Few families of compounds have been as intensely studied as iron porphyrin complexes. In spite of this, a truly four-coordinate Fe(III) porphyrin cation has never before been reported.1 The exceptional electrophilicity of the four-coordinate [FeIII(Porph)]+ cation will even coordinate arene solvent upon crystallization if the counteranion is extremely non-coordinating, as in the work of Reed with silver dihexabromocarborane,2,3 and in solution, a Br atom of the hexabromocarborane anion binds to the Fe.4
Here we present the first purely four-coordinate Fe(III) porphyrin both in the solid state and in solution. To do so, we have combined both steric and electronic factors by creating a very sterically hindered bis-pocket siloxyl porphyrin in conjunction with a bulky and very weakly coordinating anion.
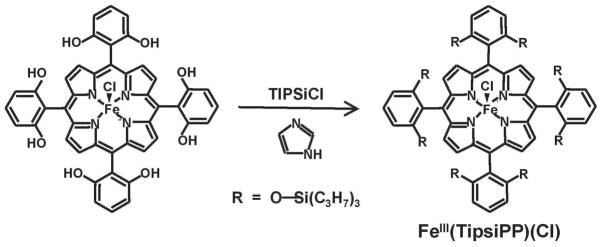
We have synthesized an extremely hindered bis-pocket siloxyl porphyrin, 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(2′,6′-bis(triisopropylsiloxy)phenyl)-porphyrin (H2TipsiPP) by the reaction of the octahydroxyl iron porphyrin5 (5,10,15,20-tetrakis(2′,6′-dihydroxyphenyl)porphyrin with triisopropyl chlorosilane using imidazole as a catalyst (Scheme 1). In spite of the driving force of strong Si–O bond formation, high temperatures (250 °C) are required to overcome steric hindrance and fully silylate all eight sites. The resulting porphyrin is extremely sterically hindered with a pocket opening of only 2 Å. Figure 1 compares the space-filling models of the simple FeTPP(Cl) and the bis-pocket siloxylporphyrin FeIII(TipsiPP)(Cl). The steric hindrance prevents anion coordination by reducing the thermodynamic binding constant.
Scheme 1.
Synthesis of a Bis-pocket Siloxylporphyrin, FeIII(TipsiPP)(Cl)
Figure 1.
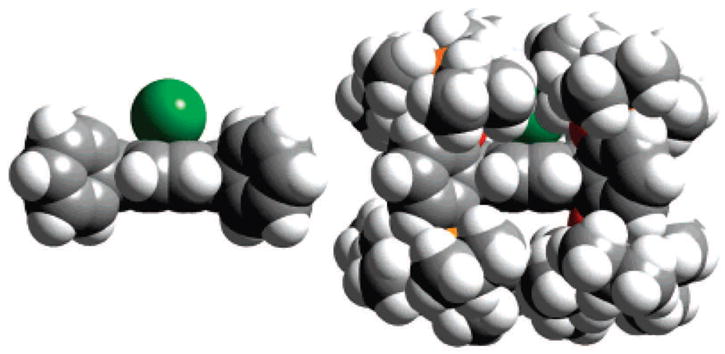
Space-filling model of FeIIITPP(Cl) (left) and FeIII(TipsiPP)-(Cl) (right); side view, same scale.
