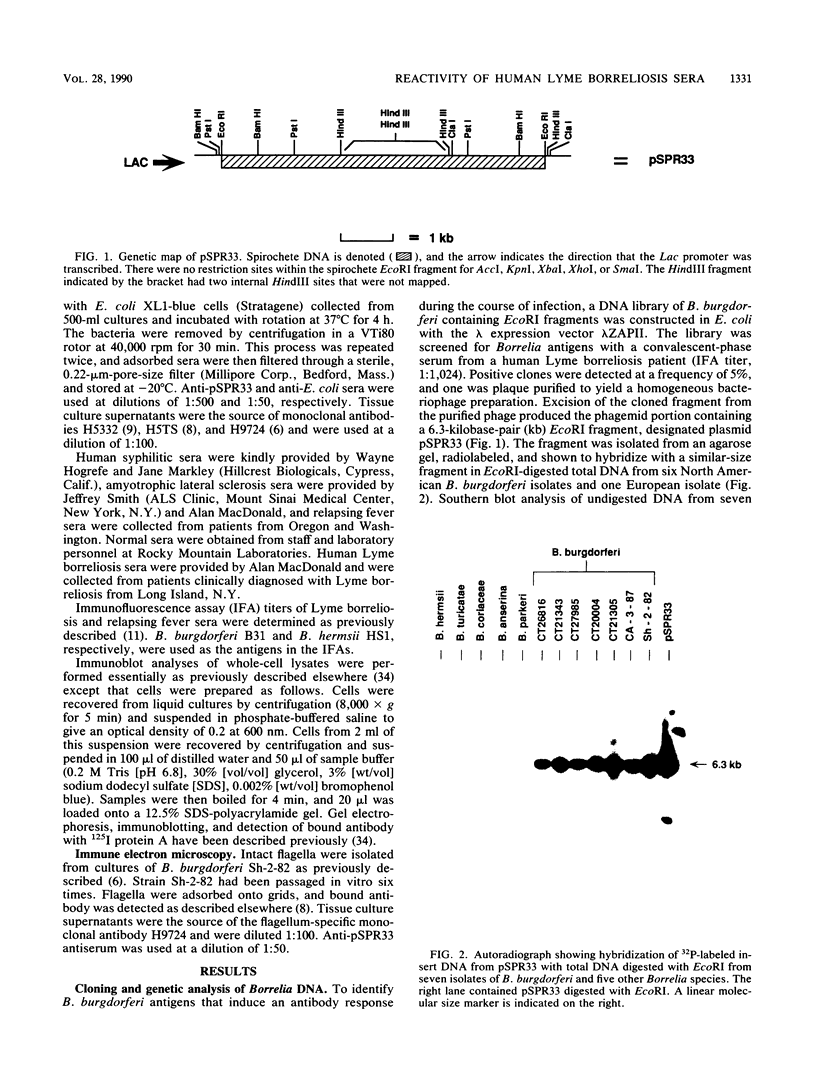
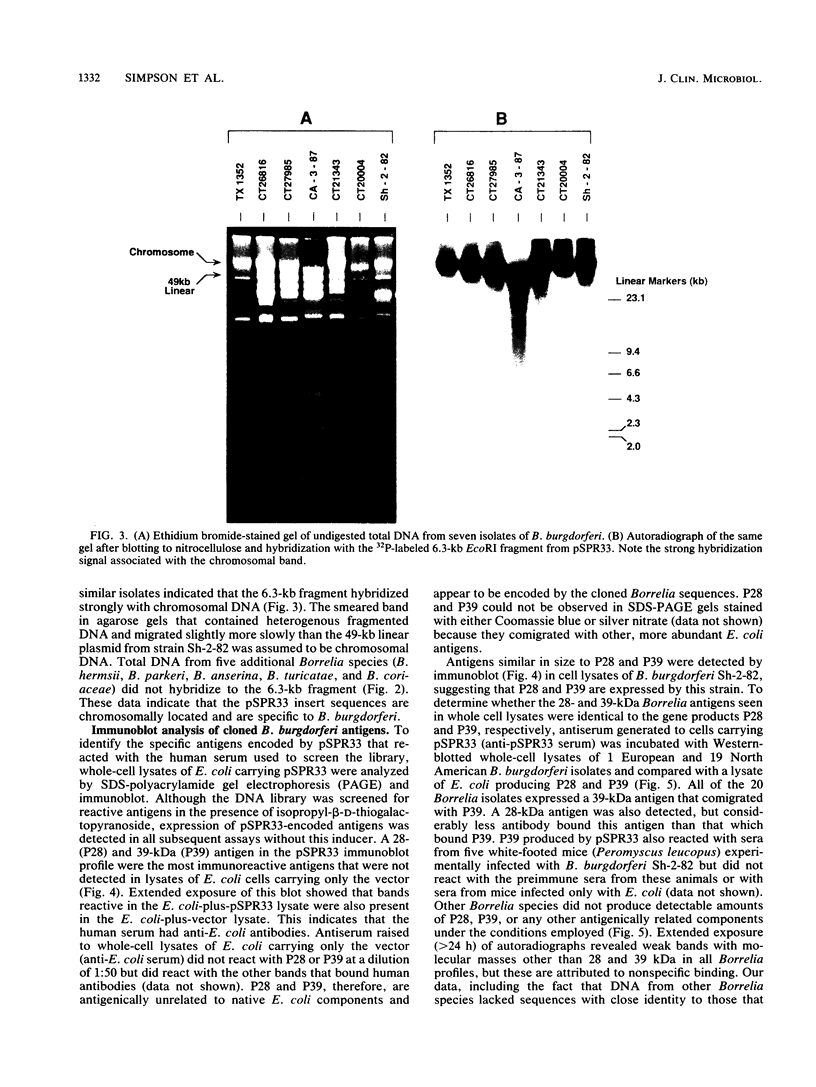
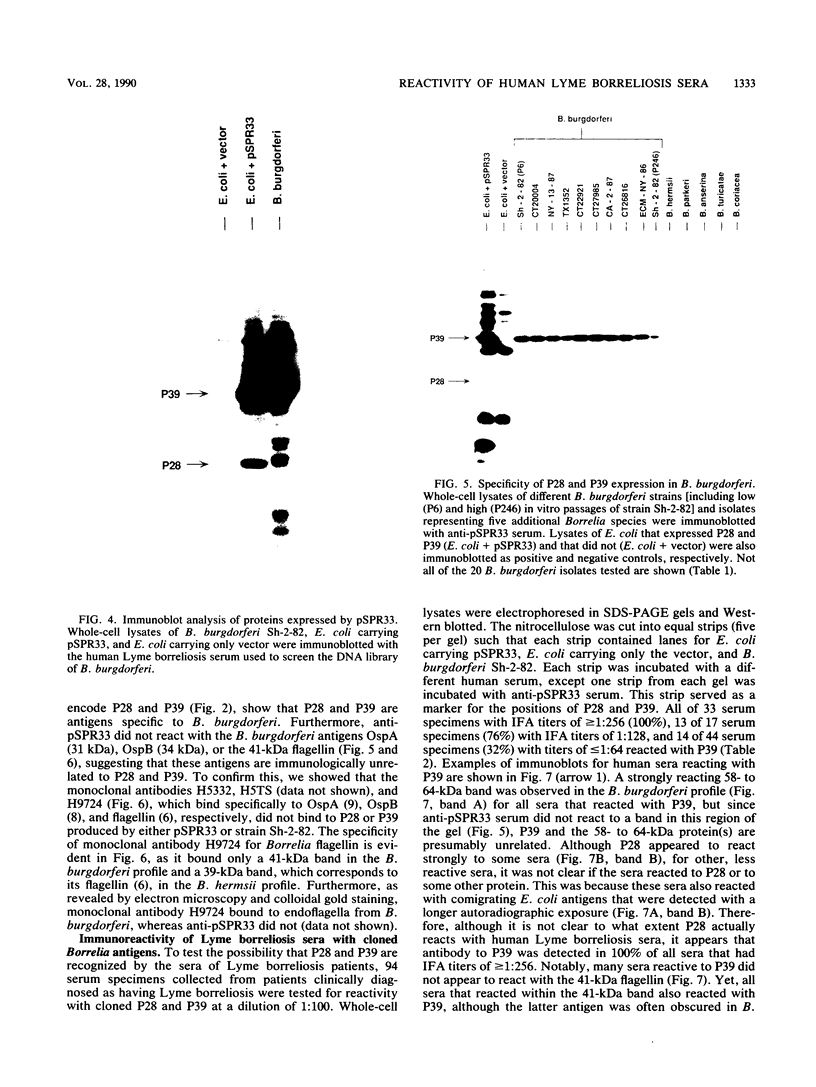
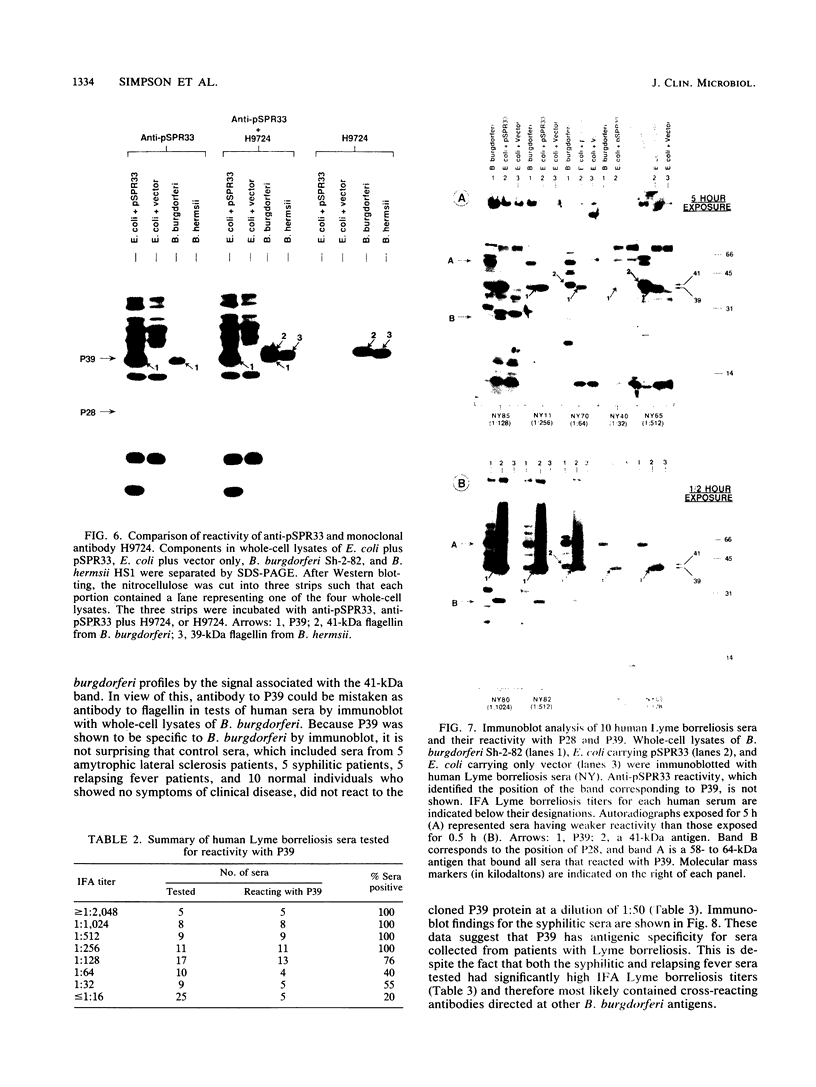
Borrelia burgdorferi is the causative agent of Lyme borreliosis, a spirochetal illness with a variety of acute clinical manifestations that may lead to debilitating neurological and arthritic complications. Diagnosis is difficult because symptoms mimic a variety of unrelated clinical conditions, spirochetes cannot always be isolated from infected patients, and current serological tests are frequently inconclusive because of the presence of cross-reacting non-B. burgdorferi antibodies. To identify antigens specific to B. burgdorferi that could be used in the serodiagnosis of Lyme borreliosis, we screened a Borrelia DNA expression library in Escherichia coli for antigens reactive with human Lyme borreliosis sera. One clone carried a 6.3-kilobase EcoRI chromosomal fragment (pSPR33), which encoded two species-specific antigens with molecular masses of 28 (P28) and 39 (P39) kilodaltons (kDa). These two antigens were immunologically distinct from OspA, OspB, and the 41-kDa flagellin. Ninety-four serum specimens from patients having Lyme borreliosis were tested for reactivity with P39. All of 33 the serum specimens with immunofluorescence assay titers of greater than or equal to 1:256, 13 of 17 serum specimens with titers of 1:128, and 14 of 44 serum specimens with titers of less than or equal to 1:64 reacted with P39. Notably, many sera reactive to P39 did not appear to react with the 41-kDa flagellin. Therefore, antibody to P39 could be mistaken for antibody to the 41-kDa flagellin in tests of human sera by Western blot (immunoblot). Twenty-five control serum specimens, which included sera from syphilitic, relapsing fever, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients as well as from 10 normal individuals, did not react to P39. Our data suggest that P39 may be a useful antigen for the serological confirmation of Lyme borreliosis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ai C. X., Wen Y. X., Zhang Y. G., Wang S. S., Qiu Q. C., Shi Z. X., Li D. Y., Chen D. Q., Liu X. D., Zhao J. H. Clinical manifestations and epidemiological characteristics of Lyme disease in Hailin county, Heilongjiang Province, China. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:302–313. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31864.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W., Grunwaldt E., Steere A. C. Antibodies of patients with Lyme disease to components of the Ixodes dammini spirochete. J Clin Invest. 