Abstract
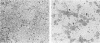
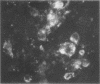
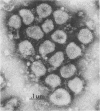
Fecal filtrates from cows with winter dysentery were inoculated into gnotobiotic and conventional calves, and a coronavirus was isolated from calf feces. Cytopathic effects were observed on human rectal tumor cells but not bovine cell cultures. The winter dysentery isolates morphologically and antigenically resembled the Mebus strain of bovine coronavirus.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akashi H., Inaba Y., Miura Y., Sato K., Tokuhisa S., Asagi M., Hayashi Y. Propagation of the Kakegawa strain of bovine coronavirus in suckling mice, rats and hamsters. Arch Virol. 1981;67(4):367–370. doi: 10.1007/BF01314841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benfield D. A., Stotz I., Moore R., McAdaragh J. P. Shedding of rotavirus in feces of sows before and after farrowing. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jul;16(1):186–190. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.1.186-190.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell S. G., Cookingham C. A. The enigma of winter dysentery. Cornell Vet. 1978 Oct;68(4):423–441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. K., Riegel C. A., Olson J. D., Fountain A. Shedding of enteric coronavirus in adult cattle. Am J Vet Res. 1987 Mar;48(3):361–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouch C. F., Acres S. D. Prevalence of rotavirus and coronavirus antigens in the feces of normal cows. Can J Comp Med. 1984 Jul;48(3):340–342. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouch C. F., Bielefeldt Ohmann H., Watts T. C., Babiuk L. A. Chronic shedding of bovine enteric coronavirus antigen-antibody complexes by clinically normal cows. J Gen Virol. 1985 Jul;66(Pt 7):1489–1500. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-7-1489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dea S., Roy R. S., Begin M. E. Bovine coronavirus isolation and cultivation in continuous cell lines. Am J Vet Res. 1980 Jan;41(1):30–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durham P. J., Stevenson B. J., Farquharson B. C. Rotavirus and coronavirus associated diarrhoea in domestic animals. N Z Vet J. 1979 Mar;27(3):30–32. doi: 10.1080/00480169.1979.34595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espinasse J., Viso M., Laval A., Savey M., Le Layec C., Blot J. P., L'Haridon R., Cohen J. Winter dysentery: a coronavirus-like agent in the faeces of beef and dairy cattle with diarrhoea. Vet Rec. 1982 Apr 17;110(16):385–385. doi: 10.1136/vr.110.16.385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEDSTROM H., ISAKSSON A. Epizootic enteritis in cattle in Sweden. Cornell Vet. 1951 Jul;41(3):251–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann M., Wyler R. Propagation of the virus of porcine epidemic diarrhea in cell culture. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Nov;26(11):2235–2239. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.11.2235-2239.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogue B. G., King B., Brian D. A. Antigenic relationships among proteins of bovine coronavirus, human respiratory coronavirus OC43, and mouse hepatitis coronavirus A59. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):384–388. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.384-388.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horner G. W., Hunter R., Kirkbride C. A. Letter: A coronavirus-like agent present in faeces of cows with diarrhoea. N Z Vet J. 1975 May;23(5):98–98. doi: 10.1080/00480169.1975.34206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komaniwa H., Makabe T., Fukusho A., Shimizu Y. Isolation of transmissible gastroenteritis virus from feces of diarrheic pigs in roller culture of CPK cells in the presence of trypsin. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1986 Dec;48(6):1245–1248. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.48.1245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macpherson L. W. Bovine Virus Enteritis (Winter Dysentery). Can J Comp Med Vet Sci. 1957 Jun;21(6):184–192. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTS S. J. Winter dysentery in dairy cattle. Cornell Vet. 1957 Jul;47(3):372–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saif L. J., Bohl E. H., Kohler E. M., Hughes J. H. Immune electron microscopy of transmissible gastroenteritis virus and rotavirus (reovirus-like agent) of swine. Am J Vet Res. 1977 Jan;38(1):13–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saif L. J., Redman D. R., Brock K. V., Kohler E. M., Heckert R. A. Winter dysentery in adult dairy cattle: detection of coronavirus in the faeces. Vet Rec. 1988 Sep 10;123(11):300–301. doi: 10.1136/vr.123.11.300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saif L. J., Redman D. R., Moorhead P. D., Theil K. W. Experimentally induced coronavirus infections in calves: viral replication in the respiratory and intestinal tracts. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Jul;47(7):1426–1432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saif L. J., Redman D. R., Smith K. L., Theil K. W. Passive immunity to bovine rotavirus in newborn calves fed colostrum supplements from immunized or nonimmunized cows. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1118–1131. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1118-1131.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storz J., Rott R., Kaluza G. Enhancement of plaque formation and cell fusion of an enteropathogenic coronavirus by trypsin treatment. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1214–1222. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1214-1222.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theil K. W., Bohl E. H., Cross R. F., Kohler E. M., Agnes A. G. Pathogenesis of porcine rotaviral infection in experimentally inoculated gnotobiotic pigs. Am J Vet Res. 1978 Feb;39(2):213–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toth T. E. Trypsin-enhanced replication of neonatal calf diarrhea coronavirus in bovine embryonic lung cells. Am J Vet Res. 1982 Jun;43(6):967–972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]