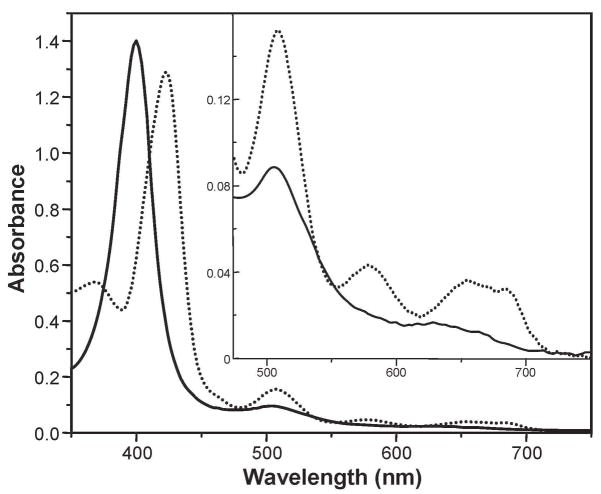
To replace the sterically undemanding chloro ligand, a dichlo-romethane solution of FeIII(TipsiPP)(Cl) was mixed with 1 equiv of AgCB11H6Br6 or AgCF3SO3, which produces a color change from yellow to red (Figure 2). NMR, MALDI-TOF, and elemental analysis were used to confirm the purity of the final products. Both complexes react with water readily to form a five-coordinate spin-admixed Fe(III) complex, which has diagnostic UV–vis and NMR features (Figures S1 and S2 in Supporting Information (SI)).
Figure 2.
UV–visible spectrum of five-coordinate starting material FeIII(TipsiPP)(Cl) (dotted line) and four-coordinate [FeIII(TipsiPP)]+[CB11H6Br6]− (solid line). Inset shows an expanded absorbance scale.
Proton NMR is a very sensitive probe for the spin state of iron.4,6,7 On the basis of the β-pyrrole proton NMR isomer shift, Reed has established a magnetochemical series for different anions.8 Surprisingly, solutions of [FeIII(TipsiPP)]+ with a variety of weakly coordinating anions (i.e., CB11H6Br6−, SbF6−, ClO4−, and CF3SO3−) all have exactly the same porphyrin 1H NMR chemical shifts with β-pyrrole proton chemical shift at −81 ppm in CD2Cl2 at 290 K (Figure S3 in SI), which corresponds to the Fe(III) intermediate spin state (S = 3/2).8 Because these anions are very different both in nucleophilicity and size, the porphyrin NMR spectra would be different if the anions were bound to the iron. This is the case for FeIIITPP+: β-pyrrole proton chemical shifts for FeTPP(X) are −60 ppm for CB11H6Br6−, −31.5 ppm for SbF6−, 13 ppm for ClO4−, and 39.3 ppm for CF3SO3−.8,9 Possible assignments to either FeIII(TipsiPP•+) porphyrin cation radicals or FeII(TipsiPP) were excluded by independent synthesis of the pure complexes, which show very different chemical shifts and have different spin states.
The solvent plays a central role in stabilization of the four-coordinate Fe(III) cation. The four-coordinate species is only stable in halogenated solvents (i.e., CH2Cl2, CHCl3, CH2Br2). In aromatic solvents, such as toluene and benzene, it converts to an admixed spin state, probably due to arene coordination to the iron center.3 The β-pyrrole chemical shift of [FeIII(TipsiPP)]+ is the same in either CH2Cl2 or CH2Br2, which shows that the halocarbons do not perturb the iron center. The compound is not soluble in aliphatic solvents.