1983 Aug;72(2):504–515. doi: 10.1172/JCI110998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Heiland R. A., Schrumpf M. E., Tessier S. L. A Borrelia-specific monoclonal antibody binds to a flagellar epitope. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):549–554. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.549-554.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Heiland R. A., Howe T. R. Heterogeneity of major proteins in Lyme disease borreliae: a molecular analysis of North American and European isolates. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):478–484. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Immunochemical analysis of Lyme disease spirochetes. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):581–586. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Laboratory aspects of Lyme borreliosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1988 Oct;1(4):399–414. doi: 10.1128/cmr.1.4.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Plasmid analysis of Borrelia burgdorferi, the Lyme disease agent. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Mar;26(3):475–478. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.3.475-478.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Tessier S. L., Hayes S. F. Variation in a major surface protein of Lyme disease spirochetes. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):94–100. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.94-100.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Tessier S. L., Todd W. J. Lyme disease spirochetes and ixodid tick spirochetes share a common surface antigenic determinant defined by a monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):795–804. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.795-804.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanco D. R., Champion C. I., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Antigenic and structural characterization of Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain) endoflagella. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):168–175. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.168-175.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Benach J. L., Grunwaldt E., Davis J. P. Lyme disease-a tick-borne spirochetosis? Science. 1982 Jun 18;216(4552):1317–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.7043737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J. L., Benach J. L. Identification and characterization of an endoflagellar antigen of Borrelia burgdorferi. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jul;84(1):322–330. doi: 10.1172/JCI114157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J. L., Benach J. L. Isolation of antigenic components from the Lyme disease spirochete: their role in early diagnosis. J Infect Dis. 1987 Apr;155(4):756–765. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.4.756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craft J. E., Fischer D. K., Shimamoto G. T., Steere A. C. Antigens of Borrelia burgdorferi recognized during Lyme disease. Appearance of a new immunoglobulin M response and expansion of the immunoglobulin G response late in the illness. J Clin Invest. 1986 Oct;78(4):934–939. doi: 10.1172/JCI112683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dattwyler R. J., Volkman D. J., Luft B. J., Halperin J. J., Thomas J., Golightly M. G. Seronegative Lyme disease. Dissociation of specific T- and B-lymphocyte responses to Borrelia burgdorferi. N Engl J Med. 1988 Dec 1;319(22):1441–1446. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198812013192203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dekonenko E. J., Steere A. C., Berardi V. P., Kravchuk L. N. Lyme borreliosis in the Soviet Union: a cooperative US-USSR report. J Infect Dis. 1988 Oct;158(4):748–753. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.4.748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodzicki R. L., Steere A. C. Comparison of immunoblotting and indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using different antigen preparations for diagnosing early Lyme disease. J Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;157(4):790–797. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.4.790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haberberger R. L., Jr, Constantine N. T., Schwan T. G., Woody J. N. Lyme disease agent in Egypt? Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1989 Jul-Aug;83(4):556–556. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(89)90293-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen K., Asbrink E. Serodiagnosis of erythema migrans and acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans by the Borrelia burgdorferi flagellum enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Mar;27(3):545–551. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.3.545-551.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen K., Hindersson P., Pedersen N. S. Measurement of antibodies to the Borrelia burgdorferi flagellum improves serodiagnosis in Lyme disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Feb;26(2):338–346. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.2.338-346.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe T. R., LaQuier F. W., Barbour A. G. Organization of genes encoding two outer membrane proteins of the Lyme disease agent Borrelia burgdorferi within a single transcriptional unit. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):207–212. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.207-212.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe T. R., Mayer L. W., Barbour A. G. A single recombinant plasmid expressing two major outer surface proteins of the Lyme disease spirochete. Science. 1985 Feb 8;227(4687):645–646. doi: 10.1126/science.3969554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnarelli L. A., Anderson J. F., Barbour A. G. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for Lyme disease: reactivity of subunits of Borrelia burgdorferi. J Infect Dis. 1989 Jan;159(1):43–49. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnarelli L. A., Anderson J. F., Johnson R. C. Cross-reactivity in serological tests for Lyme disease and other spirochetal infections. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jul;156(1):183–188. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.1.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadal D., Taverna C., Hitzig W. H. Immunoblot analysis of antibody binding to polypeptides of Borrelia burgdorferi in children with different clinical manifestations of Lyme disease. Pediatr Res. 1989 Oct;26(4):377–382. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198910000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTNOY J. MODIFICATIONS OF THE RAPID PLASMA REAGIN (RPR) CARD TEST FOR SYPHILIS, FOR USE IN LARGE SCALE TESTING. Am J Clin Pathol. 1963 Nov;40:473–479. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/40.5.473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plasterk R. H., Simon M. I., Barbour A. G. Transposition of structural genes to an expression sequence on a linear plasmid causes antigenic variation in the bacterium Borrelia hermsii. Nature. 1985 Nov 21;318(6043):257–263. doi: 10.1038/318257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid G. P. The global distribution of Lyme disease. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Jan-Feb;7(1):41–50. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.1.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan T. G., Burgdorfer W. Antigenic changes of Borrelia burgdorferi as a result of in vitro cultivation. J Infect Dis. 1987 Nov;156(5):852–853. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.5.852-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan T. G., Kime K. K., Schrumpf M. E., Coe J. E., Simpson W. J. Antibody response in white-footed mice (Peromyscus leucopus) experimentally infected with the Lyme disease spirochete (Borrelia burgdorferi). Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3445–3451. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3445-3451.