Abstract
Different synthetic DNA nucleotide sequences were evaluated as gene probes for the specific detection and differentiation of Staphylococcus aureus strains encoding enterotoxins A (SEA), B (SEB), and C (SEC) and toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 (TSST-1). Identification of sequences unique to each toxin, based on knowledge of their nucleotide sequences, led to preparation of the specific 18-base oligonucleotide probes EA1 (encoding amino acids 177 to 182 of SEA), EB2 (encoding amino acids 105 to 110 of SEB), EC5 (encoding amino acids 125 to 131 of SEC1), and TS1 (encoding amino acids 160 to 166 of TSST-1). In colony blot hybridization analyses, these probes hybridized specifically with DNA from strains that produced the respective toxin serotypes. An excellent (greater than or equal to 93%) correlation between hybridization results (genotype) and toxin protein detection by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (phenotype) was observed in the characterization of both reference and clinical strains of S. aureus for SEA, SEB, and TSST-1. A lower correlation (64%) for SEC reflected a lack of sensitivity in detecting toxin production. Our findings demonstrate that molecular DNA hybridization with synthetic oligonucleotide probes provides another approach for establishing the toxigenicity of S. aureus.
Full text
PDF

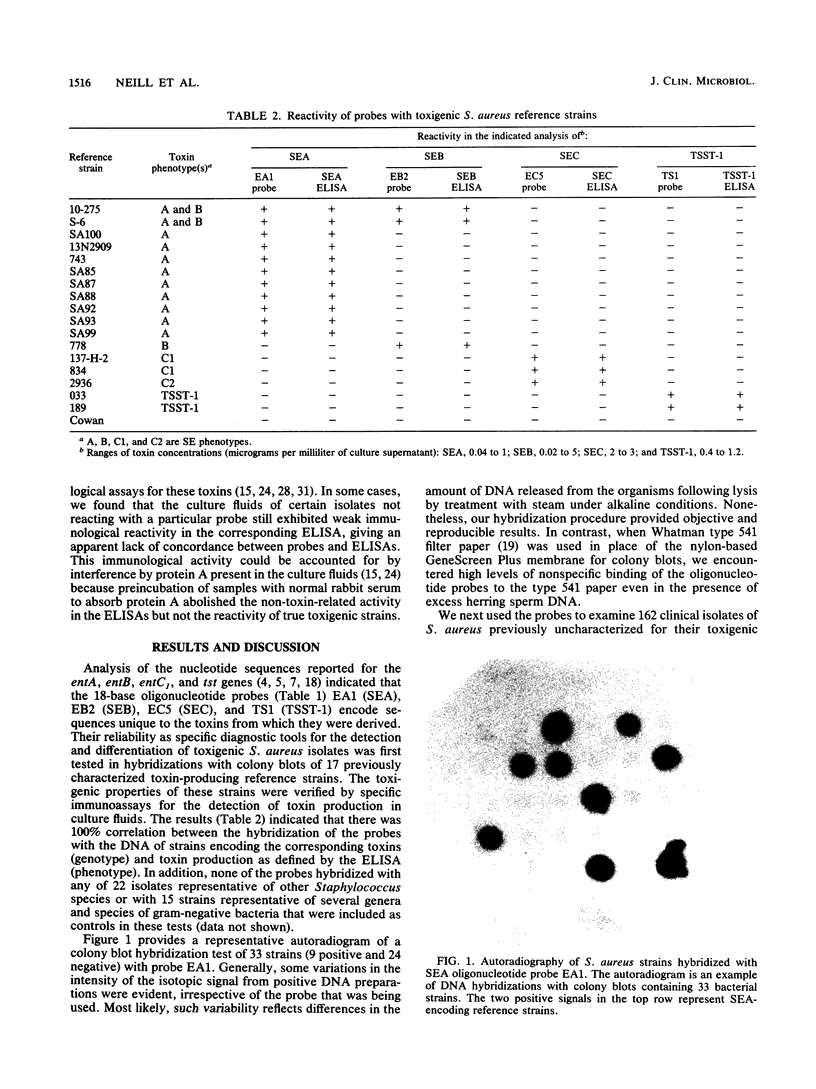

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayles K. W., Iandolo J. J. Genetic and molecular analyses of the gene encoding staphylococcal enterotoxin D. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):4799–4806. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.4799-4806.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Best G. K., Scott D. F., Kling J. M., Thompson M. R., Adinolfi L. E., Bonventre P. F. Protection of rabbits in an infection model of toxic shock syndrome (TSS) by a TSS toxin-1-specific monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):998–999. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.998-999.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betley M. J., Mekalanos J. J. Nucleotide sequence of the type A staphylococcal enterotoxin gene. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):34–41. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.34-41.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomster-Hautamaa D. A., Kreiswirth B. N., Kornblum J. S., Novick R. P., Schlievert P. M. The nucleotide and partial amino acid sequence of toxic shock syndrome toxin-1. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15783–15786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohach G. A., Kreiswirth B. N., Novick R. P., Schlievert P. M. Analysis of toxic shock syndrome isolates producing staphylococcal enterotoxins B and C1 with use of southern hybridization and immunologic assays. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Jan-Feb;11 (Suppl 1):S75–S82. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.supplement_1.s75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohach G. A., Schlievert P. M. Conservation of the biologically active portions of staphylococcal enterotoxins C1 and C2. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):2249–2252. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.2249-2252.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonventre P. F., Weckbach L., Harth G., Haidaris C. Distribution and expression of toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 gene among Staphylococcus aureus isolates of toxic shock syndrome and non-toxic shock syndrome origin. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Jan-Feb;11 (Suppl 1):S90–S95. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.supplement_1.s90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casman E. P., Bennett R. W., Dorsey A. E., Stone J. E. The micro-slide gel double diffusion test for the detection and assay of staphylococcal enterotoxins. Health Lab Sci. 1969 Oct;6(4):185–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couch J. L., Betley M. J. Nucleotide sequence of the type C3 staphylococcal enterotoxin gene suggests that intergenic recombination causes antigenic variation. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4507–4510. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4507-4510.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couch J. L., Soltis M. T., Betley M. J. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the type E staphylococcal enterotoxin gene. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):2954–2960. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.2954-2960.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fast D. J., Schlievert P. M., Nelson R. D. Toxic shock syndrome-associated staphylococcal and streptococcal pyrogenic toxins are potent inducers of tumor necrosis factor production. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):291–294. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.291-294.