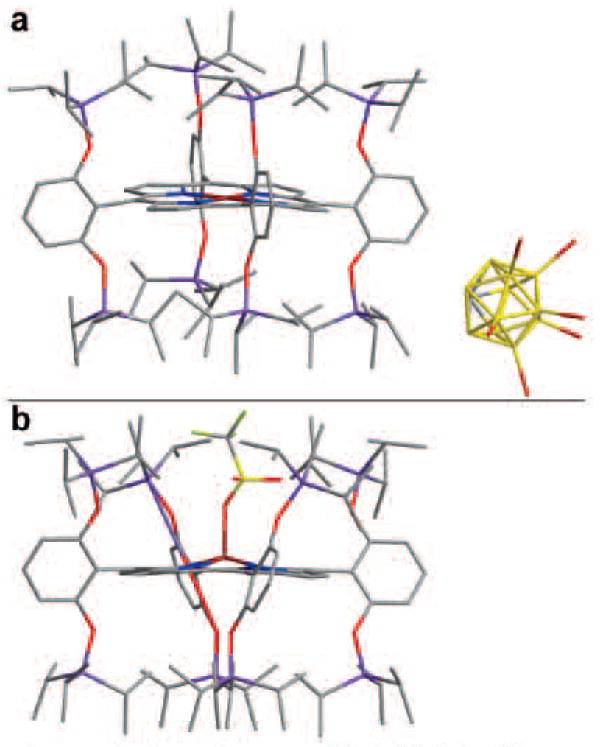
Red-brown needle-shaped crystals of [FeIII(TipsiPP)]+[CB11H6Br6]− were grown by slow evaporation of a 1:1 mixture of dichloro-methane/heptane solution inside an inert atmosphere box. The single crystals were redissolved in dry CD2Cl2 and tested by NMR to confirm no contamination with water during the crystal growing process. The crystal structure (Figure 3) confirms the absence of axial ligation to the iron porphyrin. The average Fe–N bond length is 1.94 ± 0.01 Å with the iron sitting in the porphyrin plane. This very short bond length is consistent with the removal of the unpaired electron from the dx2−y2 orbital.1,10 The porphyrin is slightly ruffled, with meso-carbons above and below the average nitrogen plane by 0.23 Å. The carborane anion is definitively not coordinated to the iron and is fully outside of the porphyrin pocket. The resulting salt has a layered structure with alternating planes of positive and negative charges (a crystal packing diagram is given as Figure S9 in SI). A similar packing structure has been reported for [FeTPP]-[Ag(CB11H6Br6)2]·4(p-xylene) with the exception of the coordination of the xylene to the iron center.2,3
Figure 3.
X-ray single-crystal structure of (a) [FeIII(TipsiPP)]+[CB11H6Br6]− and (b) FeIII(TipsiPP)(CF3SO3). Figure S9 in SI provides a crystal packing diagram for[FeIII(TipsiPP)]+[CB11H6Br6]− showing a layered salt structure with alternating planes of positive and negative charges.
In the solid state, the four-coordinate iron porphyrin cation can only be isolated with hexabromocarborane as the counterion. In crystals of solids with other anions (e.g., CF3SO3−), the anion enters the porphyrin pocket and coordinates to the iron, presumably driven by the loss of solvation of the anion. The powder X-band EPR of FeIII(TipsiPP)(CF3SO3) shows a g⊥=5.6 signal, consistent with an admixed spin assignment (Figure S4 in SI). The average Fe–N bond length in FeIII(TipsiPP)(CF3SO3) is 2.053(2) Å (which is 0.1 Å longer than in the true four-coordinate structure), and the iron atom is out of the plane of the four nitrogens by 0.406 Å. To accommodate the triflate ion, the phenyl groups rotate ~12° about the plane normal to porphyrin, which further demonstrates the interplay of electronic and steric factors in these highly hindered systems.
Further characterization data on the four-coordinate [FeIII-(TipsiPP)]+[CB11H6Br6]− are all consistent with a 3/2 intermediate spin ground state. The solution magnetic susceptibility of the four-coordinate complex is 4.1 μB in a dichloromethane solution measured by Evan’s method from room temperature to 190 K (Figure S5 in SI); SQUID data show no change in the magnetic moment between 300 and 10 K. EPR data of both frozen halocarbon solutions and the crystalline [FeIII(TipsiPP)]+[CB11H6Br6]minus; have a g⊥ = 4.2 signal (Figure S4 in SI). Mössbauer spectra were obtained with the 57Fe-enriched sample at 6 K, with an isomer shift of 0.33 mm/s (a typical value for Fe(III)), but with a very large quadrupole splitting value of 5.16 mm/s (Figure S6 in SI). Solid-state NMR also gives an upfield signal at −80 ppm for the β-pyrrole hydrogens, confirming that the four-coordinate Fe(III) porphyrin is stable both in solid and solution phases.