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan T. G., Simpson W. J., Schrumpf M. E., Karstens R. H. Identification of Borrelia burgdorferi and B. hermsii using DNA hybridization probes. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Aug;27(8):1734–1738. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.8.1734-1738.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz B. S., Goldstein M. D., Ribeiro J. M., Schulze T. L., Shahied S. I. Antibody testing in Lyme disease. A comparison of results in four laboratories. JAMA. 1989 Dec 22;262(24):3431–3434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. J., Cleary P. P. Expression of M type 12 protein by a group A streptococcus exhibits phaselike variation: evidence for coregulation of colony opacity determinants and M protein. Infect Immun. 1987 Oct;55(10):2448–2455. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.10.2448-2455.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spanier J. G., Cleary P. P. A DNA substitution in the group A streptococcal bacteriophage SP24. Virology. 1983 Oct 30;130(2):514–522. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90104-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanek G., Hirschl A., Stemberger H., Wewalka G., Wiedermann G. Does Lyme borreliosis also occur in tropical and subtropical areas? Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1987 Feb;263(3):491–495. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(87)80117-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Grodzicki R. L., Kornblatt A. N., Craft J. E., Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W., Schmid G. P., Johnson E., Malawista S. E. The spirochetal etiology of Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 31;308(13):733–740. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303313081301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Malawista S. E., Hardin J. A., Ruddy S., Askenase W., Andiman W. A. Erythema chronicum migrans and Lyme arthritis. The enlarging clinical spectrum. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Jun;86(6):685–698. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-86-6-685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Malawista S. E., Snydman D. R., Shope R. E., Andiman W. A., Ross M. R., Steele F. M. Lyme arthritis: an epidemic of oligoarticular arthritis in children and adults in three connecticut communities. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Jan-Feb;20(1):7–17. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart A., Glass J., Patel A., Watt G., Cripps A., Clancy R. Lyme arthritis in the Hunter Valley. Med J Aust. 1982 Feb 6;1(3):139–139. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1982.tb132207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]