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fey H., Pfister H., Rüegg O. Comparative evaluation of different enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay systems for the detection of staphylococcal enterotoxins A, B, C, and D. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jan;19(1):34–38. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.1.34-38.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Formal S. B., Hale T. L., Kapfer C., Cogan J. P., Snoy P. J., Chung R., Wingfield M. E., Elisberg B. L., Baron L. S. Oral vaccination of monkeys with an invasive Escherichia coli K-12 hybrid expressing Shigella flexneri 2a somatic antigen. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):465–469. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.465-469.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa H., Igarashi H. Rapid latex agglutination test for detection of staphylococcal enterotoxins A to E that uses high-density latex particles. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Oct;54(10):2345–2348. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.10.2345-2348.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. L., Khan S. A. Nucleotide sequence of the enterotoxin B gene from Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):29–33. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.29-33.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maas R. An improved colony hybridization method with significantly increased sensitivity for detection of single genes. Plasmid. 1983 Nov;10(3):296–298. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(83)90045-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller B. A., Reiser R. F., Bergdoll M. S. Detection of staphylococcal enterotoxins A, B, C, D, and E in foods by radioimnunoassay, using staphyloccal cells containing protein A as immunoadsorbent. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Sep;36(3):421–426. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.3.421-426.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notermans S., Heuvelman K. J., Wernars K. Synthetic enterotoxin B DNA probes for detection of enterotoxigenic Staphylococcus aureus strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Feb;54(2):531–533. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.2.531-533.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiser R. F., Robbins R. N., Khoe G. P., Bergdoll M. S. Purification and some physicochemical properties of toxic-shock toxin. Biochemistry. 1983 Aug 2;22(16):3907–3912. doi: 10.1021/bi00285a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosten P. M., Bartlett K. H., Chow A. W. Detection and quantitation of toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 in vitro and in vivo by noncompetitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Feb;25(2):327–332. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.2.327-332.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schantz E. J., Roessler W. G., Wagman J., Spero L., Dunnery D. A., Bergdoll M. S. Purification of staphylococcal enterotoxin B. Biochemistry. 1965 Jun;4(6):1011–1016. doi: 10.1021/bi00882a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- See R. H., Adilman S., Bartlett K. H., Chow A. W. Colony immunoblot assay for the detection of staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 (TSST-1) with anti-TSST-1 F(ab')2 fragments. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Sep;27(9):2050–2053. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.9.2050-2053.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson N. E., Ketterhagen M. J., Bergdoll M. S. Monoclonal antibodies to staphylococcal enterotoxins B and C: cross-reactivity and localization of epitopes on tryptic fragments. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):281–285. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.281-285.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson N. E., Razdan M., Kuntsmann G., Aschenbach J. M., Evenson M. L., Bergdoll M. S. Detection of staphylococcal enterotoxins by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays and radioimmunoassays: comparison of monoclonal and polyclonal antibody systems. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 May;51(5):885–890. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.5.885-890.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weckbach L. S., Thompson M. R., Staneck J. L., Bonventre P. F. Rapid screening assay for toxic shock syndrome toxin production by Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jul;20(1):18–22. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.1.18-22.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells D. E., Reeves M. W., McKinney R. M., Graves L. M., Olsvik O., Bergan T., Feeley J. C. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 and use of a monoclonal antibody in a rapid, one-step enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of picogram quantities of toxic shock syndrome toxin 1. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Mar;25(3):516–521. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.3.516-521.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]