Although four-coordinate Fe(III) heme is unlikely in any heme protein, the intermediate spin state of Fe(III) porphyrins has an interesting counterpart in nature.11–17 In cytochrome c′, the heme is believed to be a quantum admixed S = 5/2 and S = 3/2 spin state.18–20 Depending on the field strength of the ligand coordinated to the iron, the ratio of S = 5/2 to S = 3/2 character varies: as the ligand strength becomes weaker, the spin state of iron approaches the pure intermediate spin state of 3/2.
In summary, the first four-coordinate Fe(III) porphyrin complex has been isolated and fully characterized in both solution and solid state and shows a pure S = 3/2 intermediate spin state. The combination of steric hindrance of a bis-pocket porphyrin with weakly coordinating anions has proved essential in isolation of this highly elusive species, whose reactivity we are still exploring.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the assistance of Alexandre Anastácio and Prof. J. W. Stucki (Mössbauer), Prof. C. M. Rienstra, and Dr. Donghua Zhou (SSNMR), Dr. M. J. Nilges (EPR), and Jin Ho Bang (SQUID). These studies were supported by National Science Foundation (CHE03-15494).
References
- 1.Scheidt WR. In: Porphyrin Handbook. Kadish KM, Smith KM, Guilard R, editors. Vol. 3. Academic Press; San Diego, CA: 2000. pp. 49–112. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Evans DR, Fackler NLP, Xie Z, Rickard CEF, Boyd PDW, Reed CA. J Am Chem Soc. 1999;121:8466–8474. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Xie Z, Bau R, Reed CA. Angew Chem. 1994;106:2566–2568. see also Angew Chem, Int Ed Engl. 1994;2533(25232524):2433–2564.
- 4.Evans DR, Reed CA. J Am Chem Soc. 2000;122:4660–4667. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sen A, Suslick KS. J Am Chem Soc. 2000;122:11565–11566. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Walker FA. Inorg Chem. 2003;42:4526–4544. doi: 10.1021/ic026245p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Walker FA. In: Porphyrin Handbook. Kadish KM, Smith KM, Guilard R, editors. Vol. 5. Academic Press; San Diego, CA: 2000. pp. 81–183. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Reed CA, Guiset F. J Am Chem Soc. 1996;118:3281–3282. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Boersma AD, Goff HM. Inorg Chem. 1982;21:581–586. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Scheidt WR, Reed CA. Chem Rev. 1981;81:543–555. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Dolphin DH, Sams JR, Tsin TB. Inorg Chem. 1977;16:711–713. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Summerville DA, Cohen IA, Hatano K, Scheidt WR. Inorg Chem. 1978;17:2906–2910. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Reed CA, Mashiko T, Bentley SP, Kastner ME, Scheidt WR, Spartalian K, Lang G. J Am Chem Soc. 1979;101:2948–2958. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Goff H, Shimomura E. J Am Chem Soc. 1980;102:31–37. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Balch AL, Cheng RJ, La Mar GN, Latos-Grazynski L. Inorg Chem. 1985;24:2651–2656. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Schunemann V, Gerdan M, Trautwein AX, Haoudi N, Mandon D, Fischer J, Weiss R, Tabard A, Guilard R. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 1999;38:3181–3183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Nesset MJM, Cai S, Shokhireva TK, Shokhirev NV, Jacobson SE, Jayaraj K, Gold A, Walker FA. Inorg Chem. 2000;39:532–540. doi: 10.1021/ic9907866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Maltempo MM, Moss TH. Q Rev Biophys. 1976;9:181–215. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Zeng Y, Caignan GA, Bunce RA, Rodriguez JC, Wilks A, Rivera M. J Am Chem Soc. 2005;127:9794–9807. doi: 10.1021/ja0425987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Weiss R, Gold A, Terner J. Chem Rev. 2006;106:2550–2579. doi: 10.1021/cr040416l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.